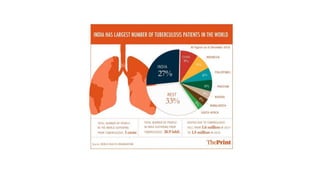
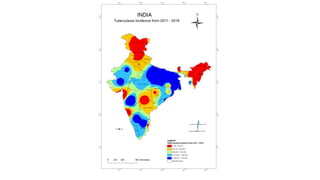
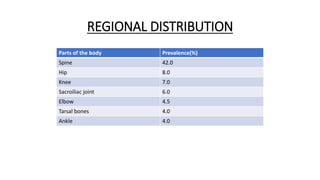
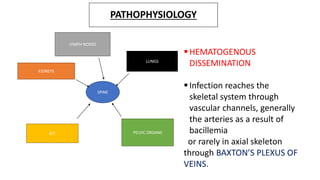
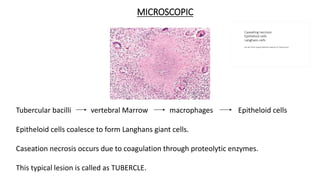
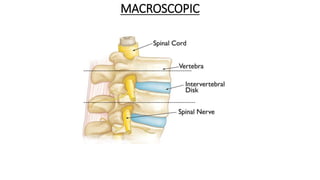
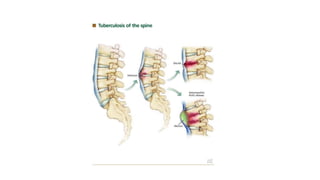
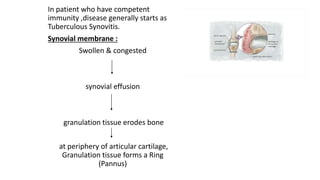
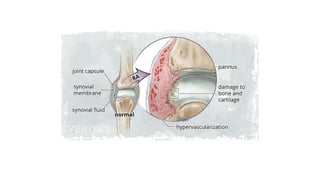
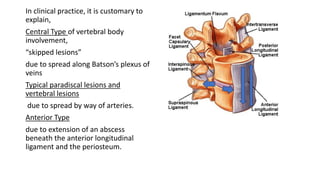
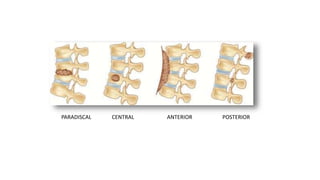
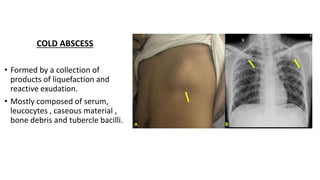
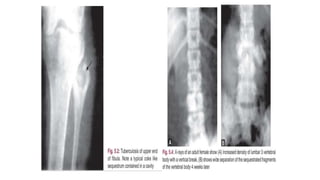
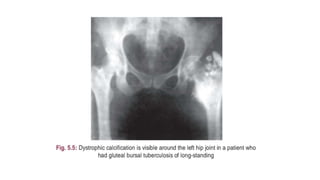
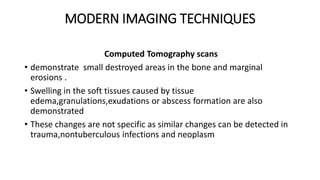
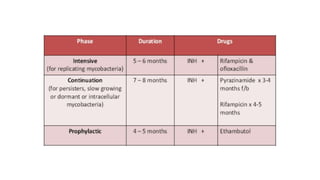
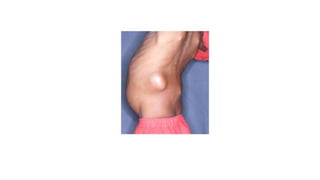
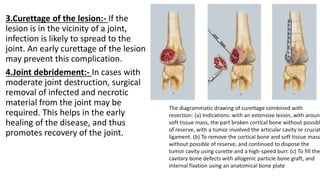
The document summarizes an orthopaedics seminar on skeletal tuberculosis. It discusses the epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, investigations and management of skeletal tuberculosis. Key points include that tuberculosis can affect bones and joints secondary to a primary lung or lymph node infection. Spinal tuberculosis is most common, often affecting the pediatric population. Diagnosis involves x-rays, biopsy and culture. Treatment consists of antibiotic therapy for 9-24 months as well as surgery if needed to drain abscesses, debride joints or stabilize bones.