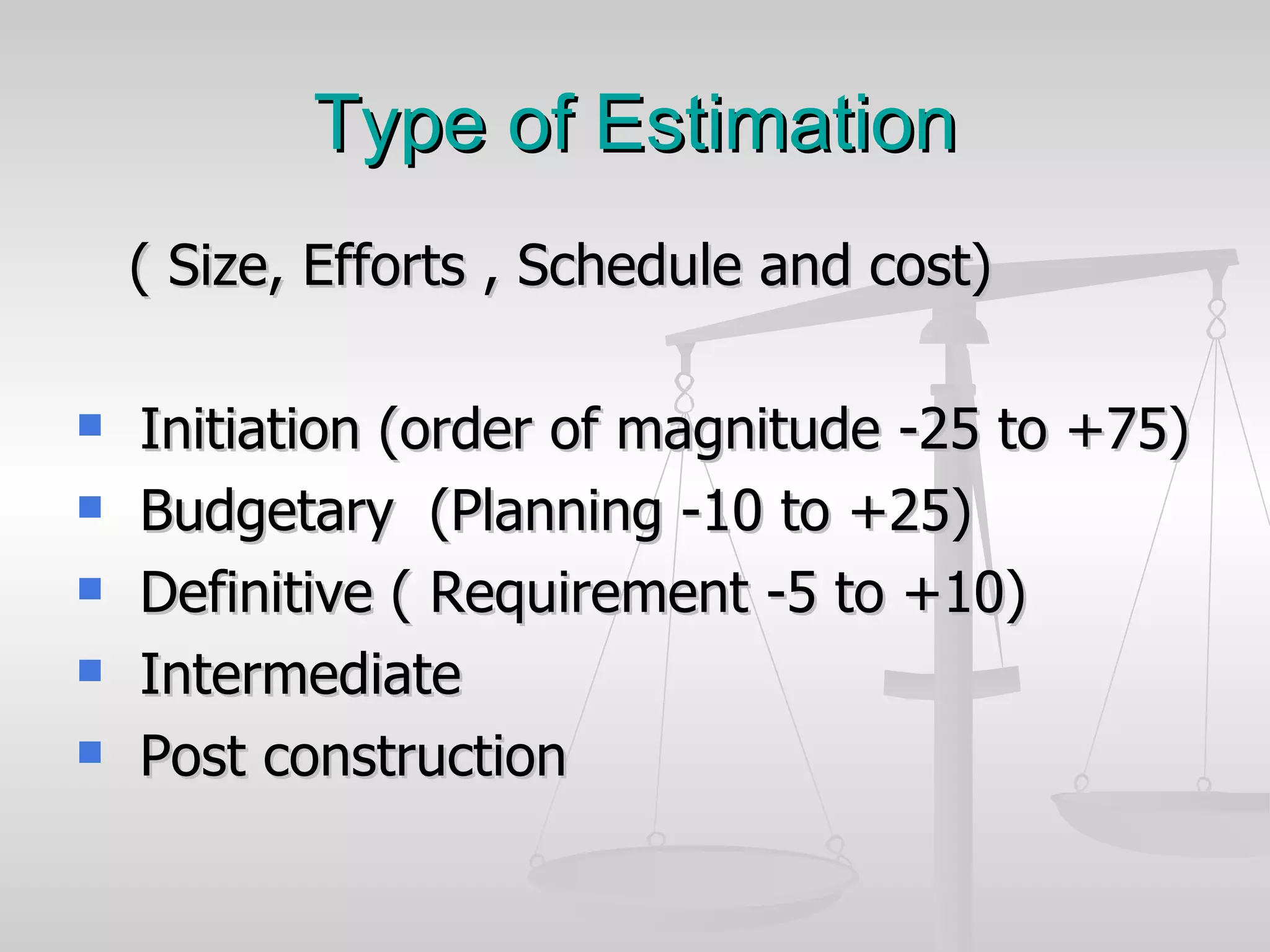
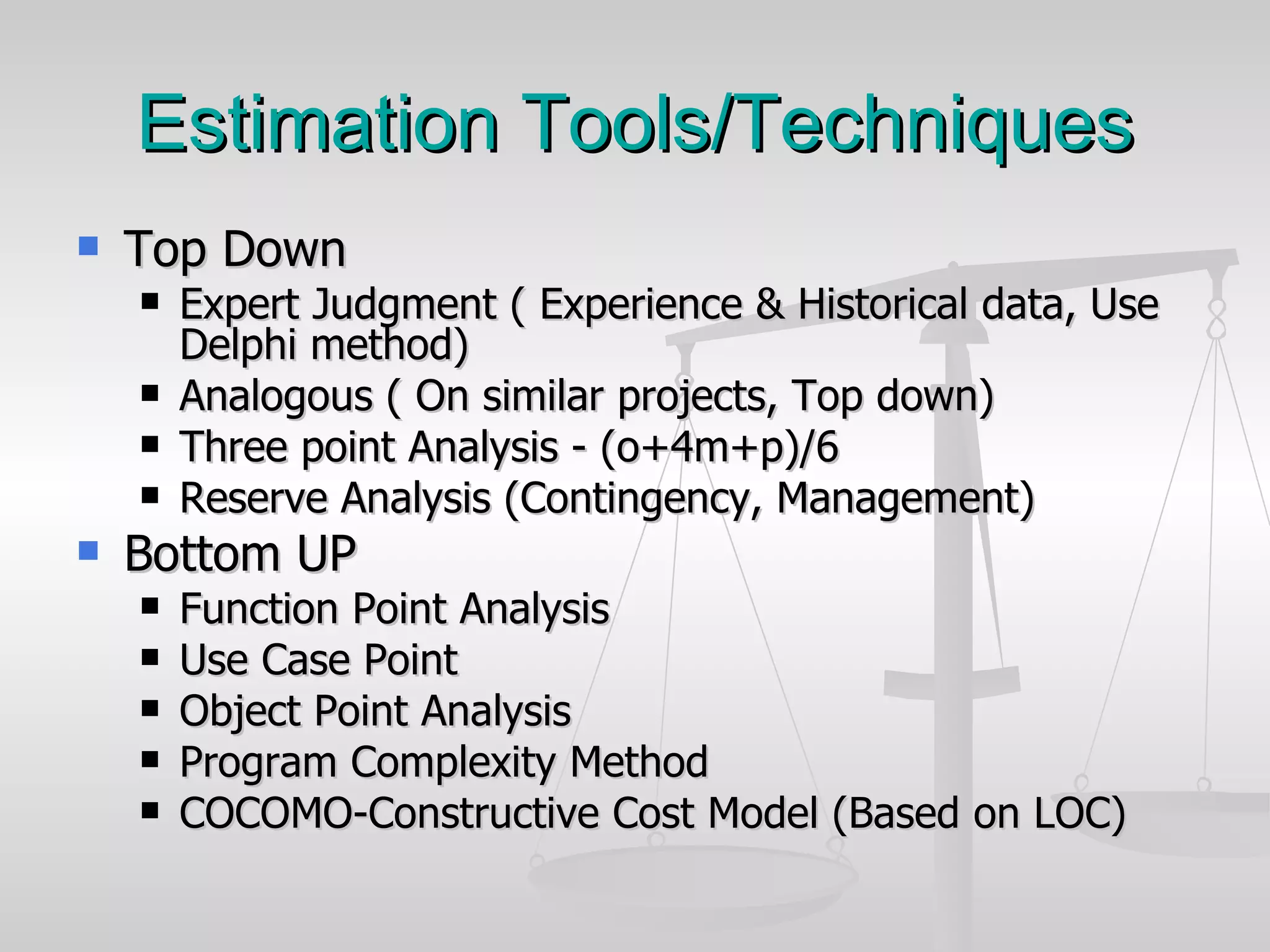
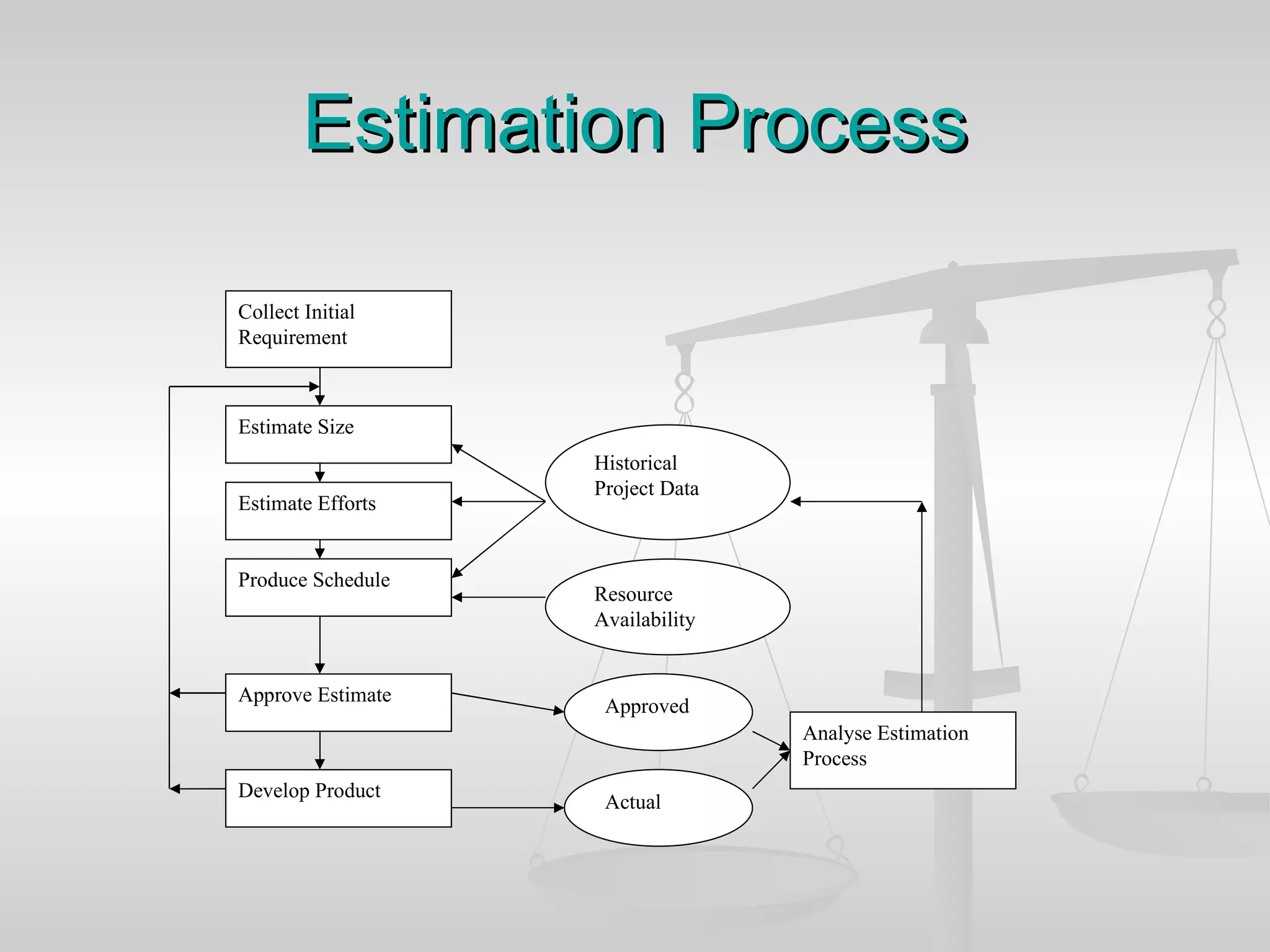
