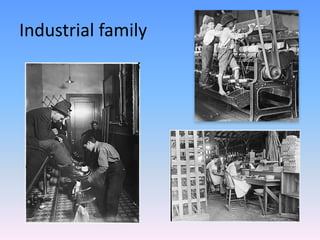
This document discusses how childhood is a social construction that has changed over time and varied between cultures. It outlines that pre-industrial societies viewed children as small adults and did not distinguish childhood from adulthood. During industrialization, children from working-class families still worked in mines and factories, though middle-class attitudes started seeing children as investments to nurture. By the 20th century, childhood emerged as child-centered, as improved living standards and contraception allowed parents to have fewer children and invest more in each one through love, education, and legal protections. Overall, the document examines how ideas of childhood being a protected stage separate from adulthood developed recently in history.