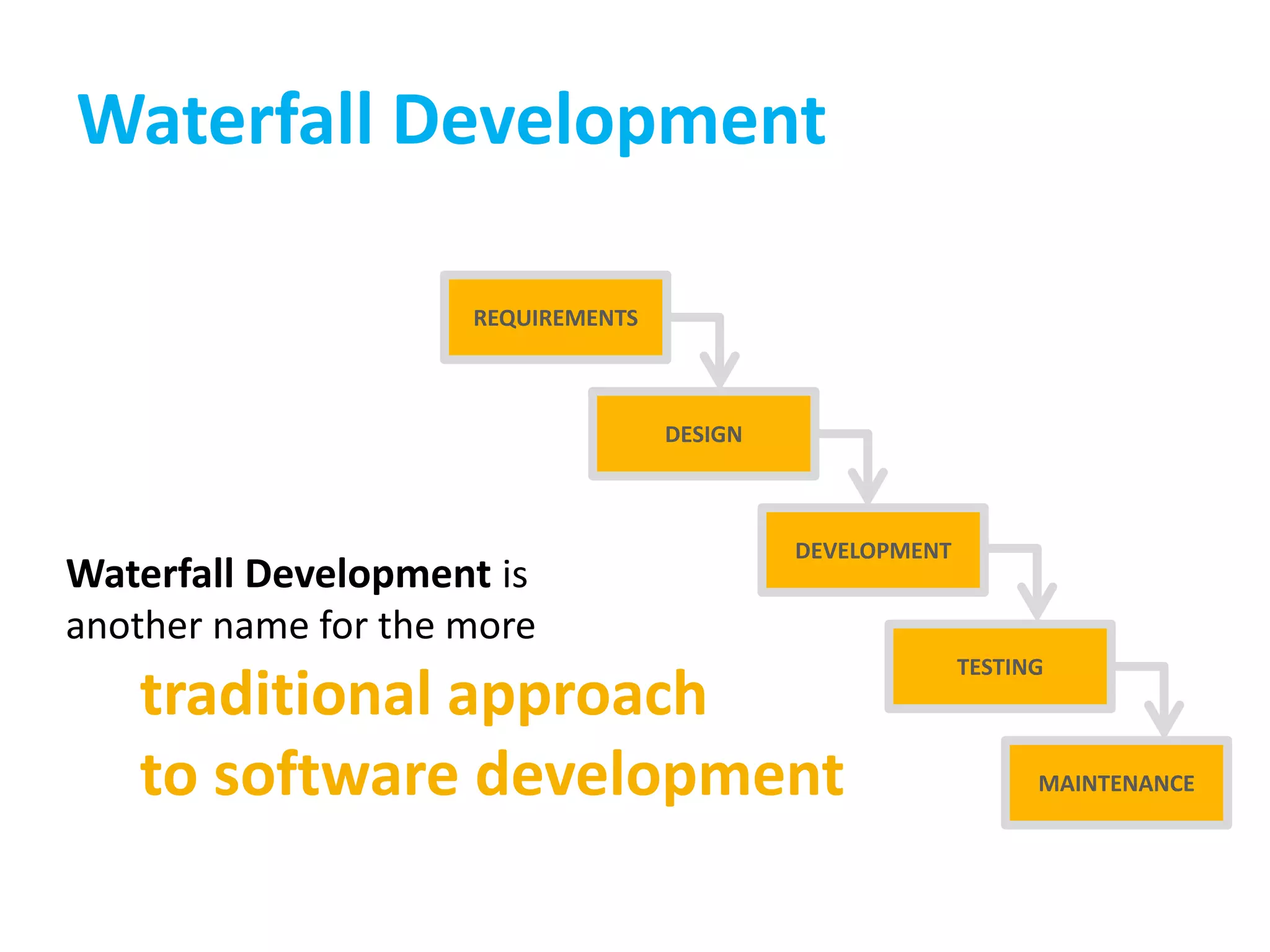
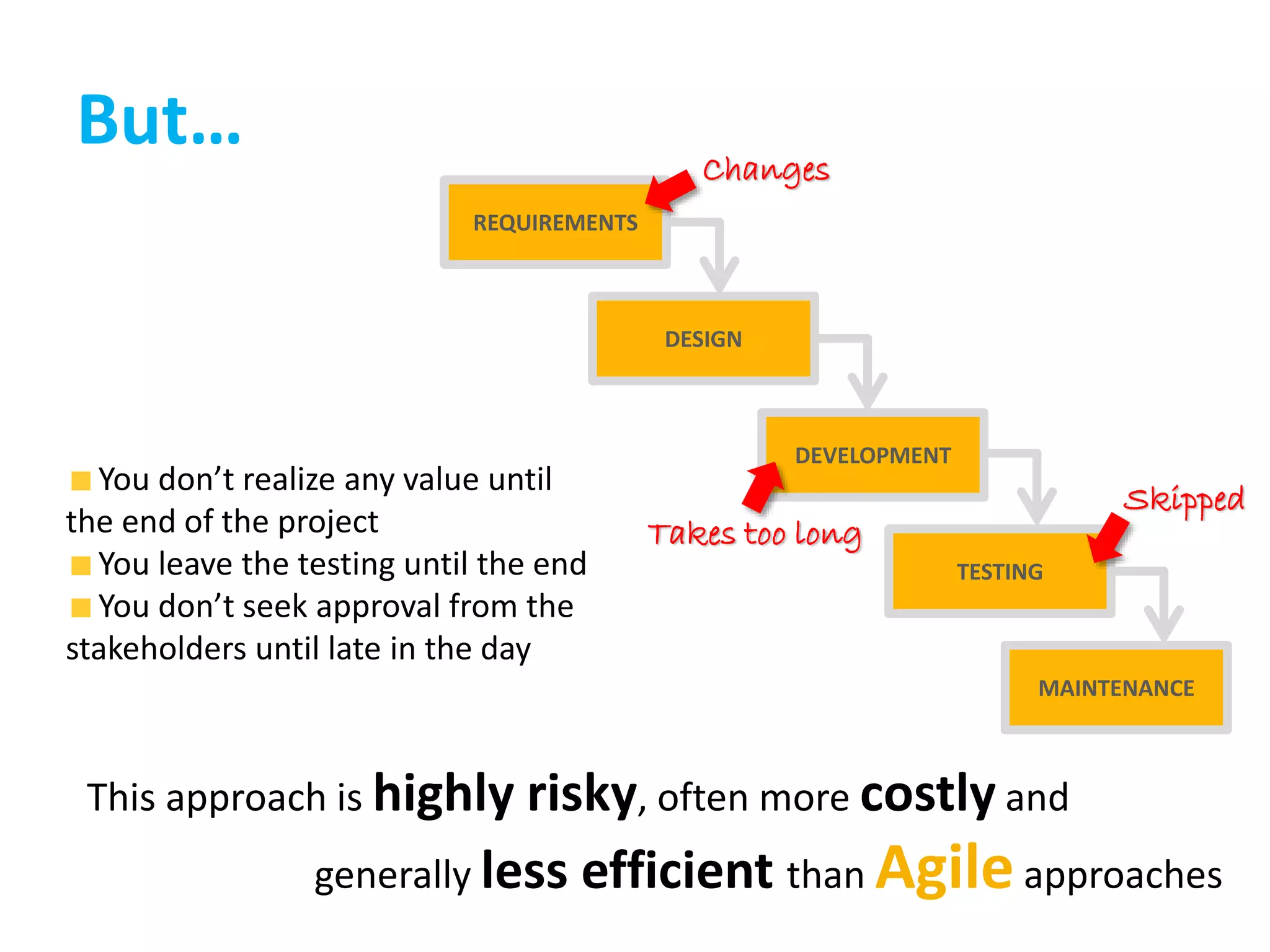
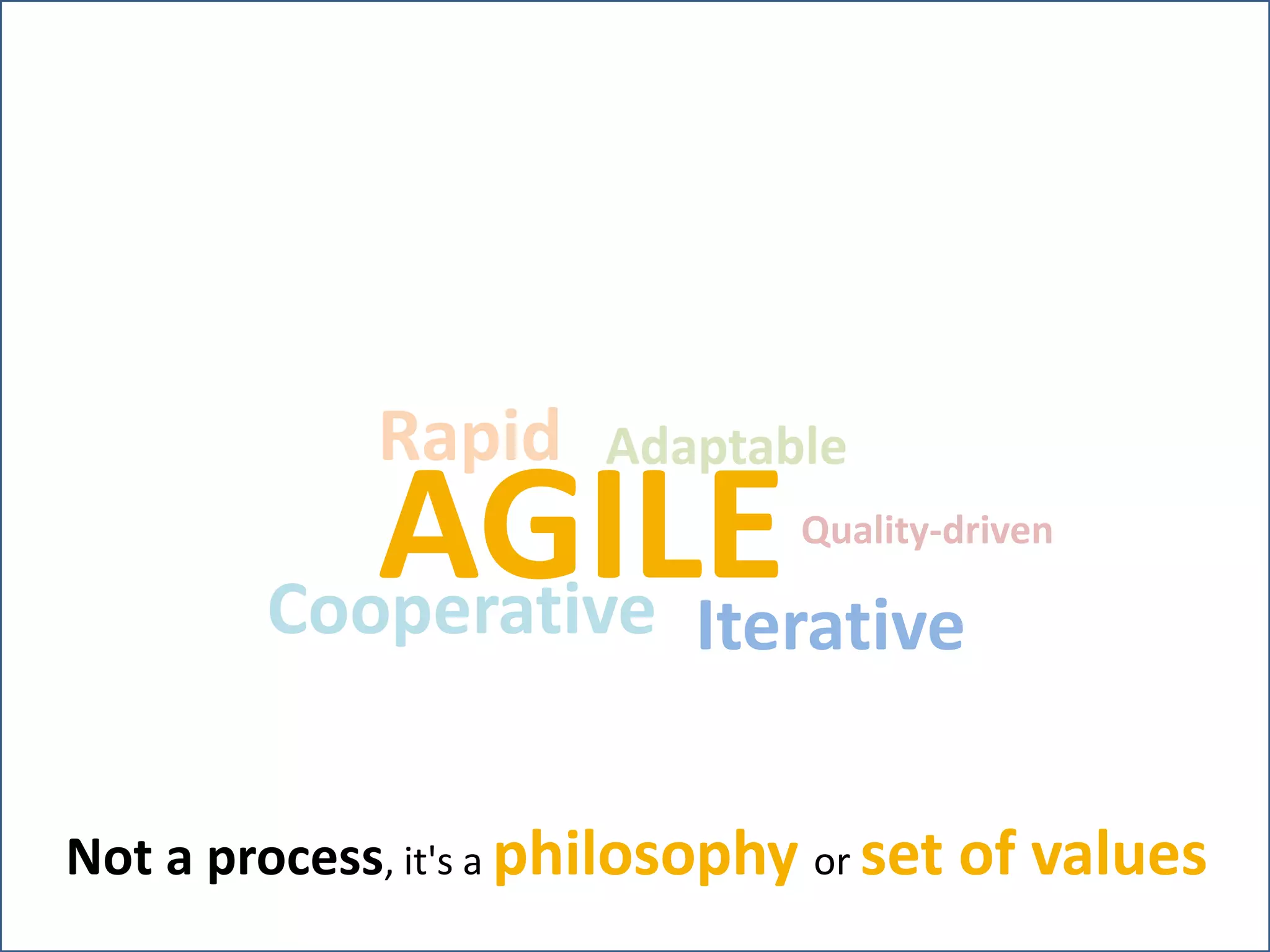
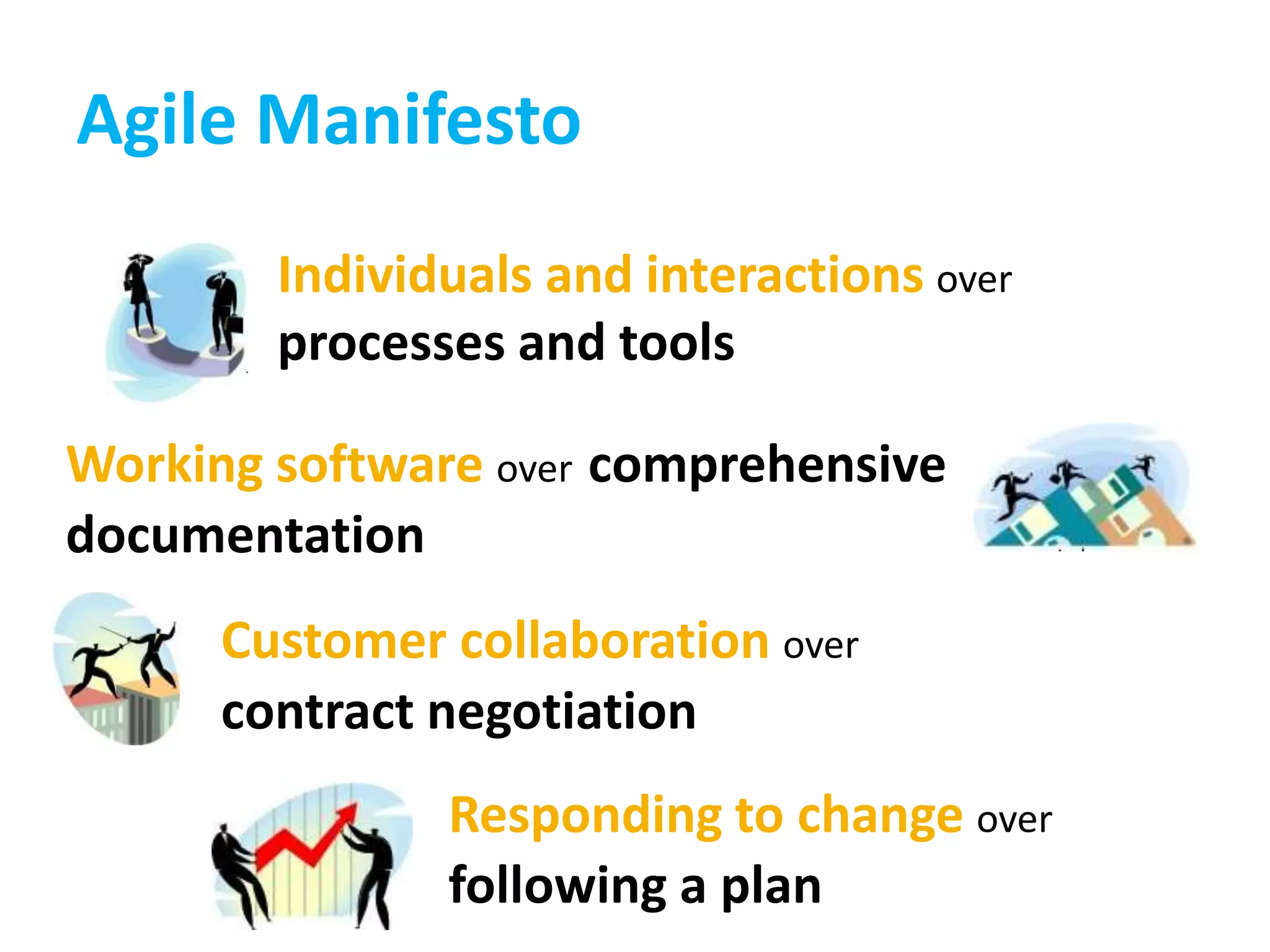
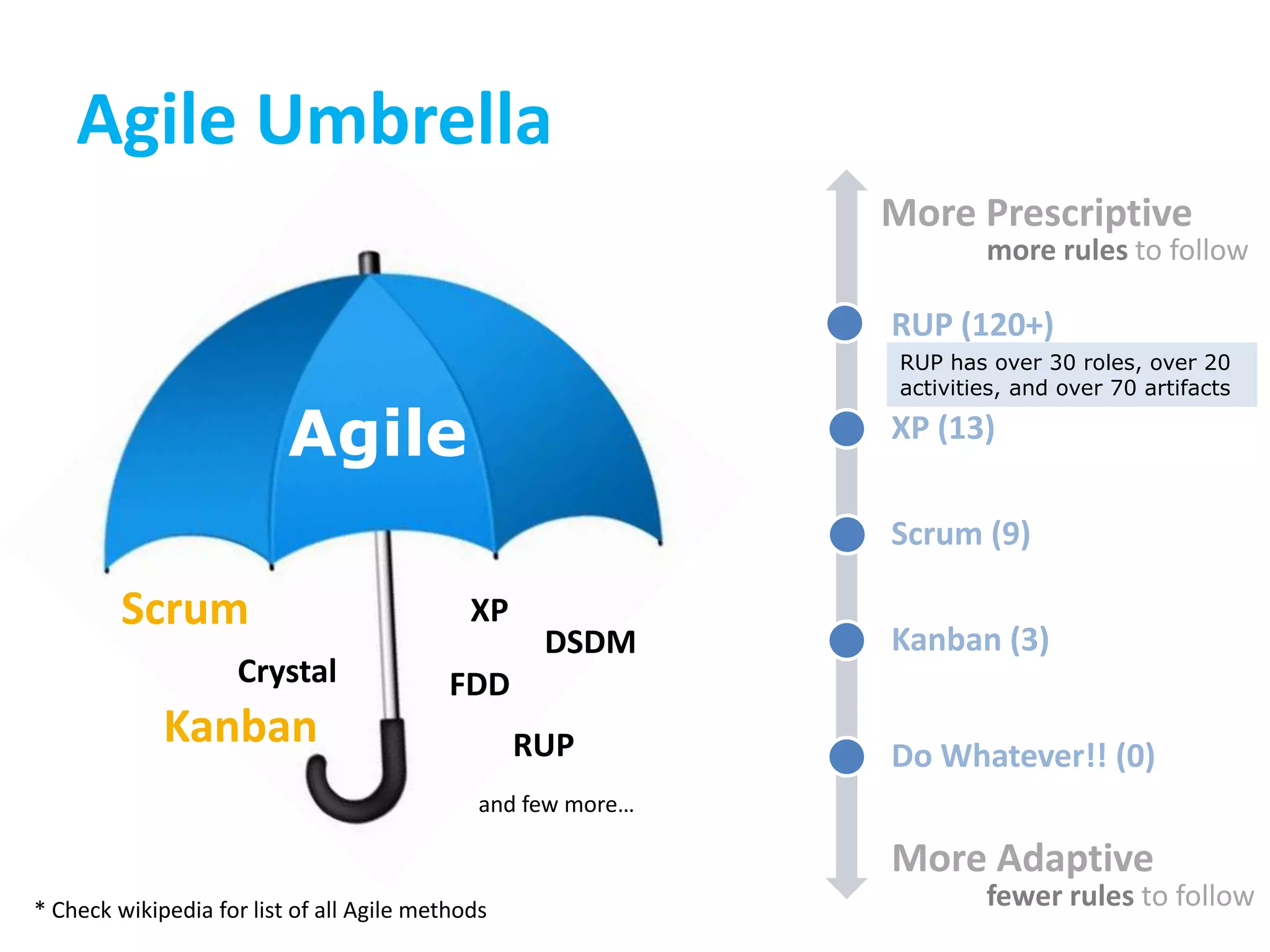
