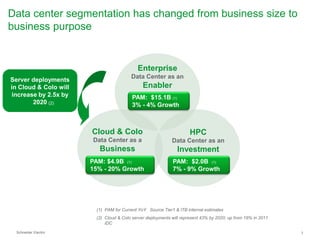
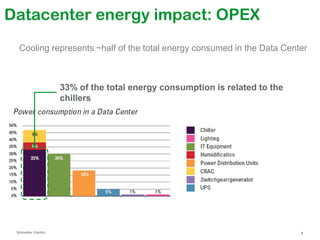
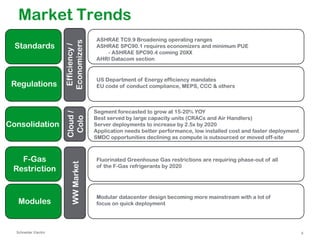
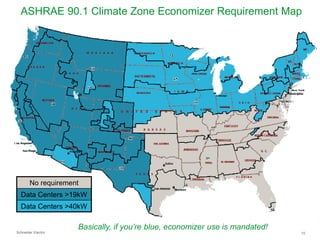
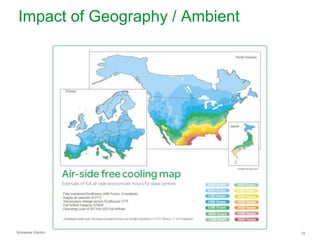
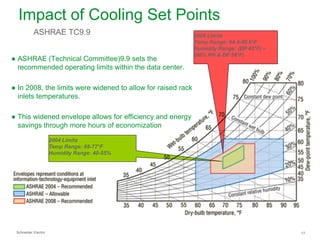
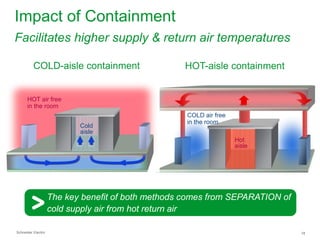
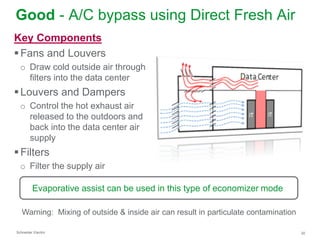
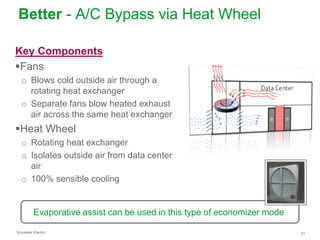
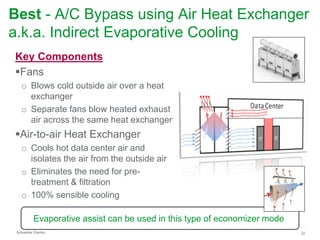
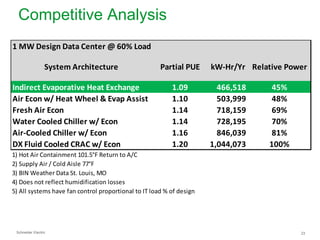
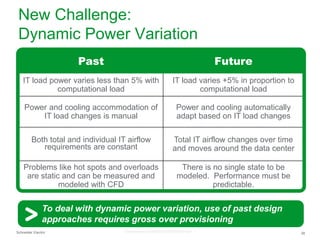
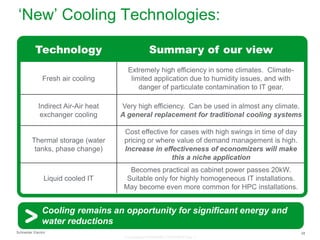
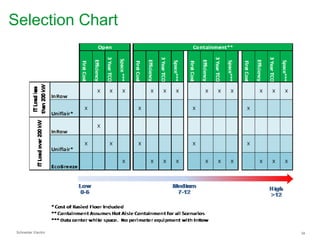
The document summarizes a presentation on trends in North American data center cooling. The top 3 trends discussed are: 1) Increased use of economizers as the primary cooling mode rather than supplemental to reduce energy costs; 2) Regulations requiring economizer use in most climate zones; and 3) Data center workloads becoming more dynamic, requiring cooling systems to adapt quickly. Indirect air-to-air heat exchangers are presented as the most efficient economizer option. Liquid cooling is discussed but seen as mainly suitable for niche HPC applications currently. Established technologies like perimeter cooling and containment are evolving to higher efficiencies.