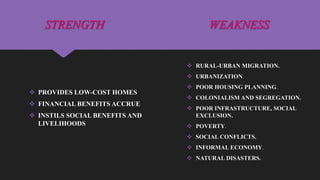
Slum upgrading is a strategy to improve living conditions in slums through physical, social, economic and environmental upgrades done cooperatively between residents, community groups, businesses and local authorities. The main objective is to alleviate poor living standards. Upgrades involve improving both physical infrastructure like water, sanitation and housing as well as social conditions. Challenges include rapid urbanization, achieving community participation, and securing technical and government support. Solutions that have shown success include solar powered water pumps, waste management, and upgrading slums instead of relocating residents.