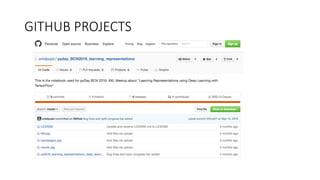
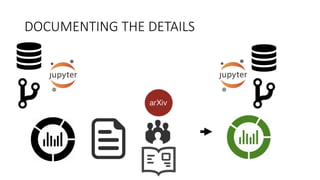
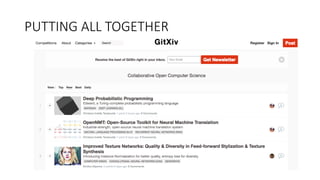
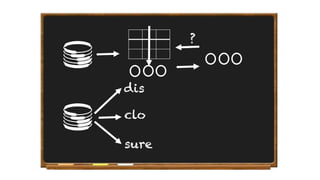
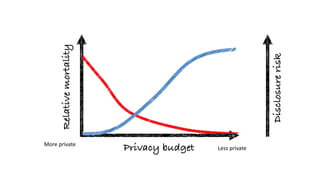
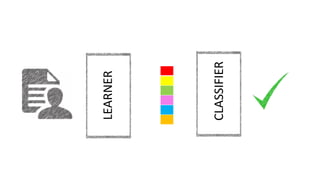
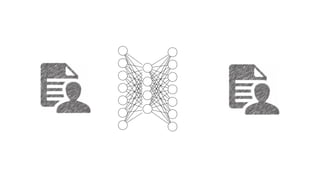
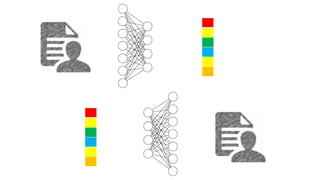
Oriol Pujol discusses the importance of data in machine learning, emphasizing the need for quality assessment and reproducibility in research. He highlights challenges in sharing sensitive data and the fast-paced nature of machine learning dissemination, advocating for detailed documentation and transparency. Ultimately, he argues that effective data sharing and methodological rigor are essential for advancing the field and ensuring the integrity of research.