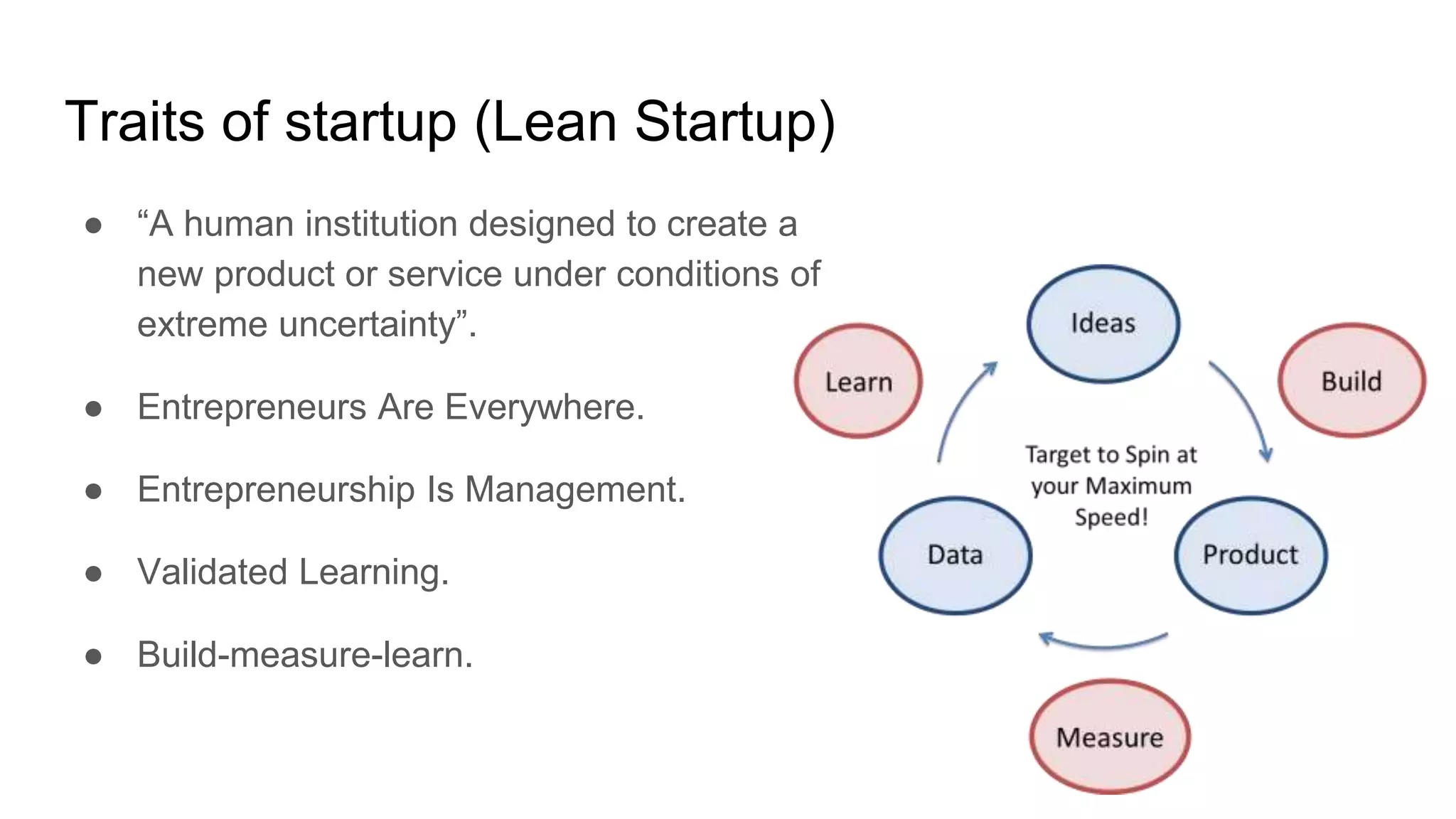
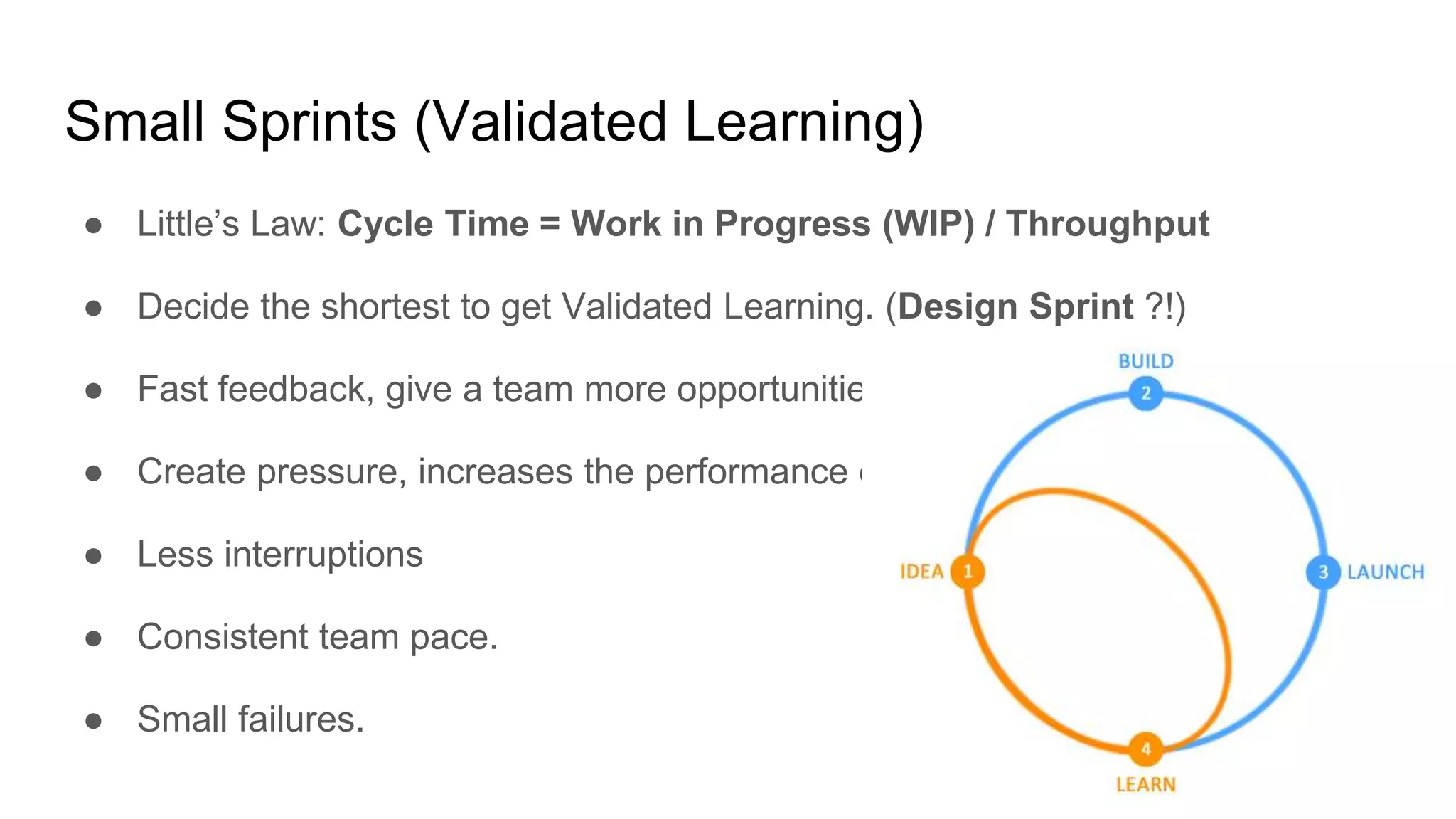
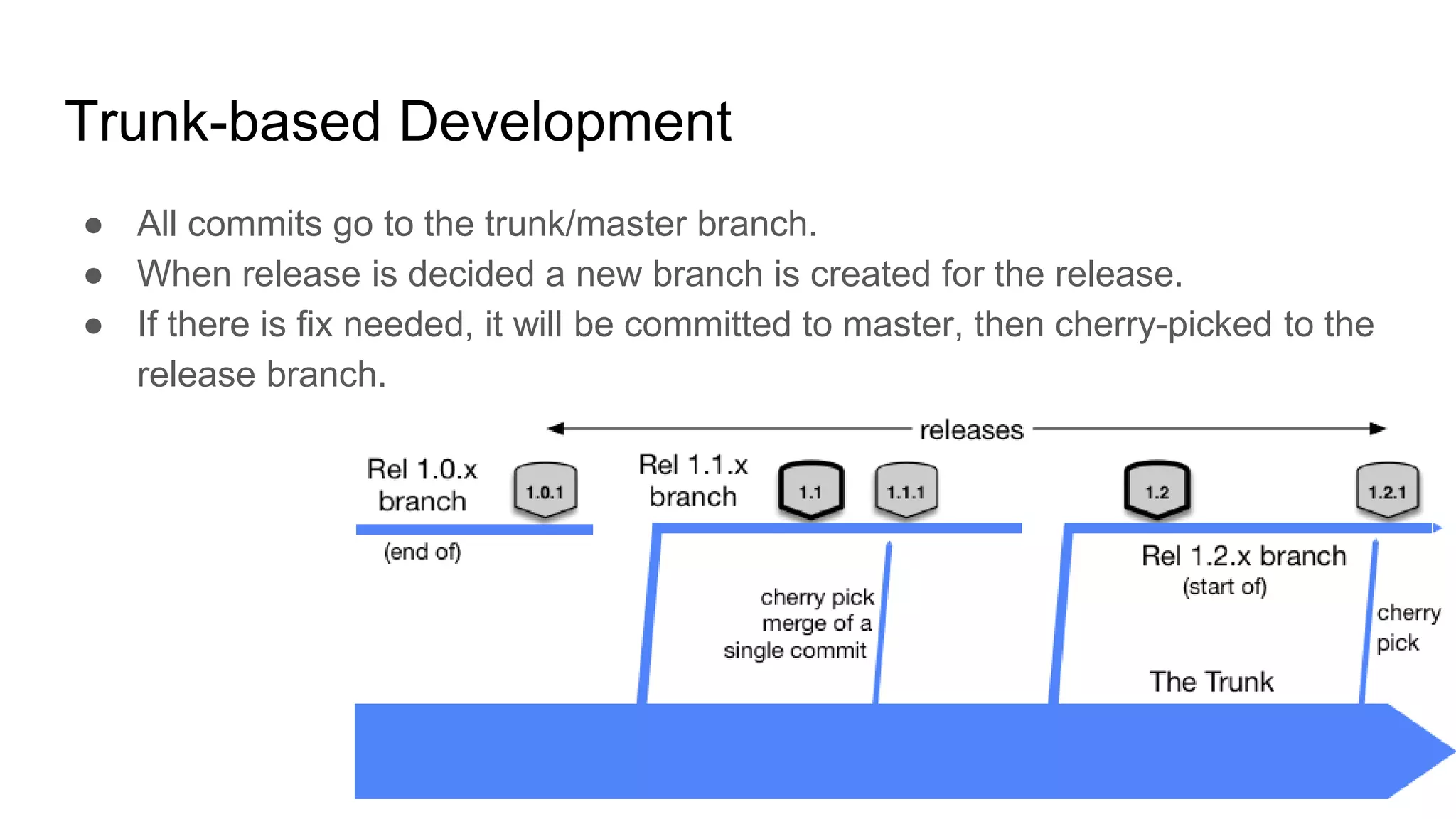
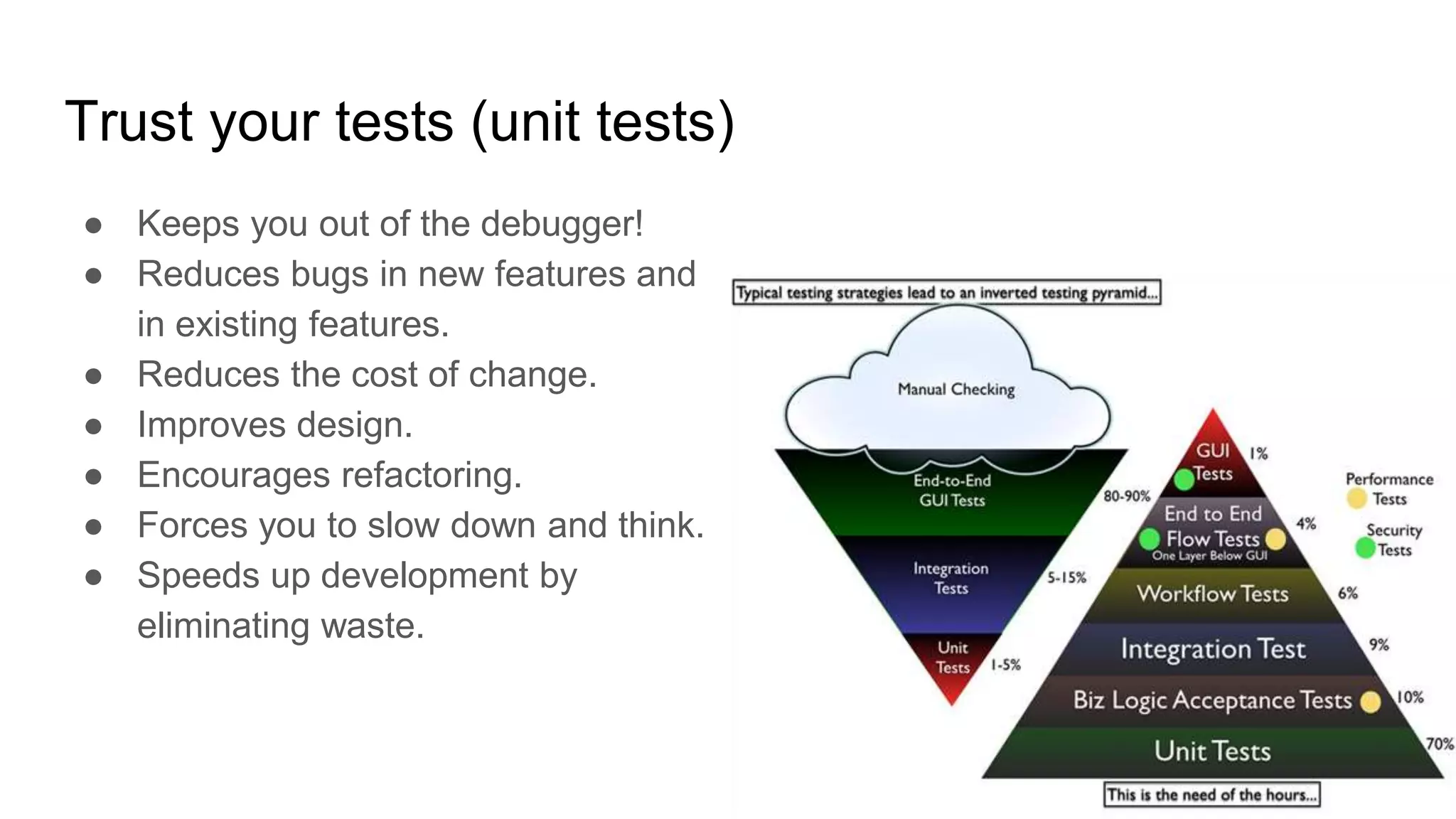
