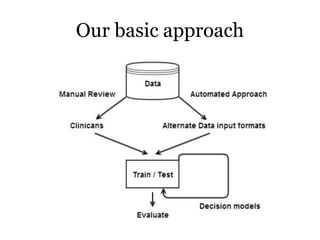
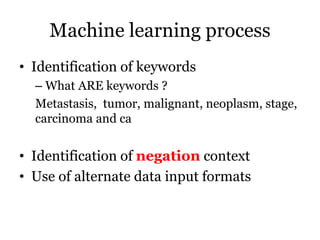
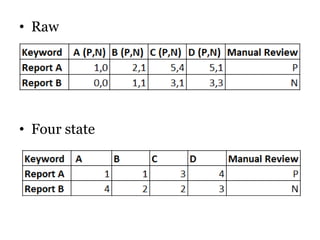
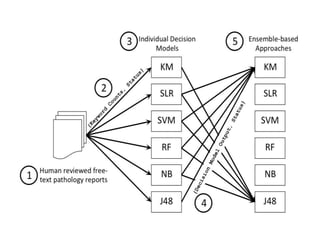
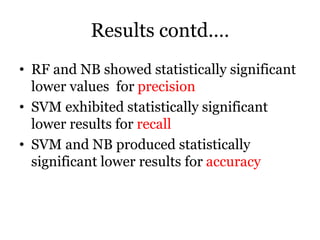
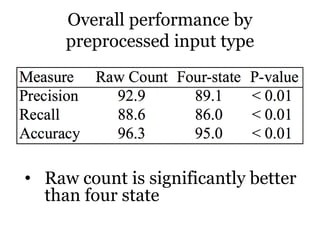
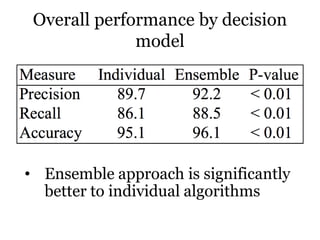
The document discusses a study on improving cancer identification in pathology reports using machine learning and data preprocessing techniques, emphasizing automation to enhance reporting speed, accuracy, and efficiency. The authors implemented various decision models and data input formats, evaluating their effectiveness through metrics such as precision, recall, and accuracy. Overall, a combination of models with raw data input showed better performance compared to individual algorithms and four-state data inputs.