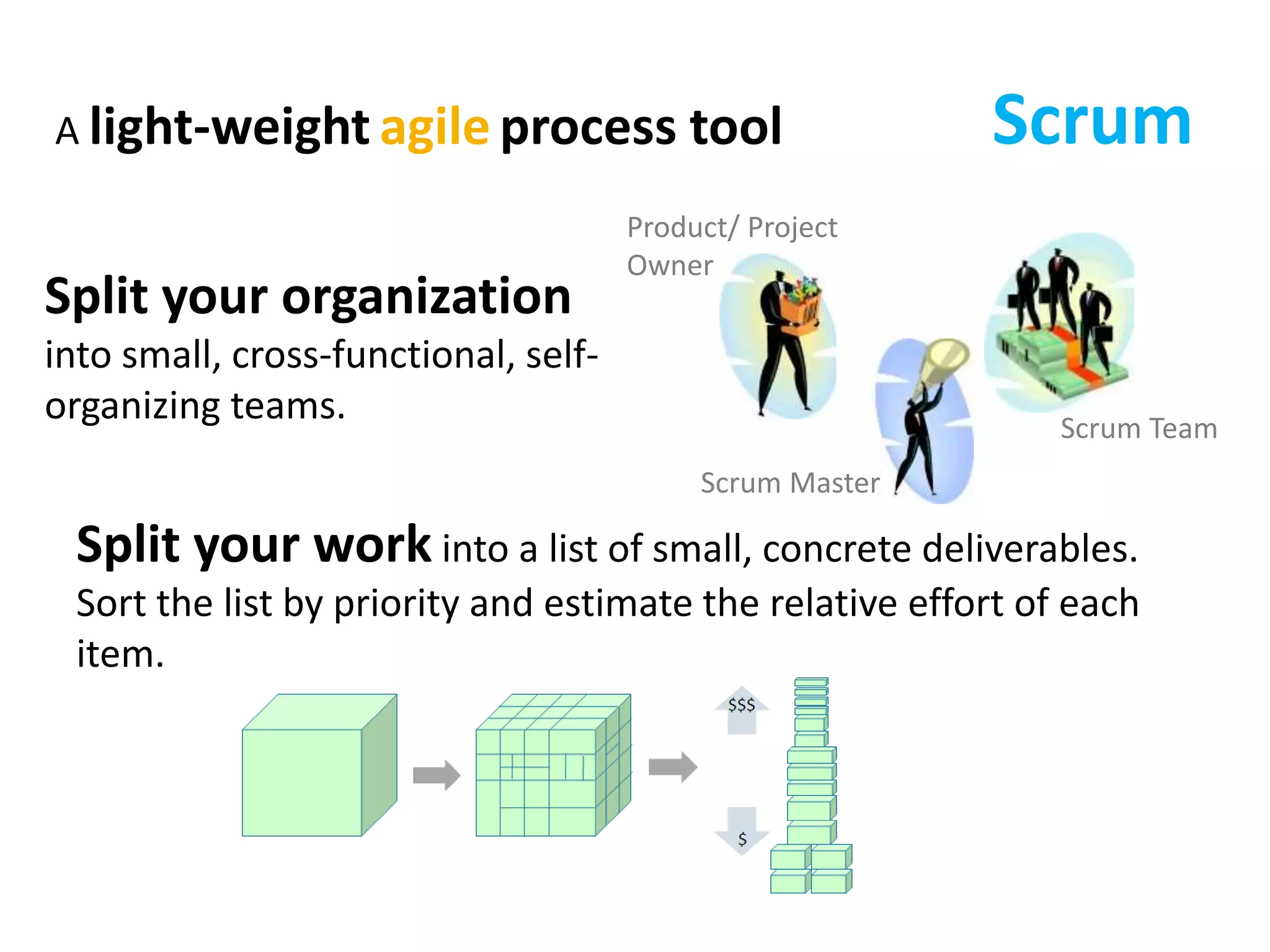
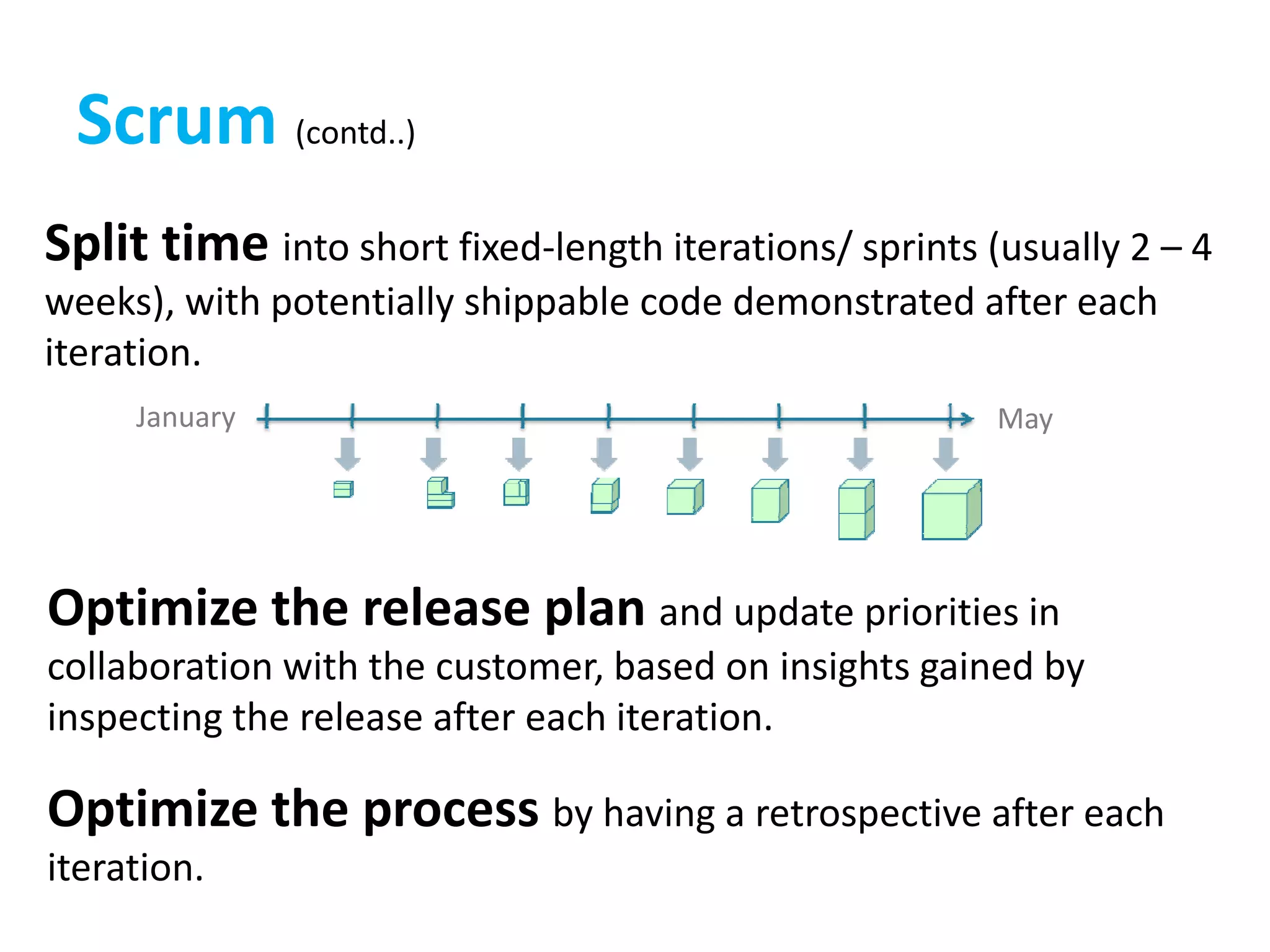
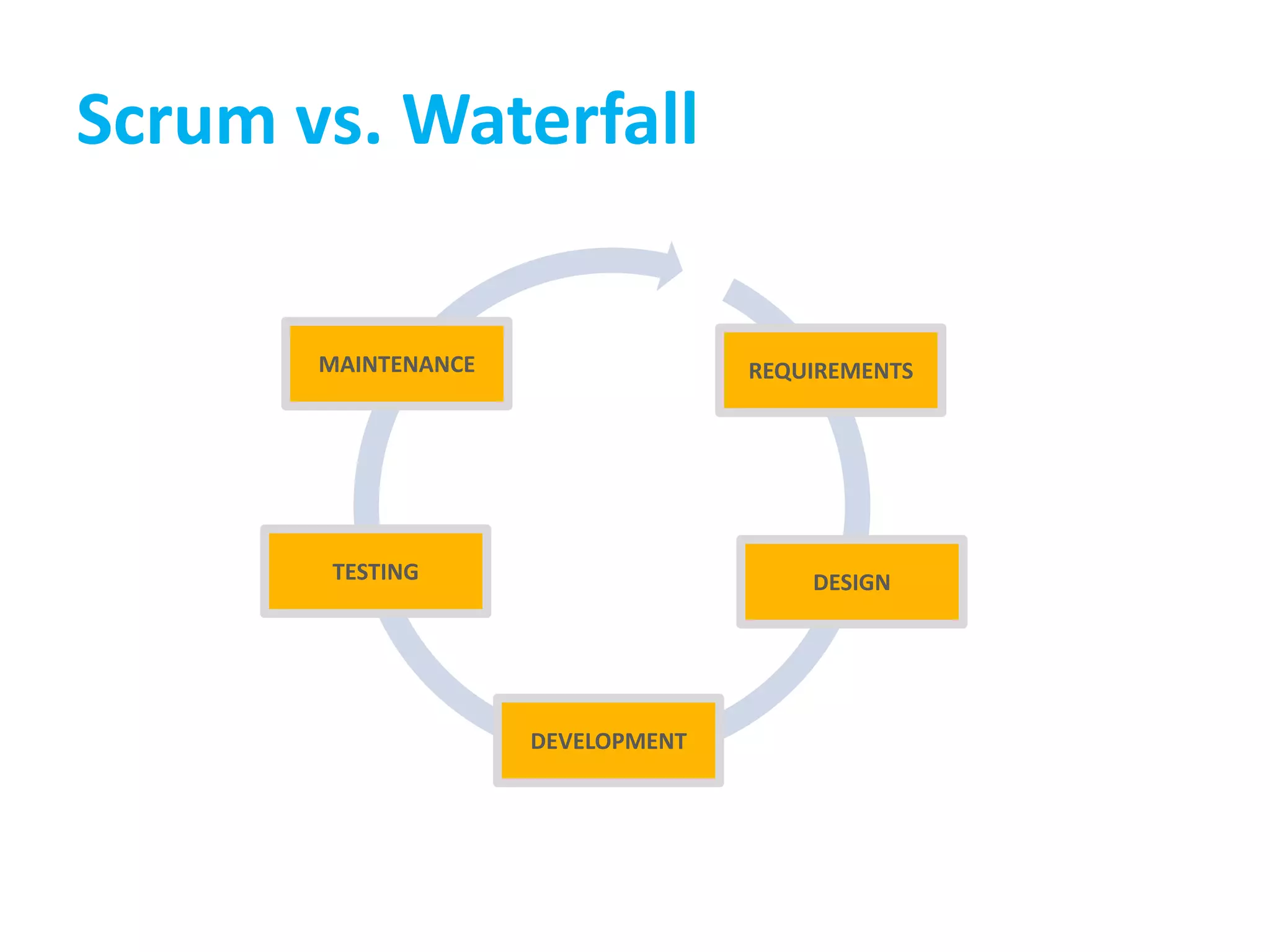
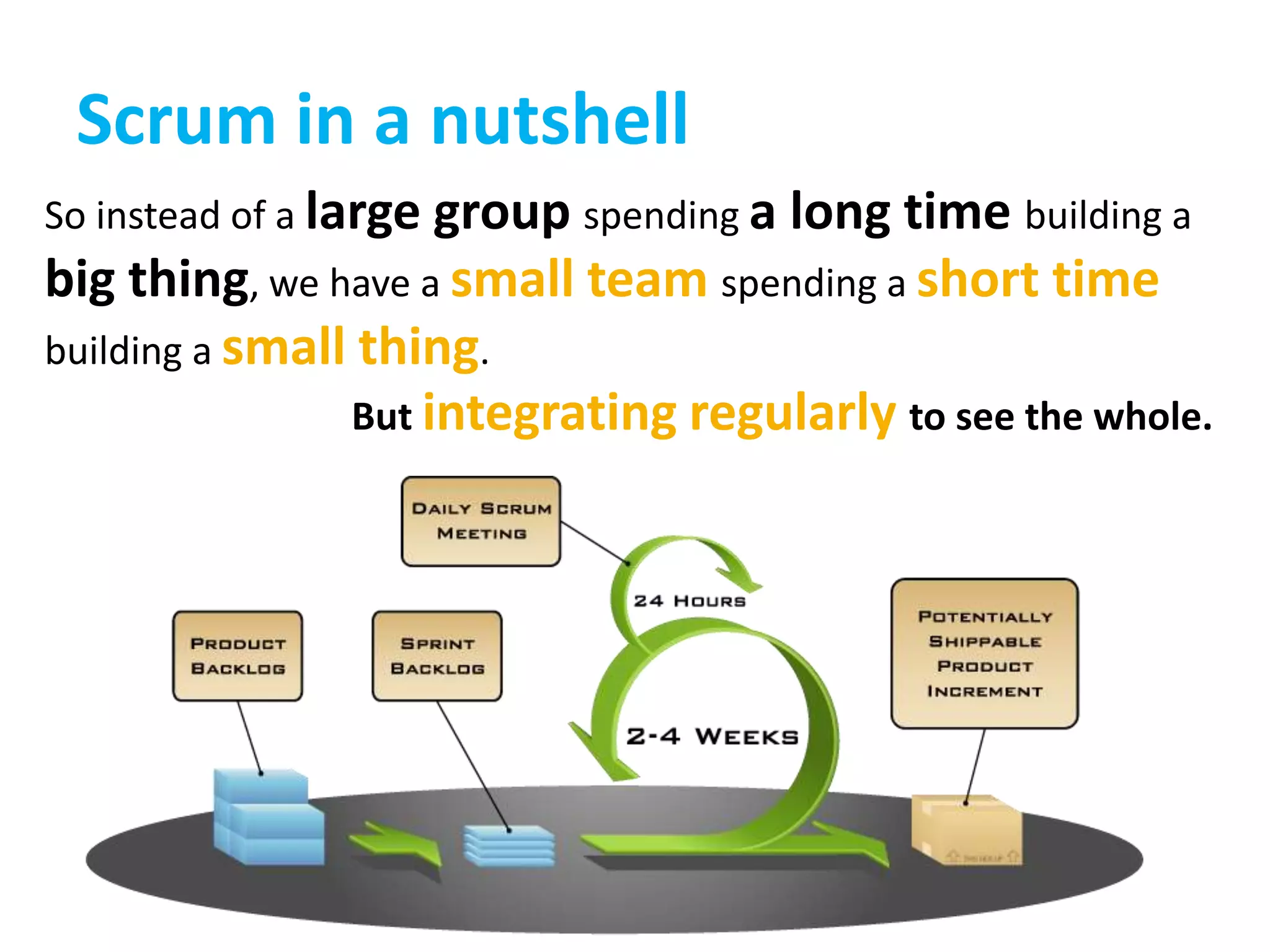