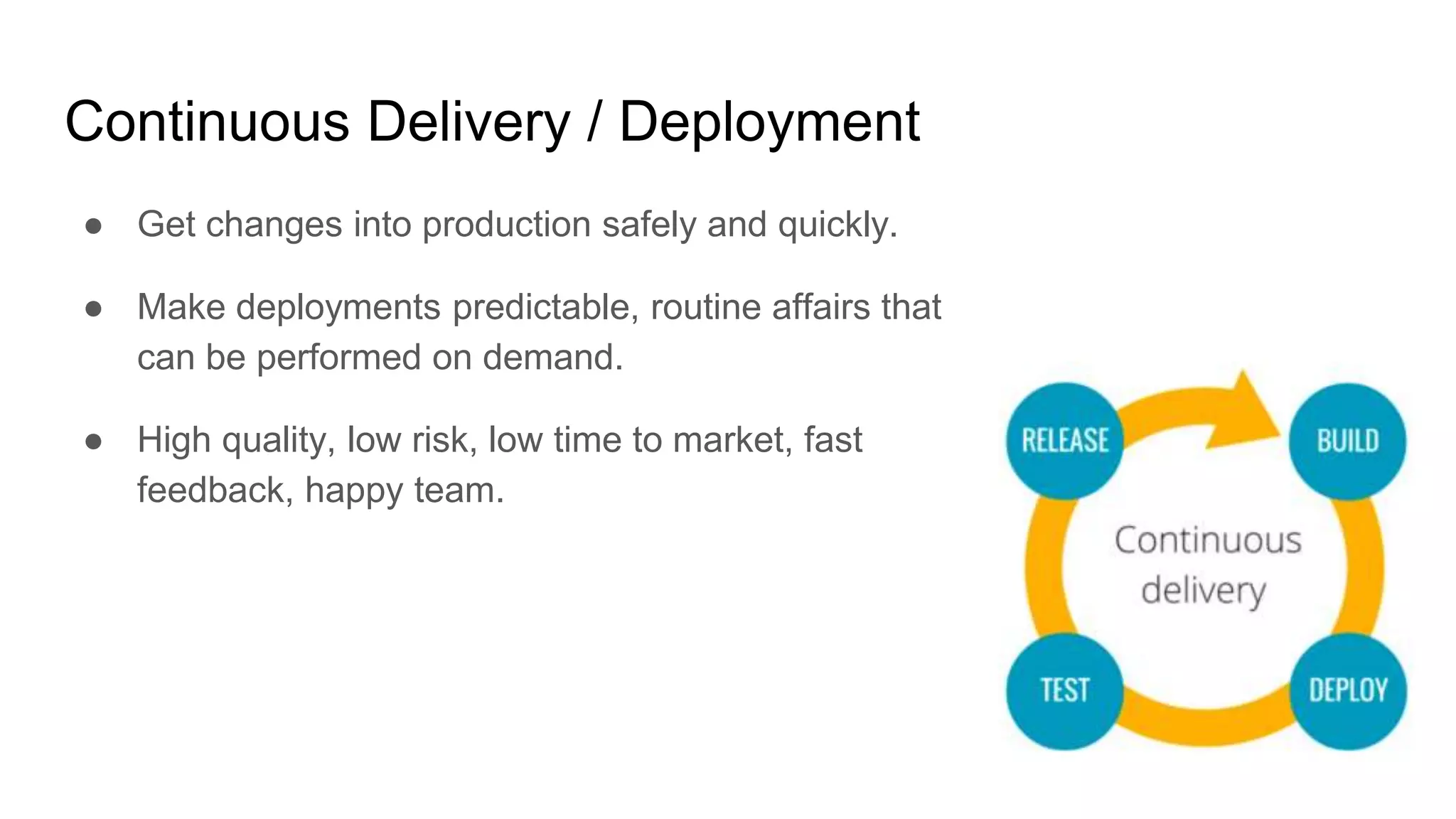
This document provides guidance on software management practices for tech startups. It recommends using small sprints for validated learning, maintaining a lean backlog focused on the minimum viable product, trunk-based development, unit testing to reduce bugs and costs, testing features on production through techniques like A/B testing, continuous delivery to get changes to production quickly, and an evolutionary architecture designed for incremental change. The overall message is that startups need agile practices that provide fast feedback to validate ideas and rapidly adapt to uncertainty.