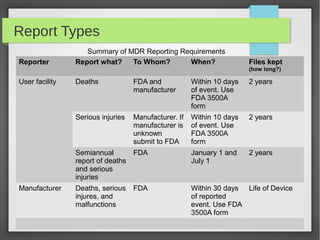
The Safe Medical Device Act of 1990 requires device manufacturers and user facilities like hospitals to report device-related deaths and serious injuries to the FDA. It aims to increase information about safety issues. Under the Act, manufacturers must report deaths, injuries, and device malfunctions to the FDA within 30 days. User facilities must report deaths to the FDA and the manufacturer within 10 days. The FDA can enforce the Act through criminal penalties, civil money penalties, recalls, and suspending device approvals.