Embed presentation
Download to read offline




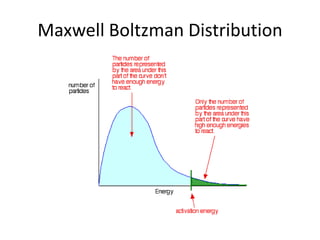
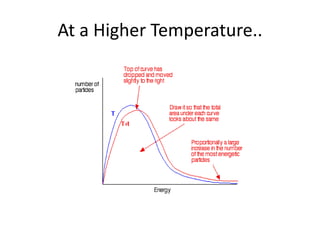
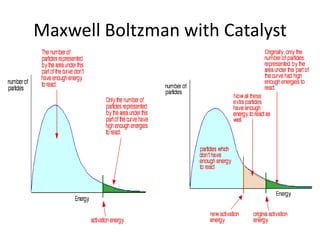





1. The document discusses collision theory and how various factors affect the rate of a chemical reaction. It defines rate of reaction and lists collision frequency, number of particles with energy greater than or equal to the activation energy, and proper collision geometry as factors that reaction rate depends on. 2. It explains Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution and how increasing temperature, concentration, pressure, decreasing particle size, or adding a catalyst can increase the rate of reaction by altering the distribution. 3. It defines a catalyst as a substance that speeds up a reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, but is unchanged at the end and recovered in the same amount.











