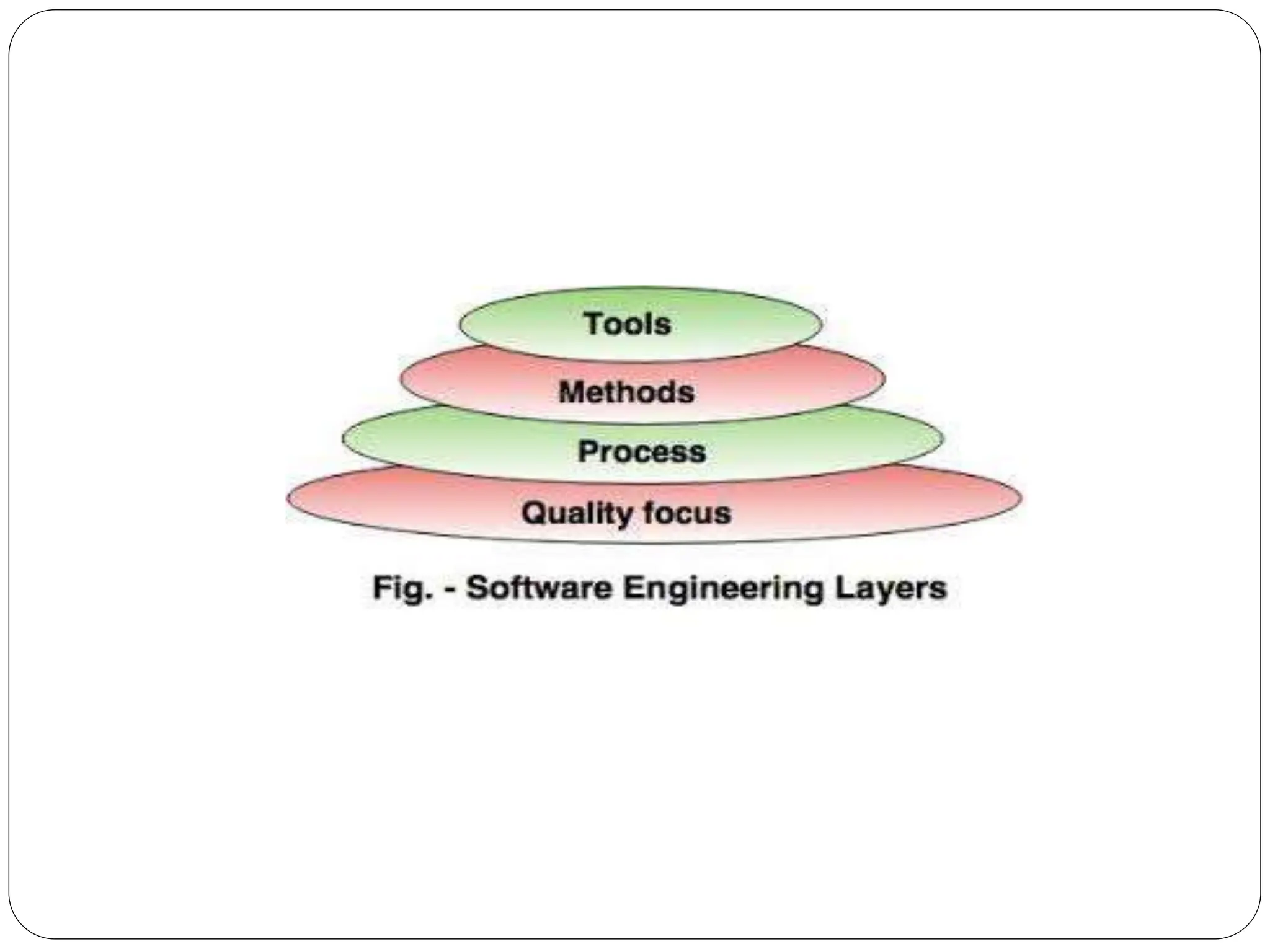
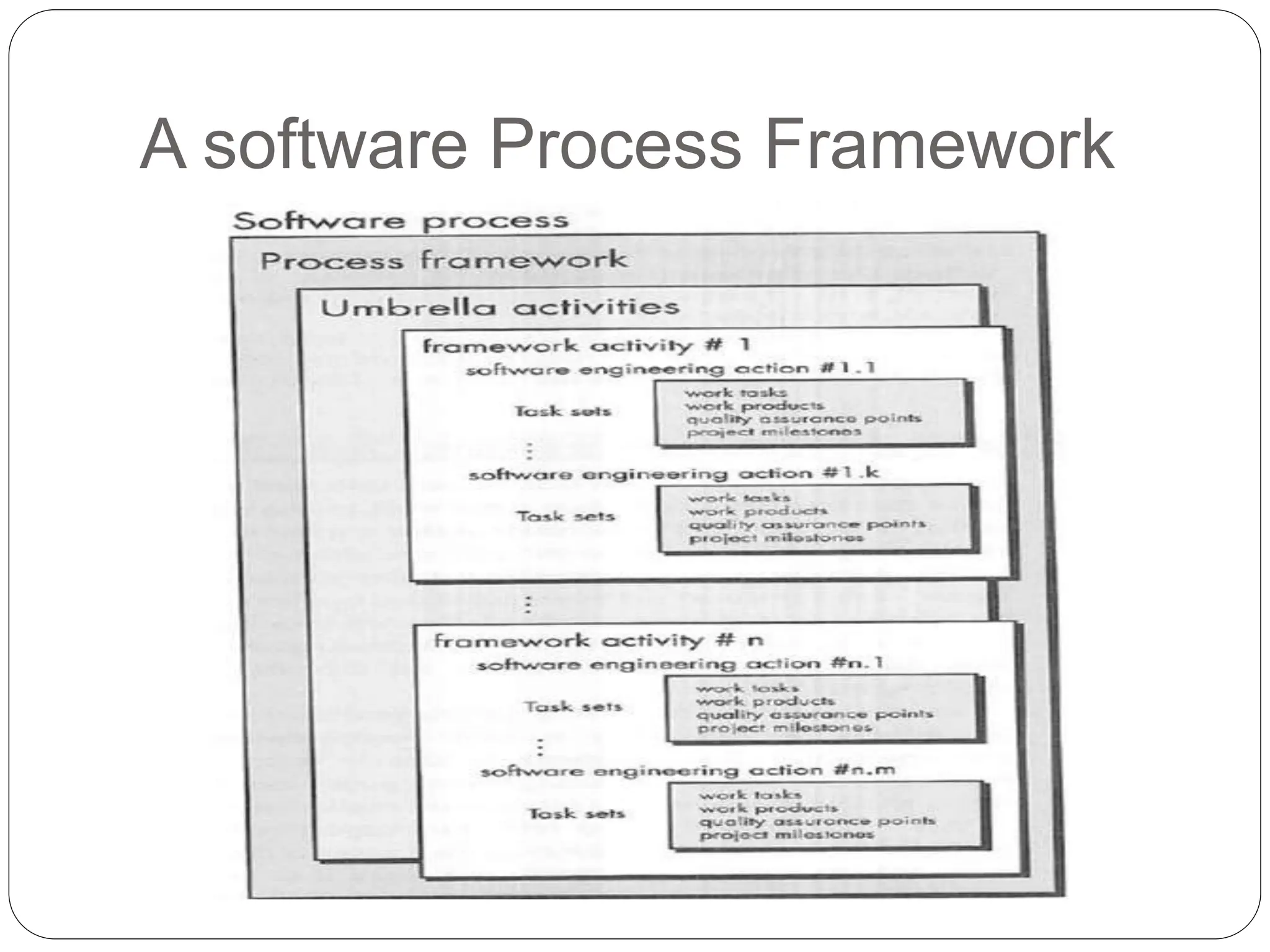
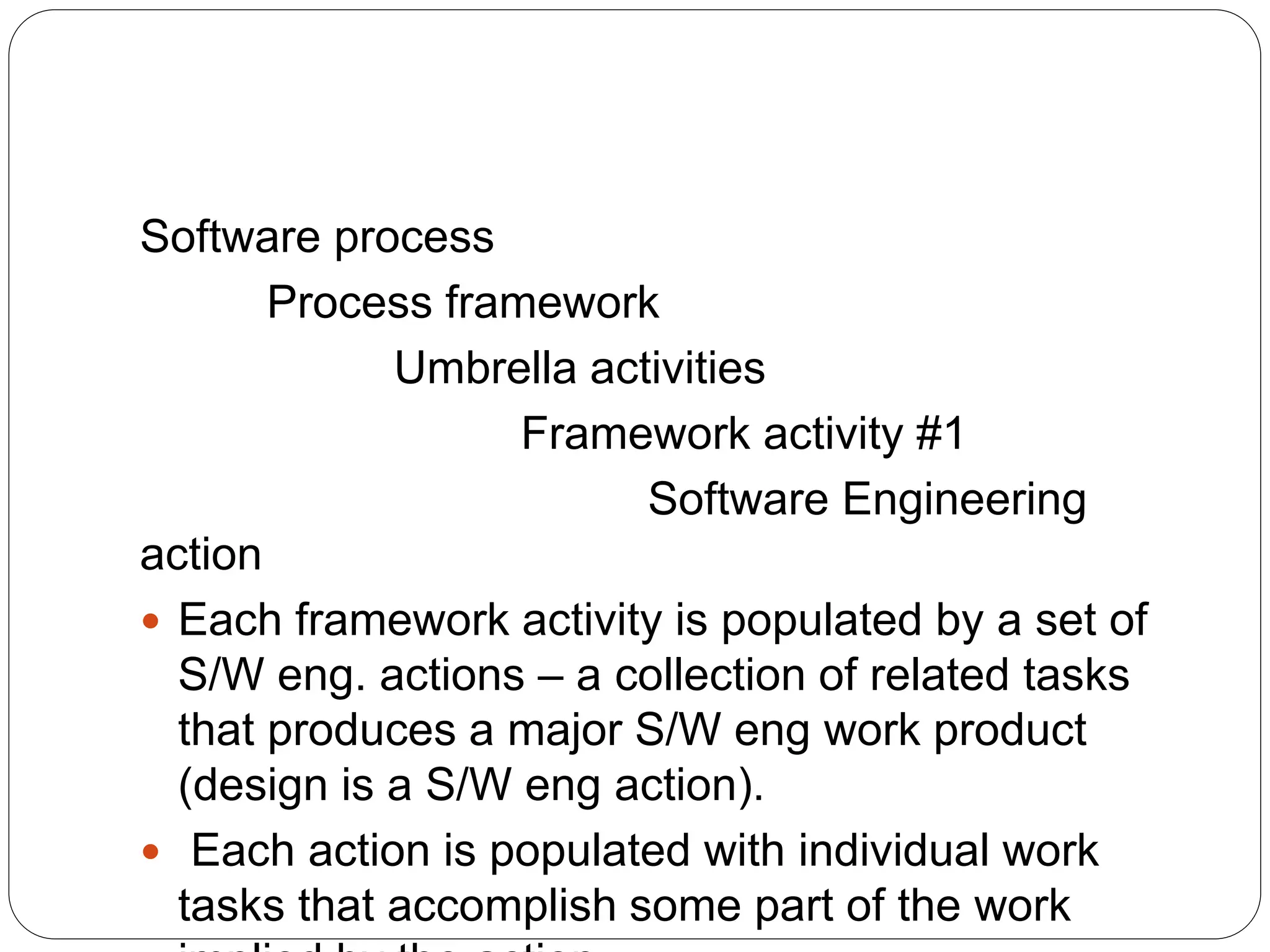
The document discusses software development processes. It defines software and the need for software engineering. It describes the characteristics of good software and different types of software. It then explains that a software process framework establishes foundational activities for software projects and includes umbrella activities. Process models provide specific guidance on how to conduct the framework activities and actions.