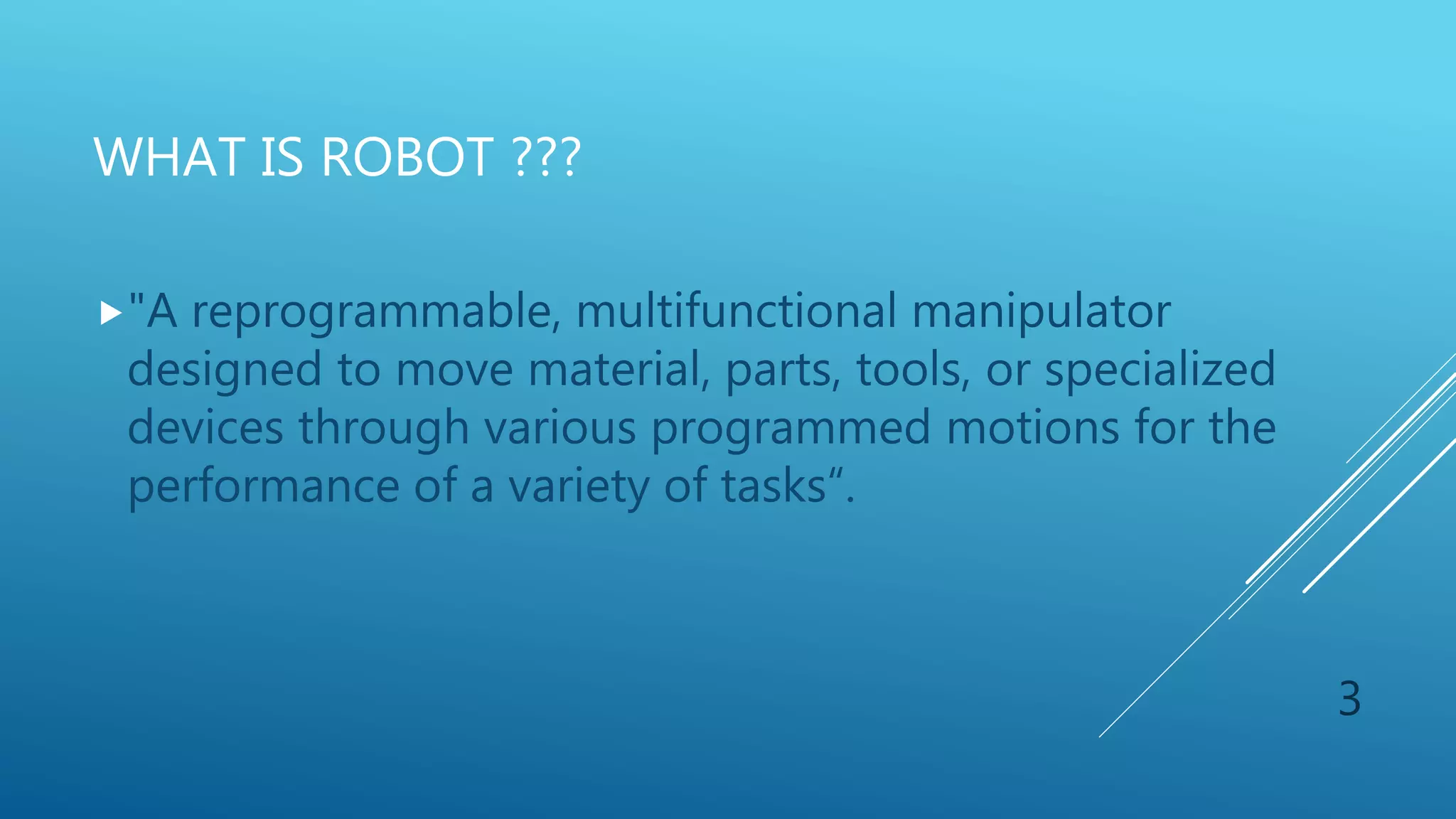
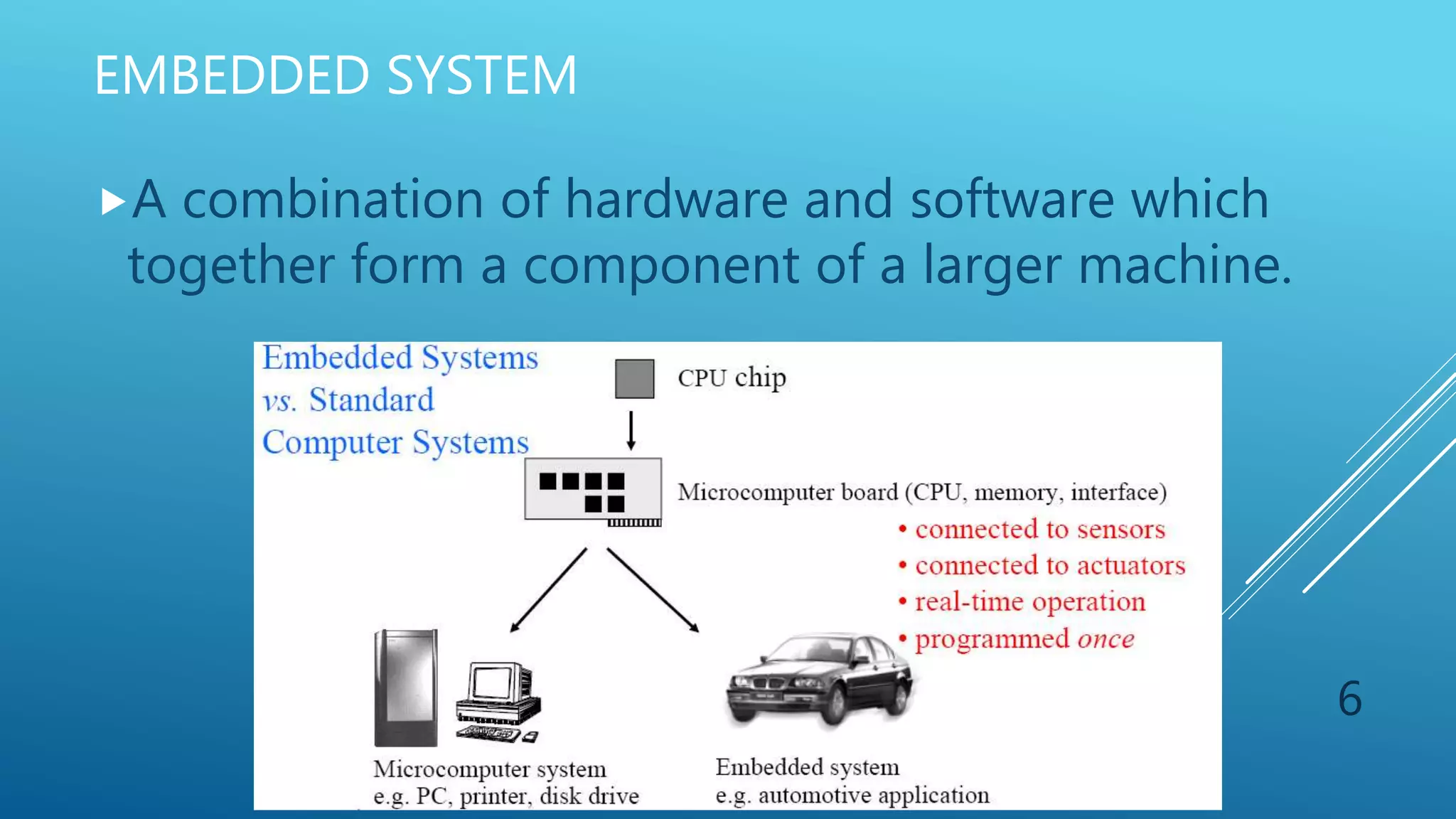
This document discusses embedded robotics systems. It defines a robot as a reprogrammable device that moves materials or tools to perform tasks. Robots are classified as manipulators, mobile robots, or hybrid robots. Embedded systems combine hardware and software to form components of larger machines. Embedded robotics systems use microcontrollers and can be applied in medical equipment, offices, tools, banking, transportation, automobiles, buildings, agriculture, and space.


![APPLICATION AREAS
Medical Systems
pace maker, patient monitoring systems, injection systems, intensive care units, …
Office Equipment
printer, copier, fax, …
Tools
multimeter, oscilloscope, line tester, GPS, …
Banking
ATMs, statement printers, …
Transportation
(Planes/Trains/[Automobiles] and Boats)
radar, traffic lights, signaling systems, … 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ep1312-160904110131/75/Embedded-Robotics-8-2048.jpg)

