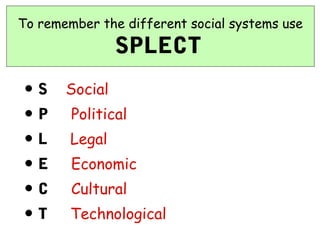
This document provides memory hooks and tools to help students remember important concepts in sociology. It includes acronyms and phrases to summarize key ideas related to topics like family, education, crime and deviance, religion, research methods, and functionalist theory. Color-coded memory hooks are organized by theme to aid recall of sociological information.