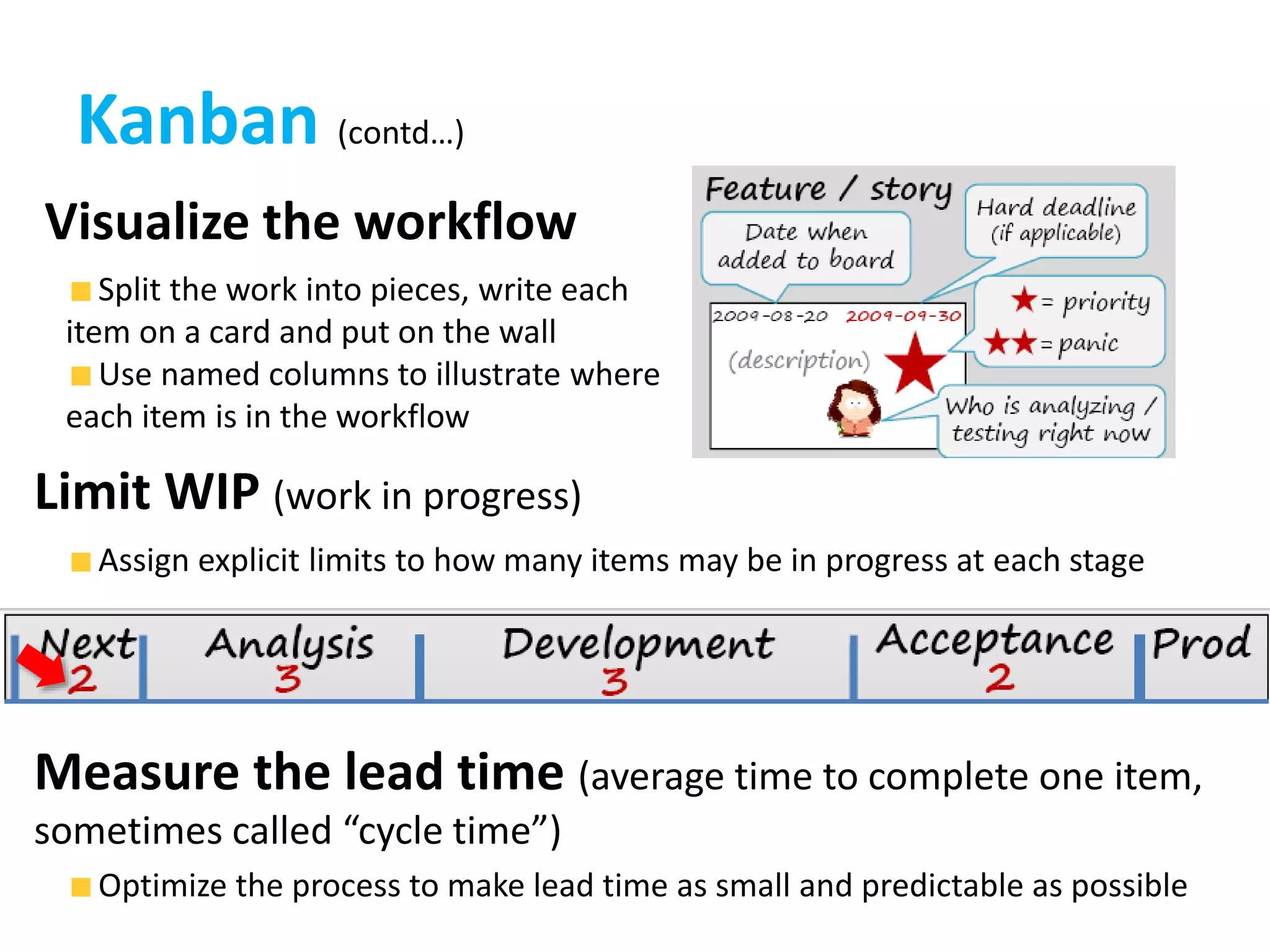
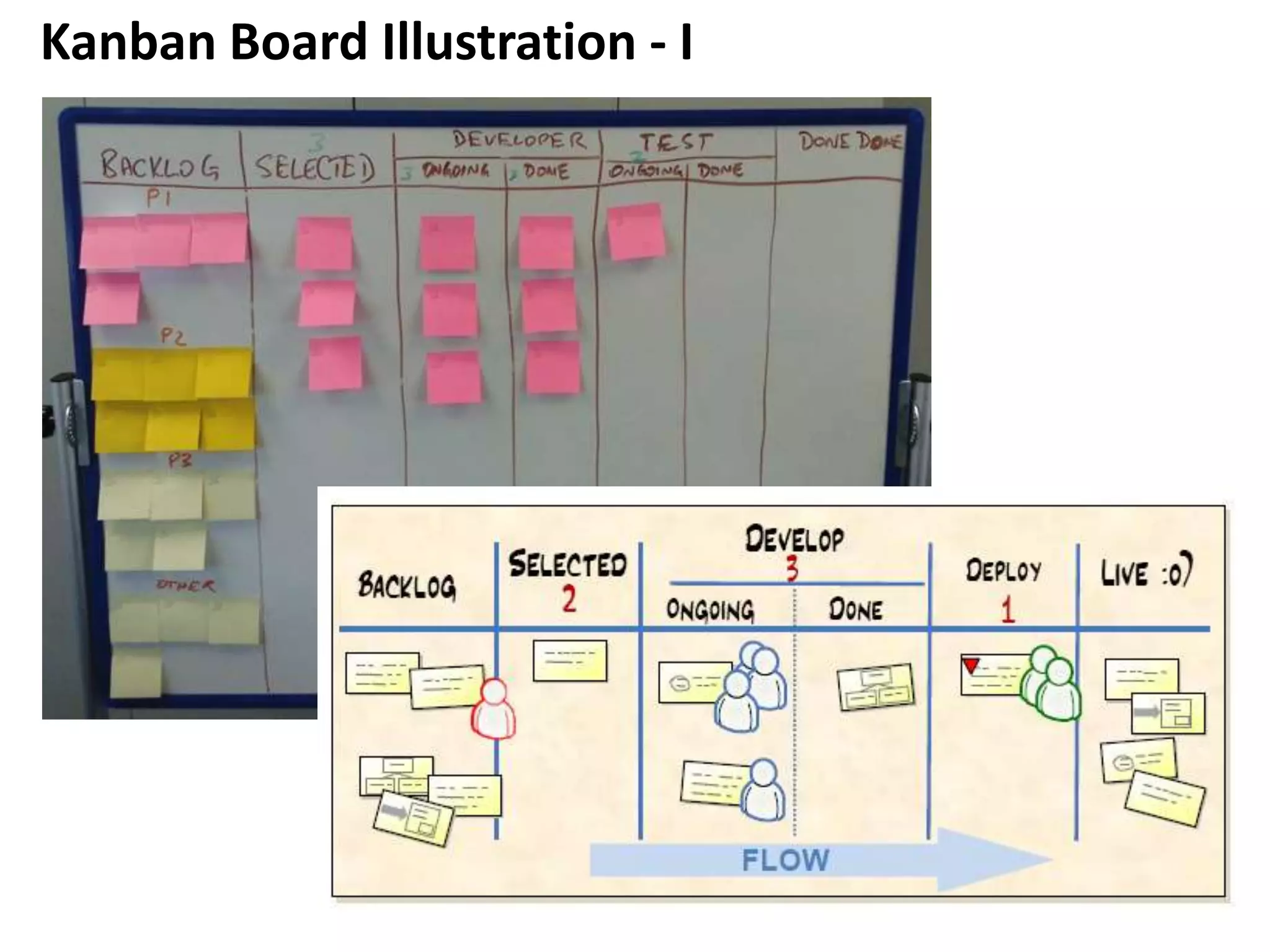
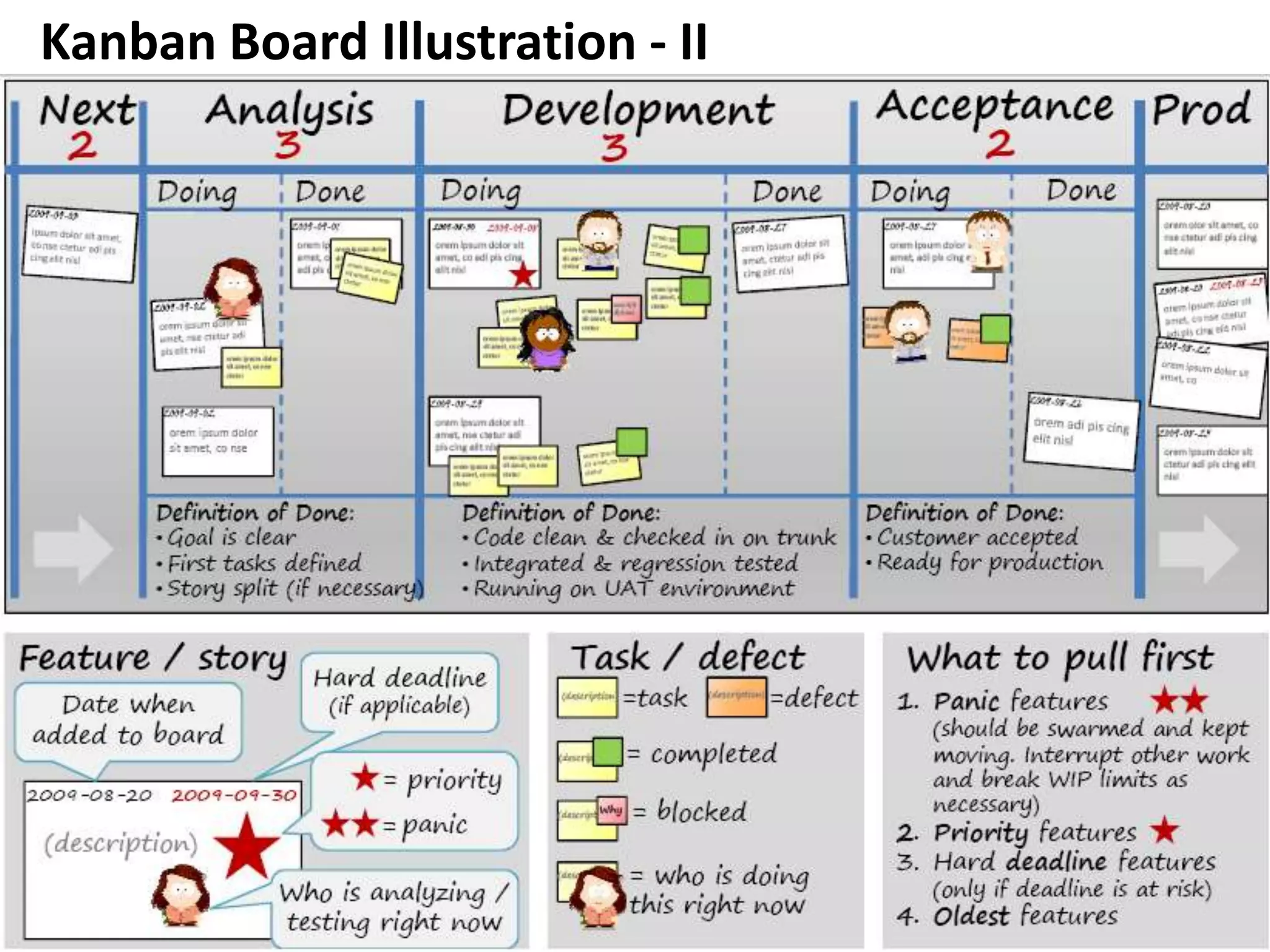
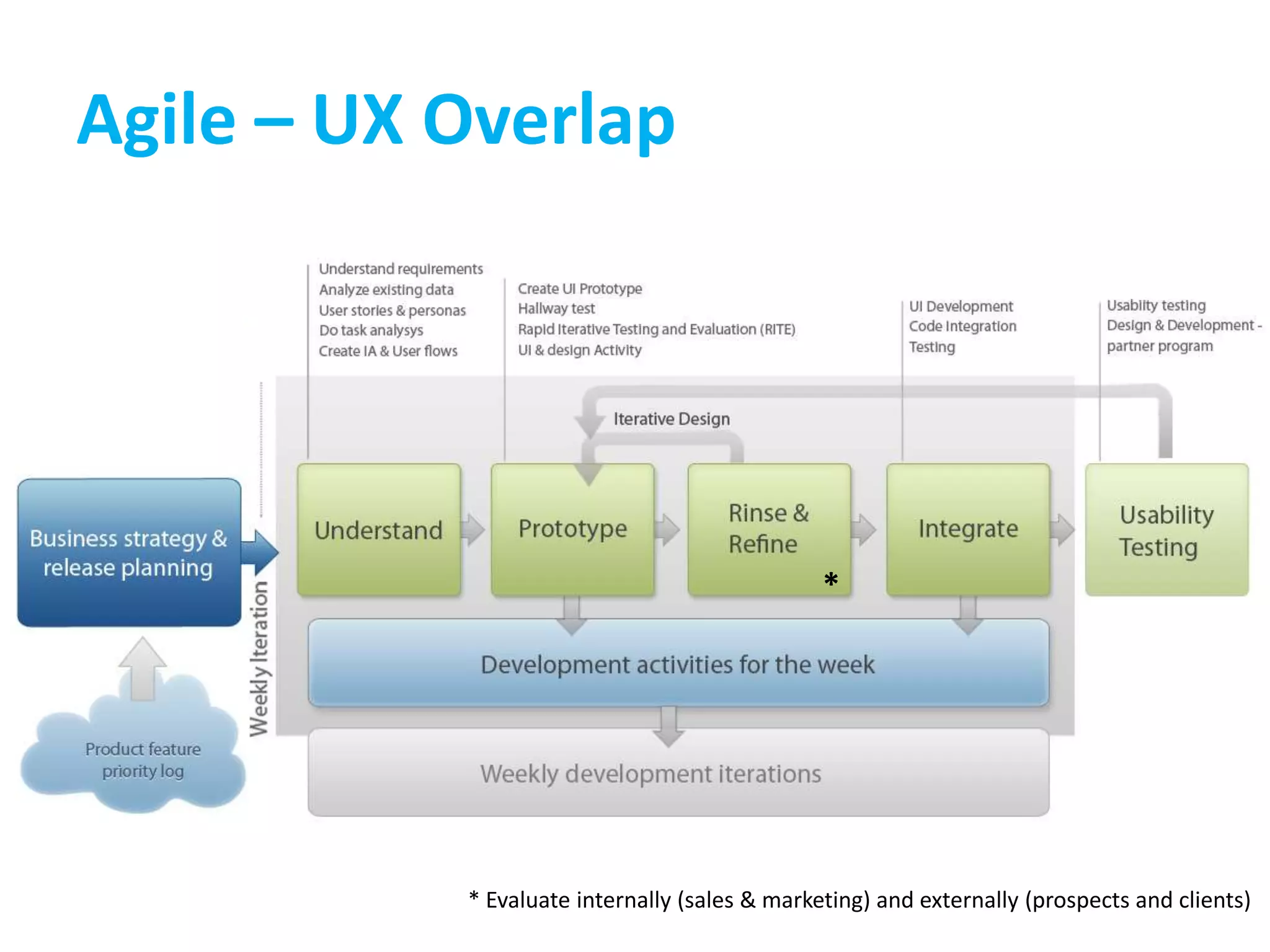
This document provides an overview of agile methodology and compares it to traditional waterfall development processes. It describes how agile is iterative and adaptive rather than moving in sequential phases. Specific agile frameworks like Scrum and Kanban are then explained. Scrum uses short sprints, daily stand-ups, and prioritized backlogs. Kanban uses visualization, limits work-in-progress, and aims to eliminate waste. Both frameworks emphasize iterative development, collaboration, and responding to change over rigid plans.
![Overview of
Agile Methodology
Prepared by: Haresh Karkar [Information Architect]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overviewofagilemethodology-150715163226-lva1-app6892/75/Overview-of-agile-methodology-1-2048.jpg)
![Software development processes
A [really] short history of](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overviewofagilemethodology-150715163226-lva1-app6892/75/Overview-of-agile-methodology-2-2048.jpg)