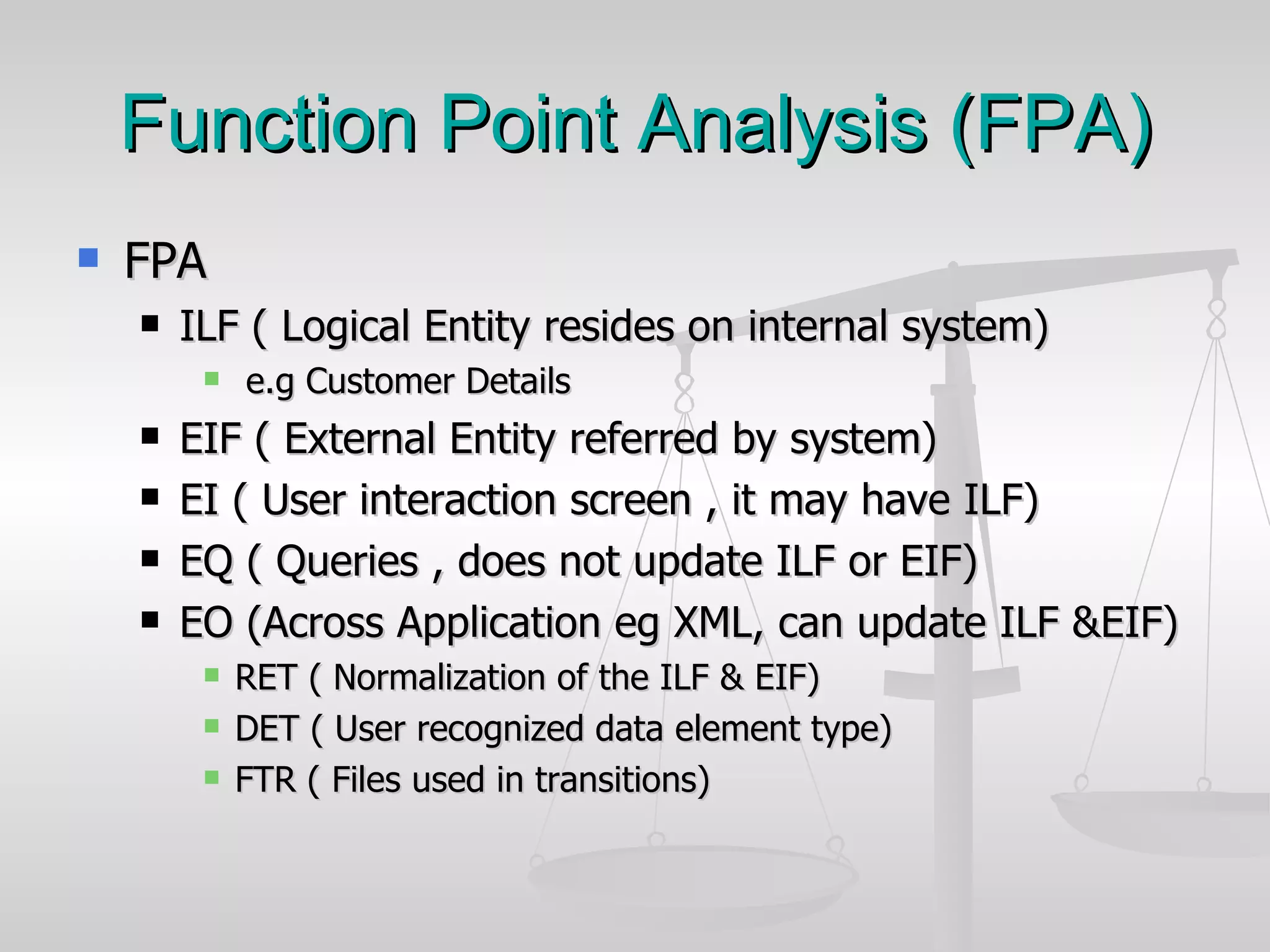
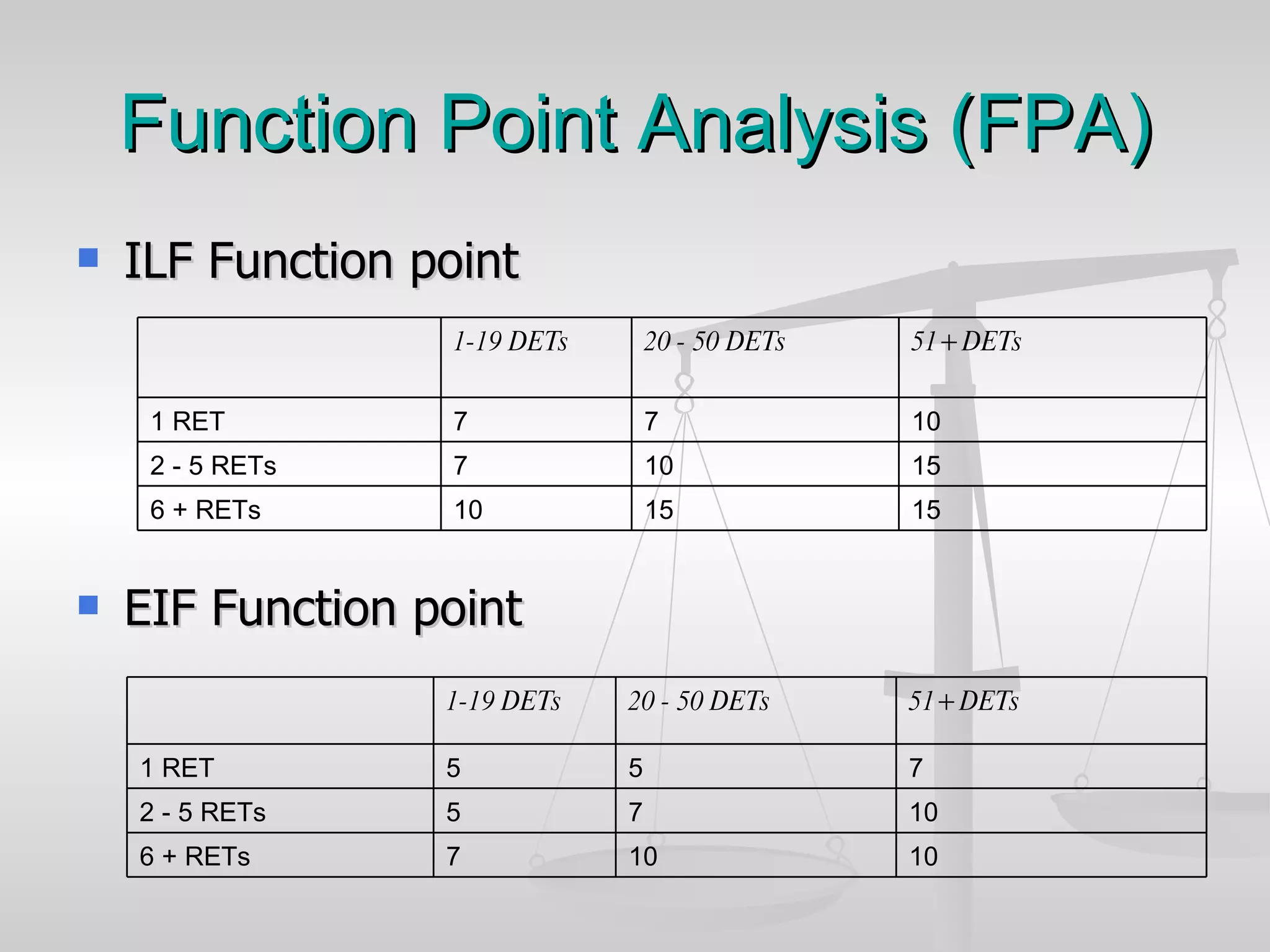
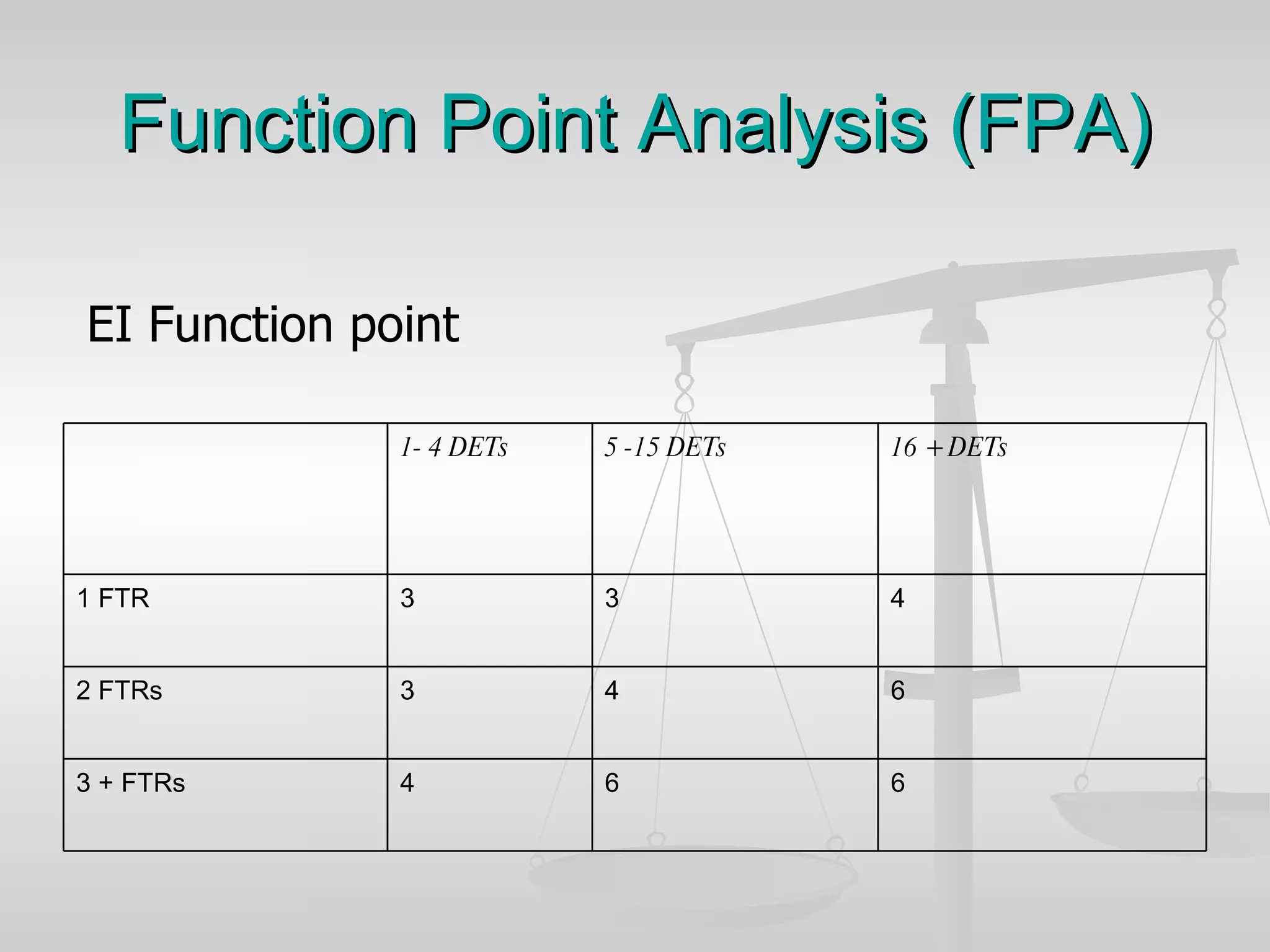
