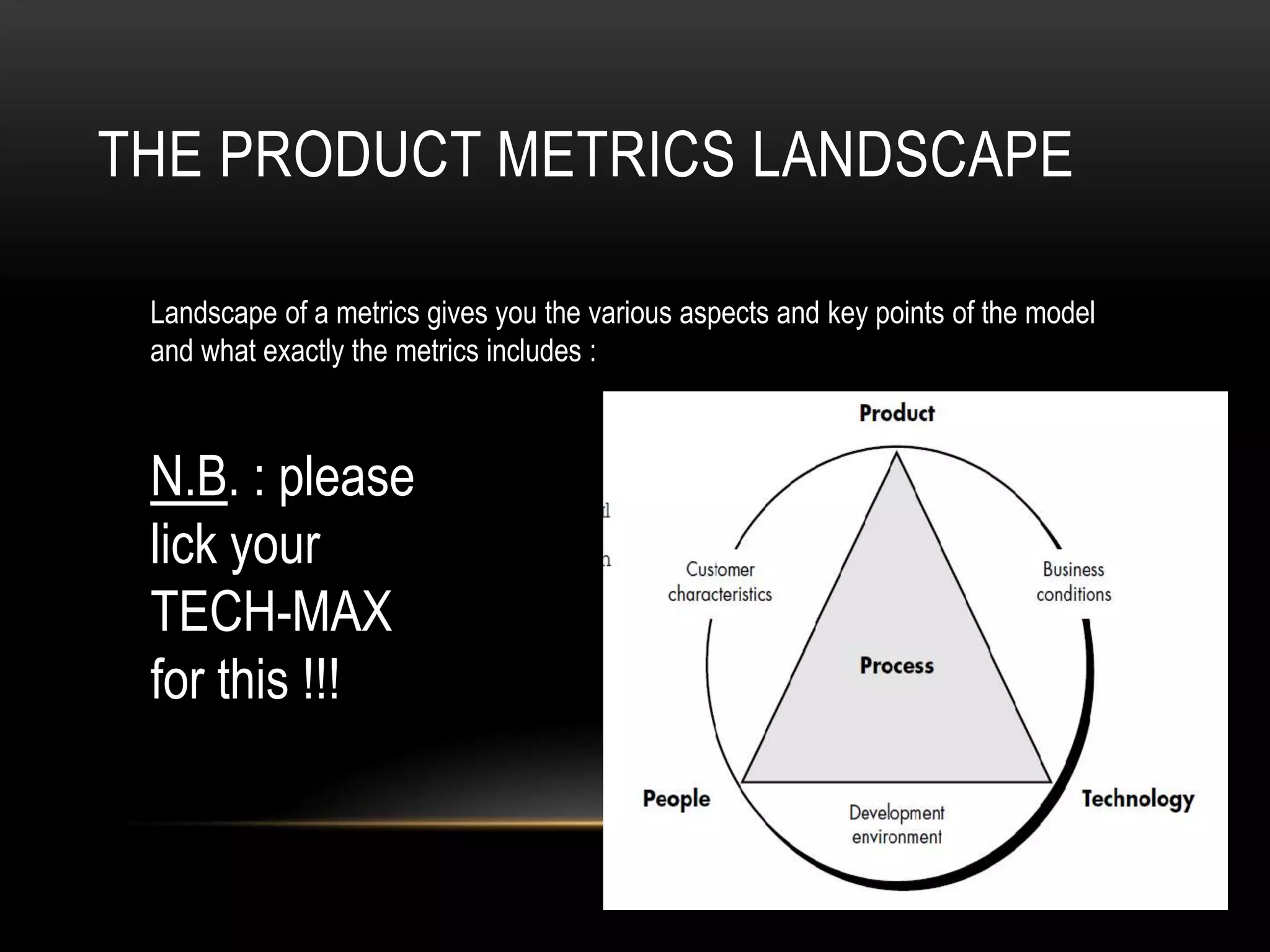
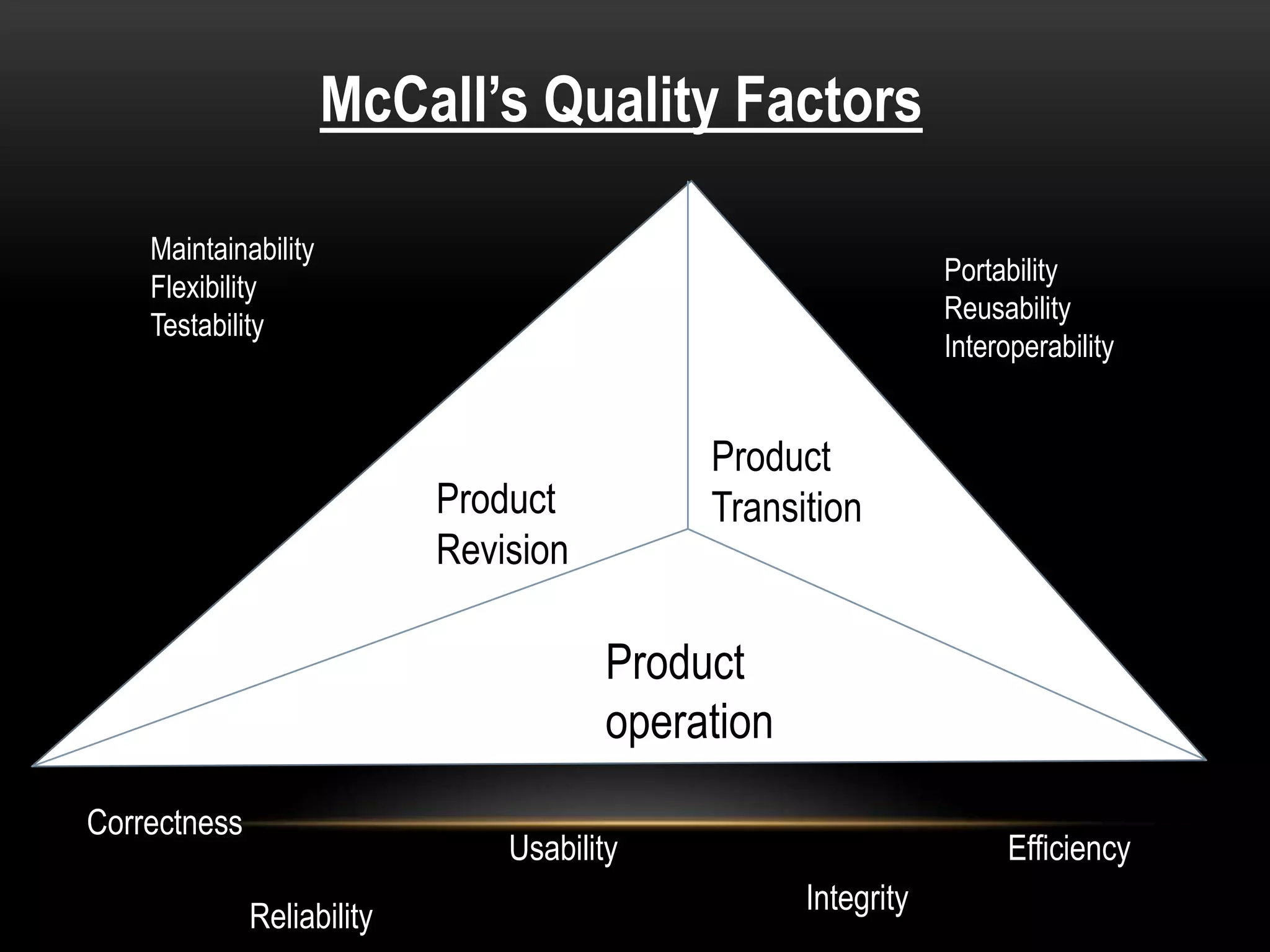
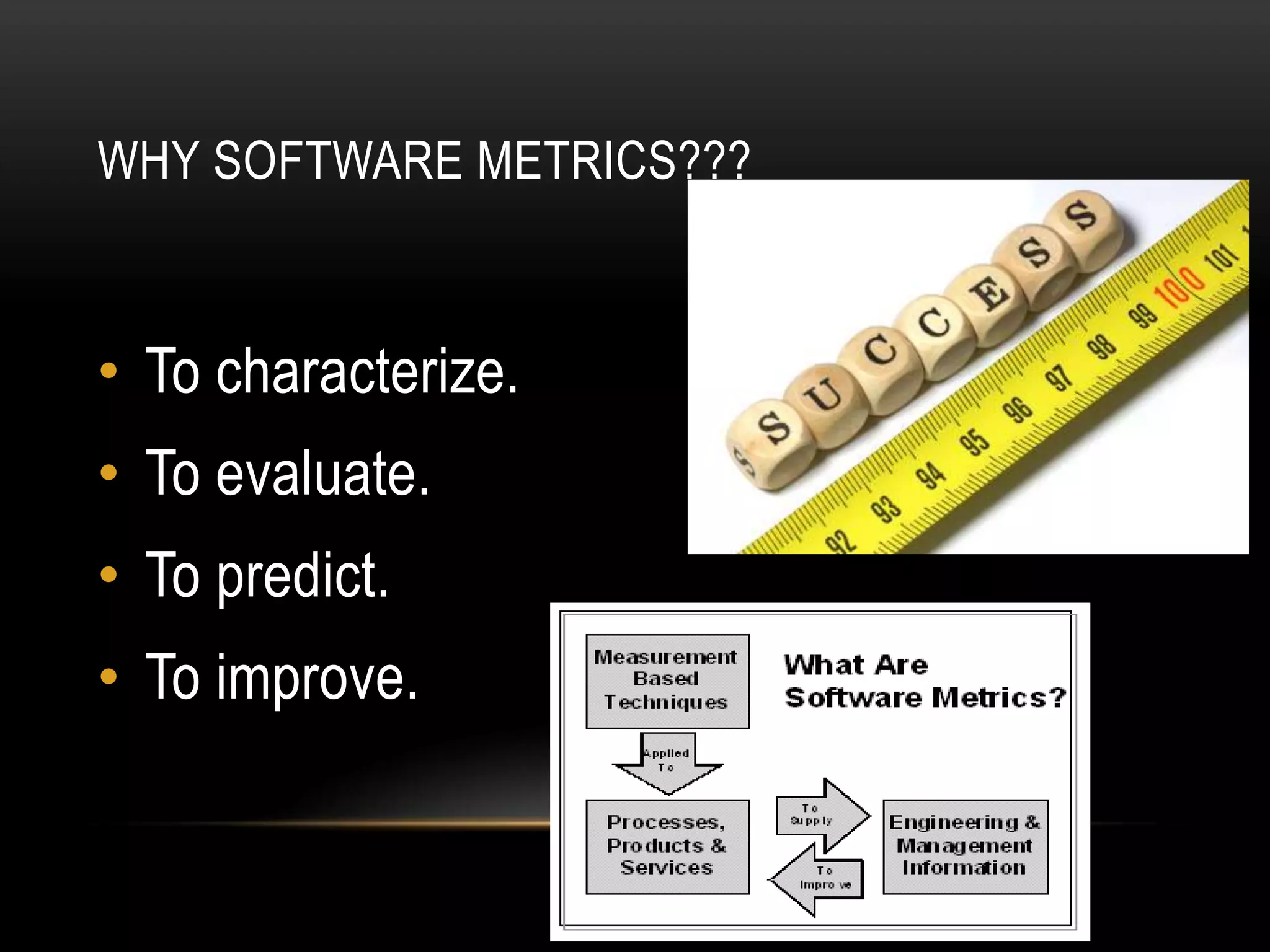
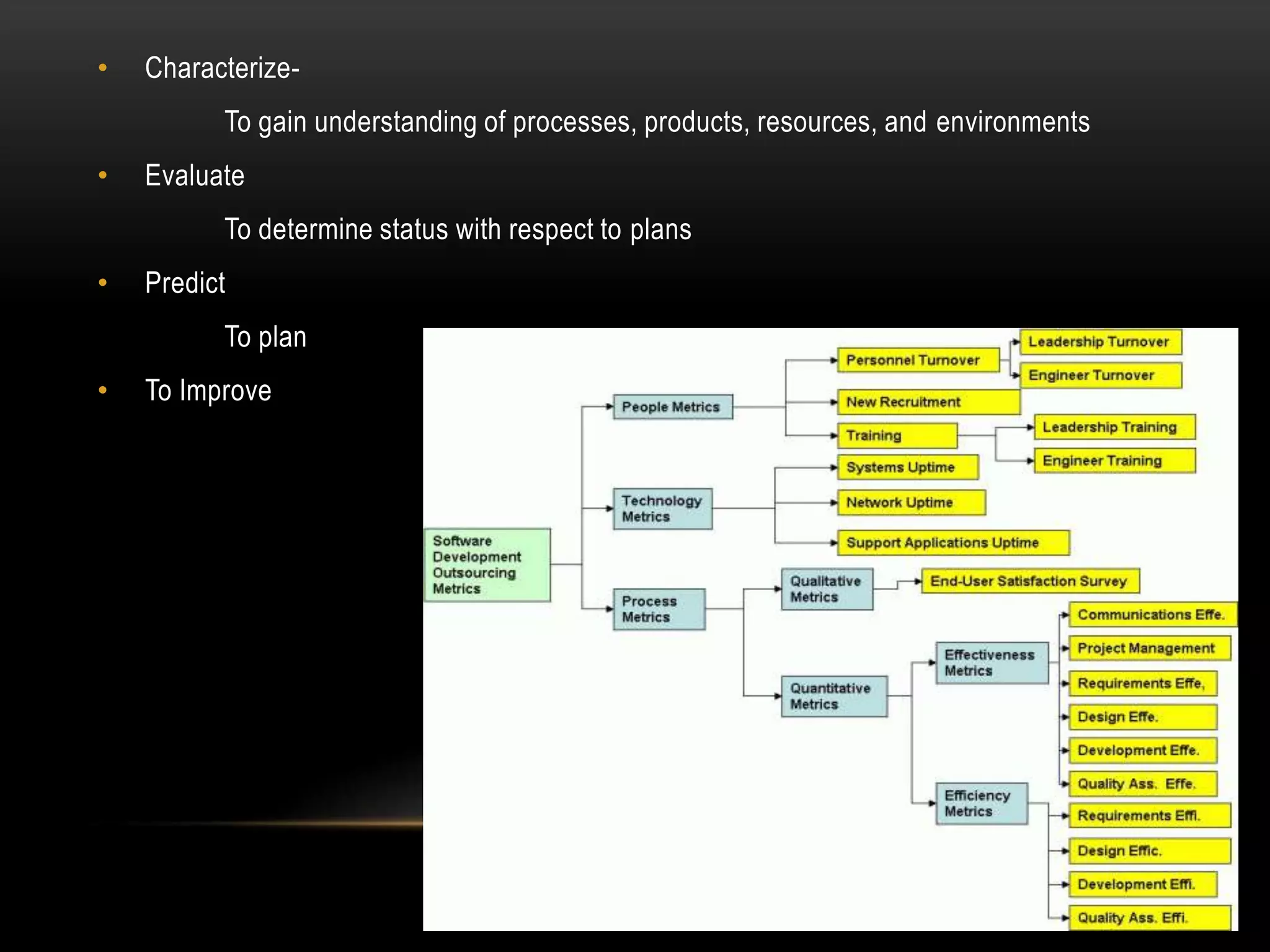
Software metrics provide quantitative measures to gain insight into software processes and projects. They are used to characterize, evaluate, predict, and improve software. There are challenges to defining effective metrics. Measurement principles include formulating appropriate metrics, collecting data, analyzing results, and providing feedback. Common software quality attributes defined by McCall and ISO standards include functionality, reliability, usability, efficiency, maintainability, and portability. Goal-oriented measurement identifies metrics to answer questions and achieve goals related to software processes and products.


![MEASUREMENT METRIC AND INDICATOR
• Measurement is the act of determining a measure.
• The IEEE Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terms [IEE93] defines
metric as
“a quantitative measure of the degree to which a system, component,
or process possesses a given attribute.”
• An indicator is a metric or combination of metrics that provide insight into the
software process, a software project, or the product itself](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/productmetrics-111021073430-phpapp01/75/Product-metrics-5-2048.jpg)