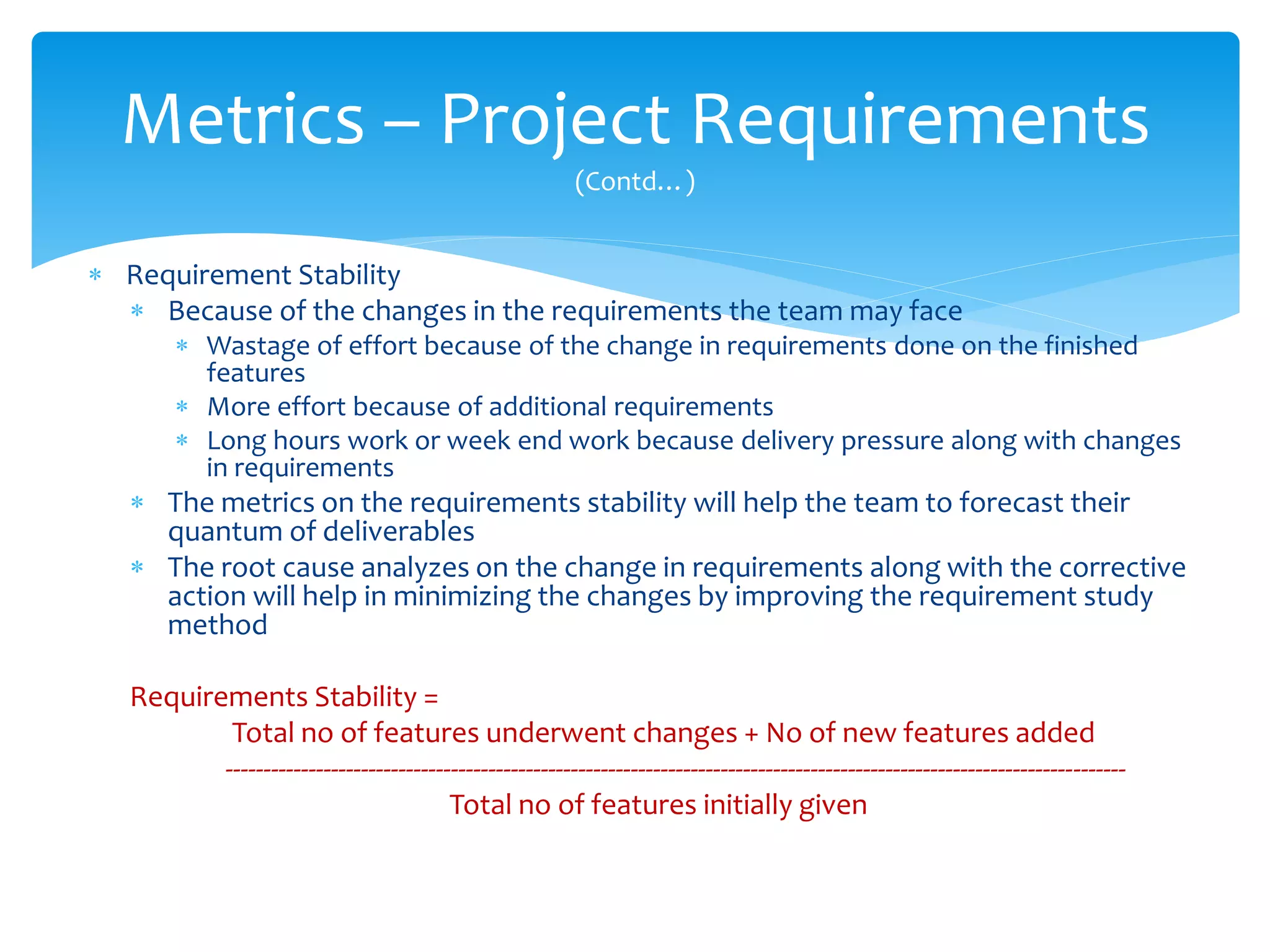
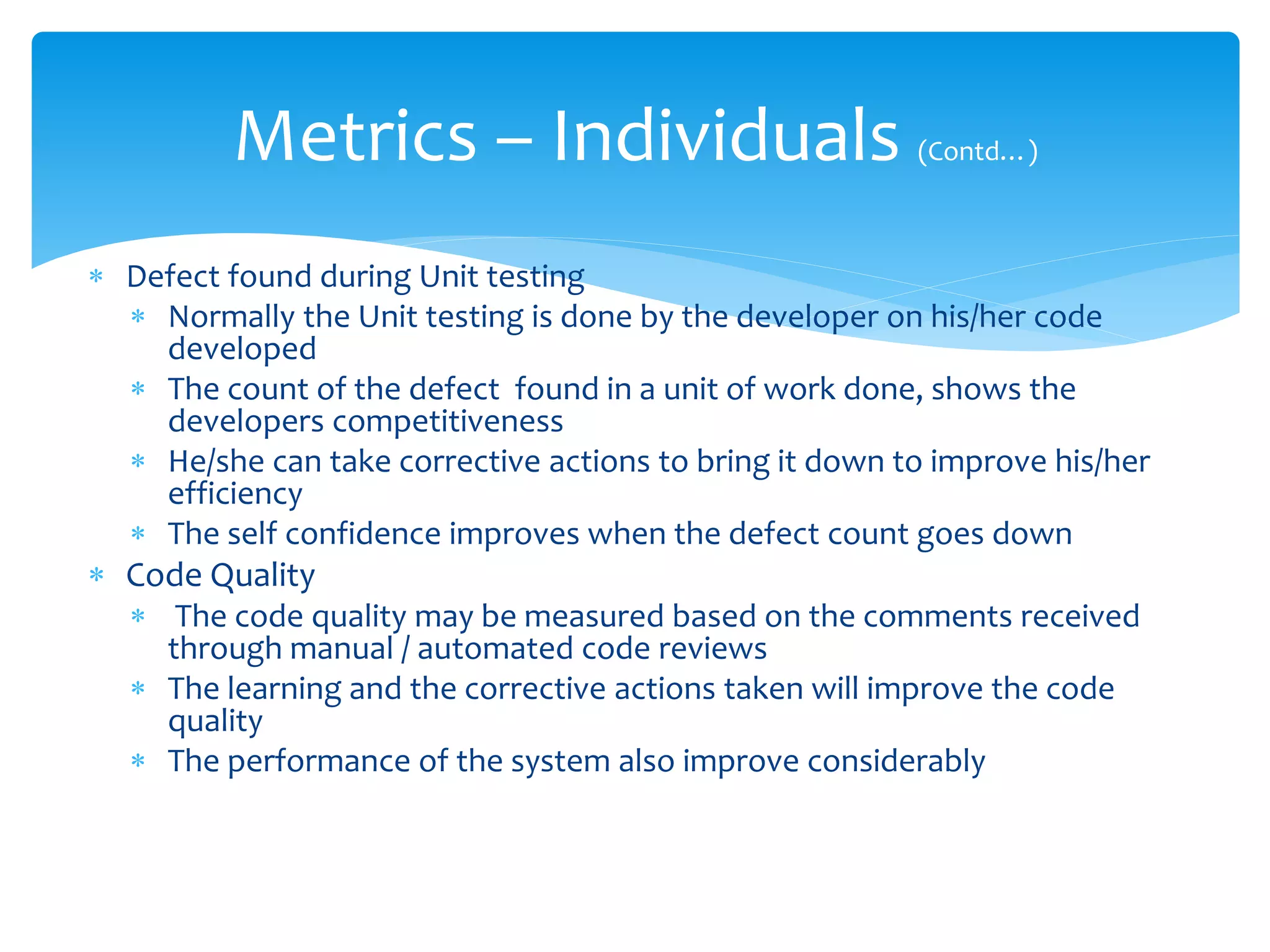
This document discusses various software metrics that can be used at the organization, project, and individual level. At the organization level, key metrics include effort variation, size variation, and schedule variation which impact profitability. Project-level metrics like requirements stability and defect leakage are also important. Individual developers may track defects found during unit testing and code quality metrics. Software metrics provide valuable insight for process improvement, resource allocation, and performance measurement.