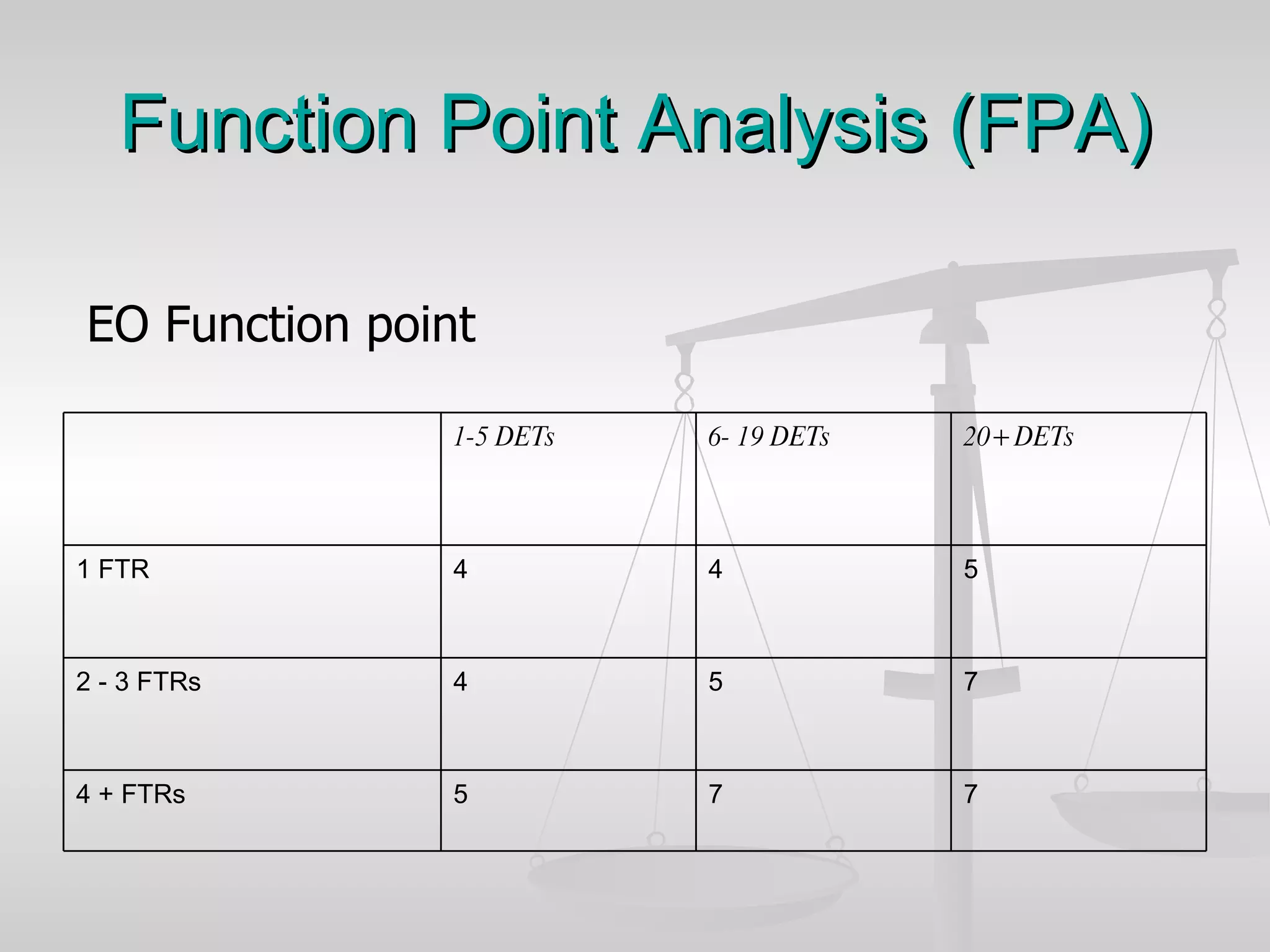
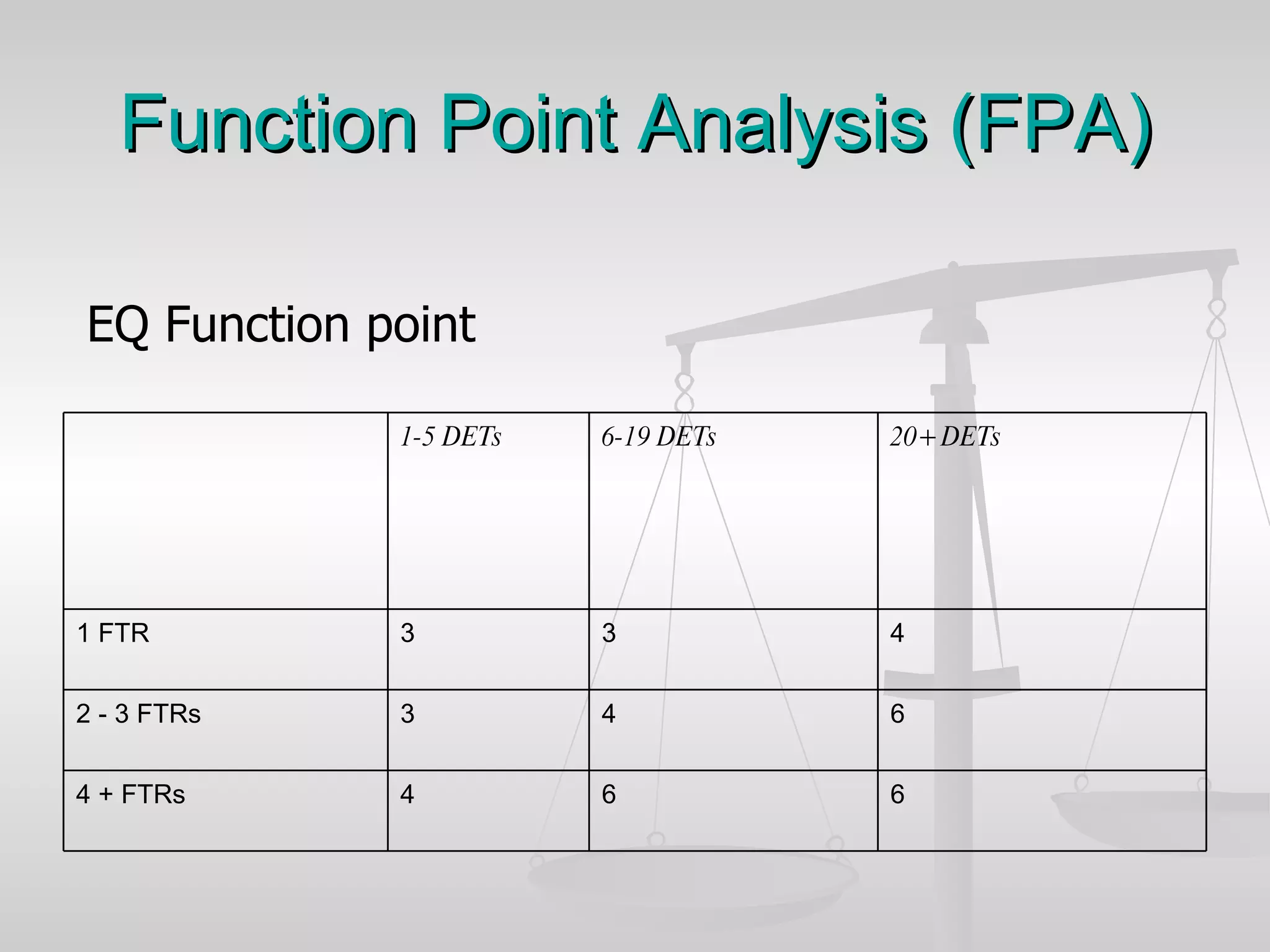
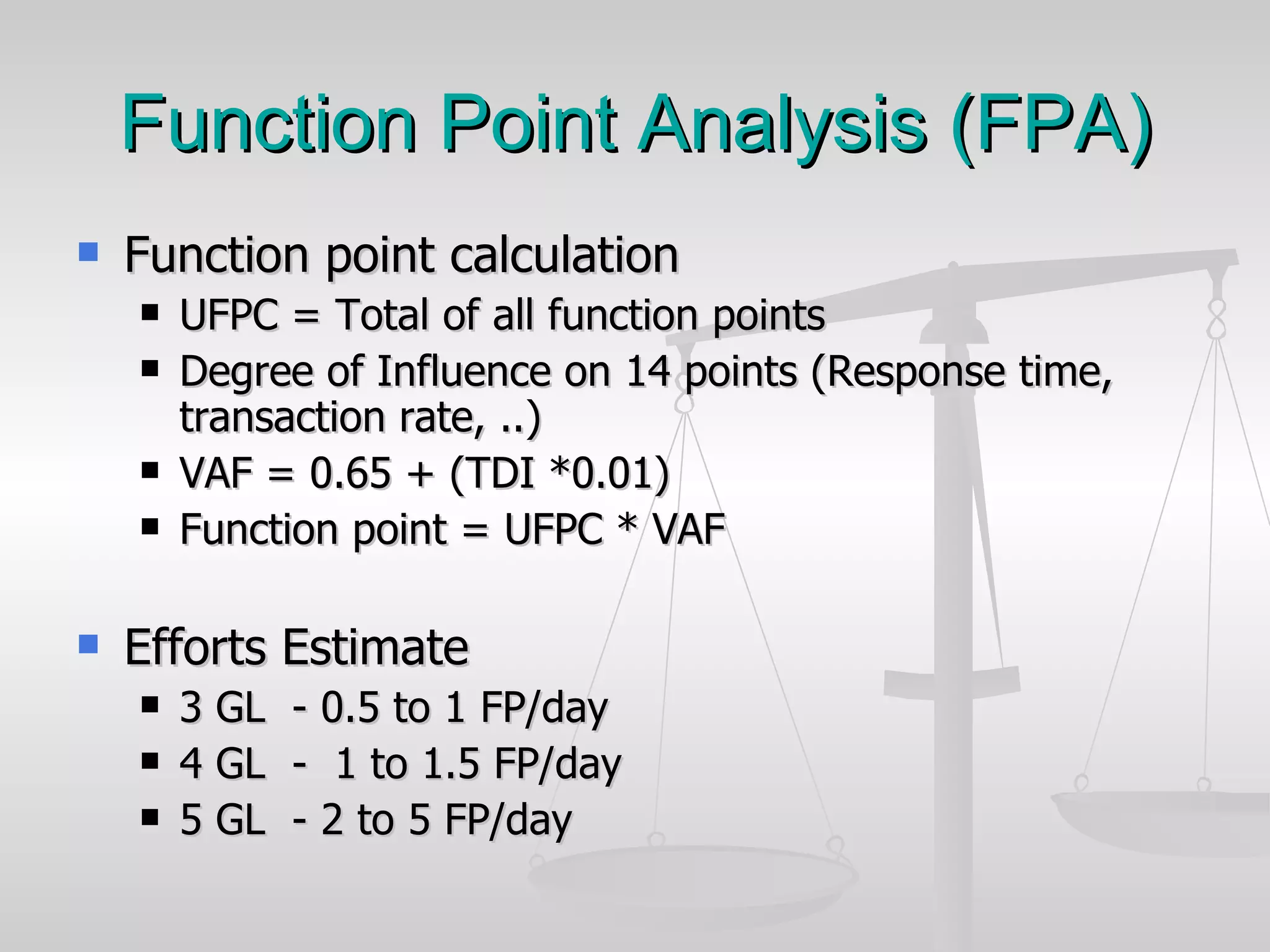
The document discusses various software estimation techniques including function point analysis, three point estimation, and COCOMO. It outlines the importance of estimation for budgeting, planning, and customer satisfaction. Different techniques are suited for different project stages and sizes. Function point analysis involves counting logical files, external inputs, external outputs, external queries, and other factors to estimate effort. Three magic formulae can also help estimate project duration, staffing needs, and minimum time. Metrics like effort slippage and percentage of efforts used help evaluate estimation accuracy.