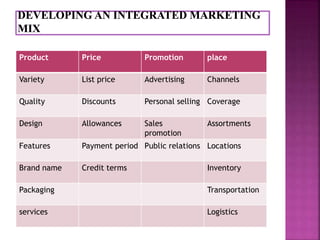
This document discusses company growth strategies and marketing strategies. It provides examples of Starbucks' growth, including market penetration by opening more stores, market development by targeting new demographic groups, product development by introducing new products, and diversification through partnerships. The document also covers market segmentation, target marketing, product differentiation, market positioning, and the marketing mix of product, price, promotion, and place from both the seller and buyer perspectives.