This document discusses various topics related to information security including:
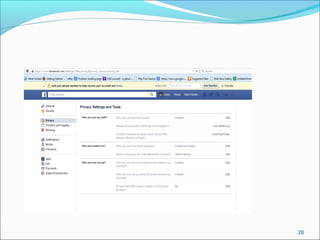
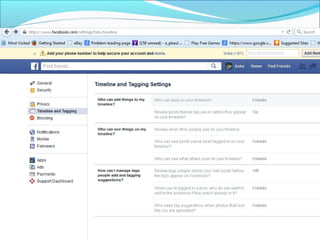
- It defines data and information, and information security as preserving the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronically stored and transmitted data.
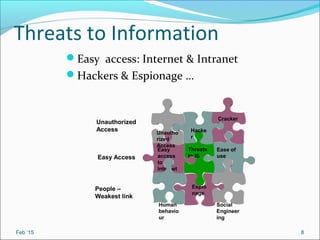
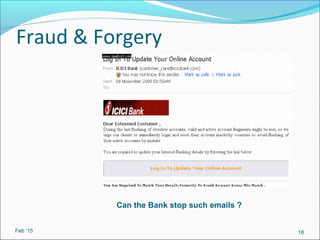
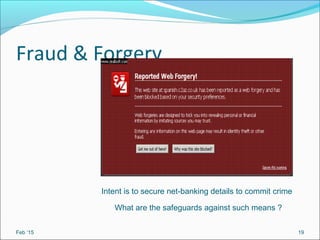
- It outlines common threats to information security like hackers, espionage, social engineering, and unauthorized access.
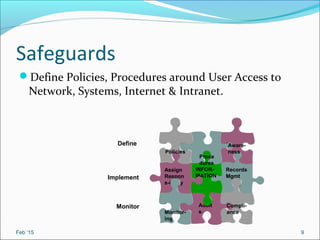
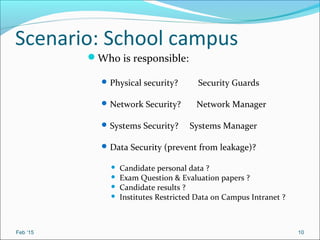
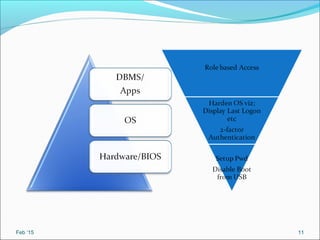
- It recommends defining policies and procedures around user access, monitoring, and increasing security awareness as important safeguards.