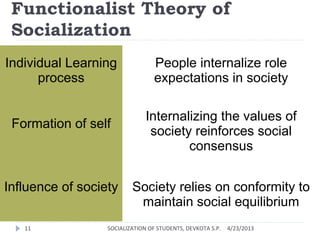
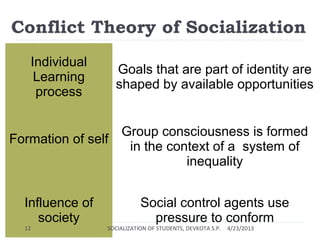
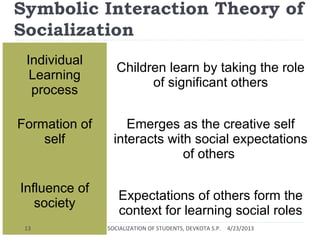
This document discusses the socialization of students through various agents and theoretical perspectives. It defines socialization as the process by which people learn to participate in society and develop a sense of self. The key agents of socialization are identified as family, school, peers, and media. The document then analyzes socialization from the perspectives of functionalism, conflict theory, and symbolic interactionism before concluding that socialization teaches students the expectations of society and helps them learn social roles and develop a sense of identity.