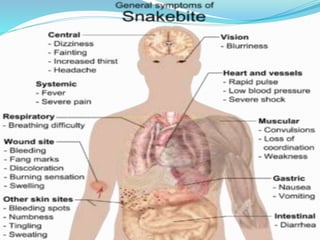
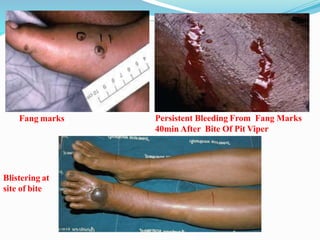
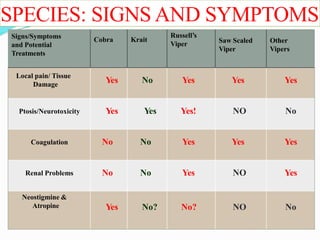
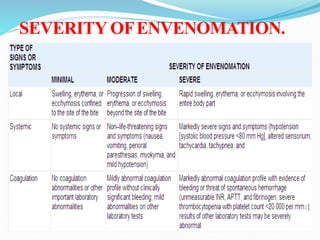
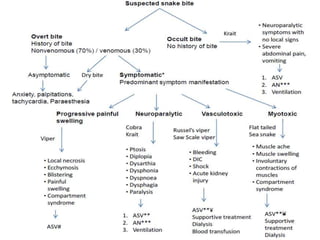
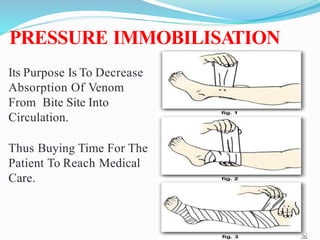
This document provides information on snake envenomation and its management in India. It discusses that India has the highest snakebite mortality in the world, with an estimated 83,000 bites and 11,000 deaths annually. The four main venomous snakes in India are cobras, kraits, Russell's vipers, and saw-scaled vipers. Symptoms of envenomation depend on the snake species but can include local tissue damage, neurotoxicity, coagulopathy, renal toxicity, and myotoxicity. First aid involves reassuring the patient, immobilizing the bite area, and rapidly transporting to a hospital. At the hospital, investigations are carried out and antivenom is administered via intravenous route in





![ Snake Envenomation Is Known As OPHITOXEMIA.
Almost 2/3 Deaths Due To Krait Bite.
Mostly Snake Bite During Mansoon Months
[June To Sep]
Krait Active During Night , Cobra And Vipers Bite
Occur During Day Or Early Darkness.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/snakebitedrhanuman-191218131730/85/Snake-bite-dr-hanuman-6-320.jpg)















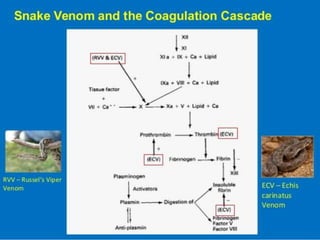
![Mechanism Of Hemostatic Toxin
Procoagulants [ Factor V, Factor X ]
β Bungarotoxins [Phospholipase A2]
Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase
Hyluronidase
Haemorrhagin Cause Direct Endothelial Damage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/snakebitedrhanuman-191218131730/85/Snake-bite-dr-hanuman-26-320.jpg)























![ANTI SNAKE VENOM (ASV)
Anti snake Venom (ASV)Is Mainstay Of Treatment Antivenom Is
Immunoglobulin [Usually Pepsin refined Fab2 Fragment Of Whole
IgG ] Purified From The Plasma Of Horse.
• In India, Polyvalent ASV- Effective Against All The Four Common
Species; Russell’s Viper, Common Cobra, Common Krait And Saw-
scaled Viper
• No Monovalent AsvsAre Available
• ASV Is Produced Both In LiquidAnd Lyophilized Forms’
• LyophilizedASV Freeze Dried Powder [Heat Stable] 5-year Shelf
Life.
• LiquidAsv [Heat Labile] 2-year Shelf Life.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/snakebitedrhanuman-191218131730/85/Snake-bite-dr-hanuman-60-320.jpg)































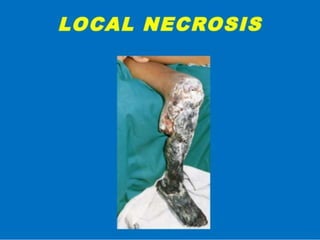
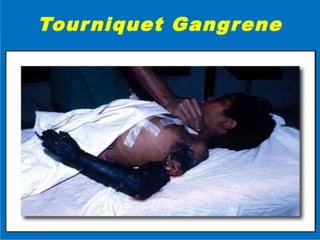
![MANAGEMENT OF SEVERE
LOCAL ENVENOMING
Give Prophylactic Broad-spectrum Antimicrobial Treatment For
Cellulitis
Inj. Amoxiciilin+ Clavulanic Acid IV For First 7 Days Then Switch To
Oral Therapy
Alternatively Inj Ceftriaxone If Amoxiciilin+clavulanic Acid Is Not
Available.
Inj. Metronidazole IV Infusion For 7 Days
Administer Booster Dose Of Tetanus Toxoid Injection.
For Mild Pain Give Paracetamol But Not Use Aspirin Or Other Nsaids
[In Children Ibuprofen Cautiously 5-10 Mg/Kg/Dose Every 8 Hourly
May Use]
In Case Of Severe Pain Inj. Tramadol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/snakebitedrhanuman-191218131730/85/Snake-bite-dr-hanuman-92-320.jpg)


