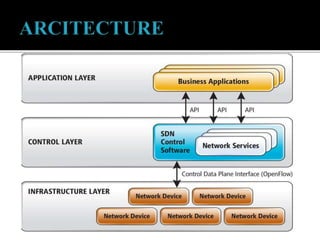
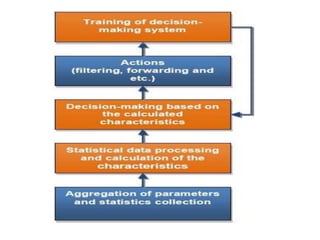
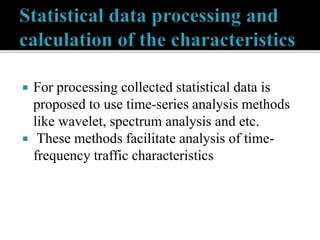
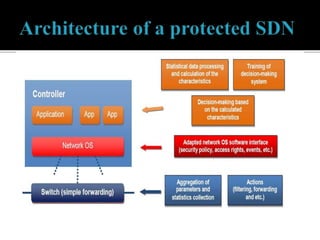
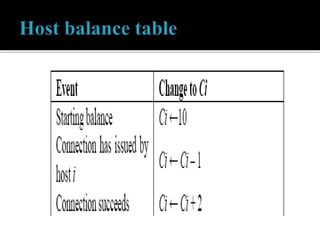
This document discusses SDN and network security. It proposes an anomaly detection algorithm to identify malicious activity on an SDN network. The algorithm involves collecting switch statistics, processing the data using time-series analysis, making decisions with fuzzy logic, and training the system with short-term and long-term learning modules. It also describes implementing two SDN security applications: TRW-CB for detecting SYN flooding attacks and rate limiting to control bursty traffic. The document concludes that SDN provides opportunities for effective network security through technologies like OpenFlow.