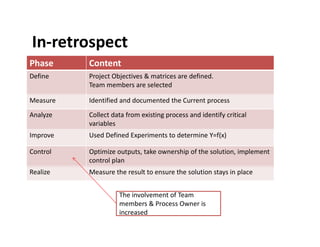
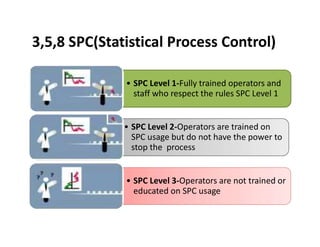
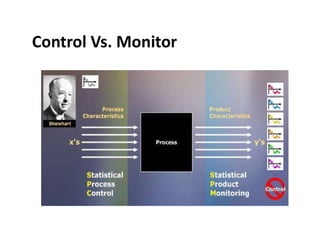
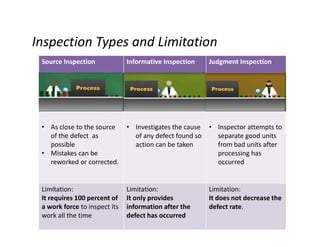
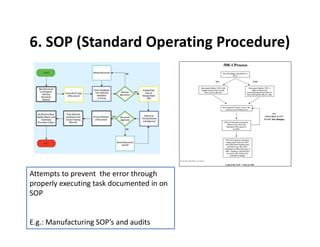
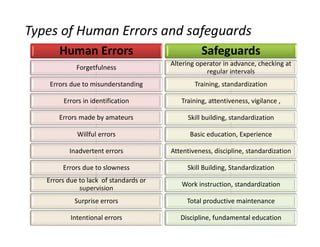
This document discusses various control methods for processes including mistake proofing, flags, statistical process control (SPC), inspection, standard operating procedures (SOPs), and warning signals. It provides examples and benefits of each method. Mistake proofing aims to eliminate error conditions through long-term process improvements. Flags detect errors and stop defective products. SPC involves training operators and monitoring processes with statistical methods. Inspection checks for defects but is not always accurate. SOPs standardize tasks to prevent errors. Warning signals aim to detect defects but operators can become desensitized over time.