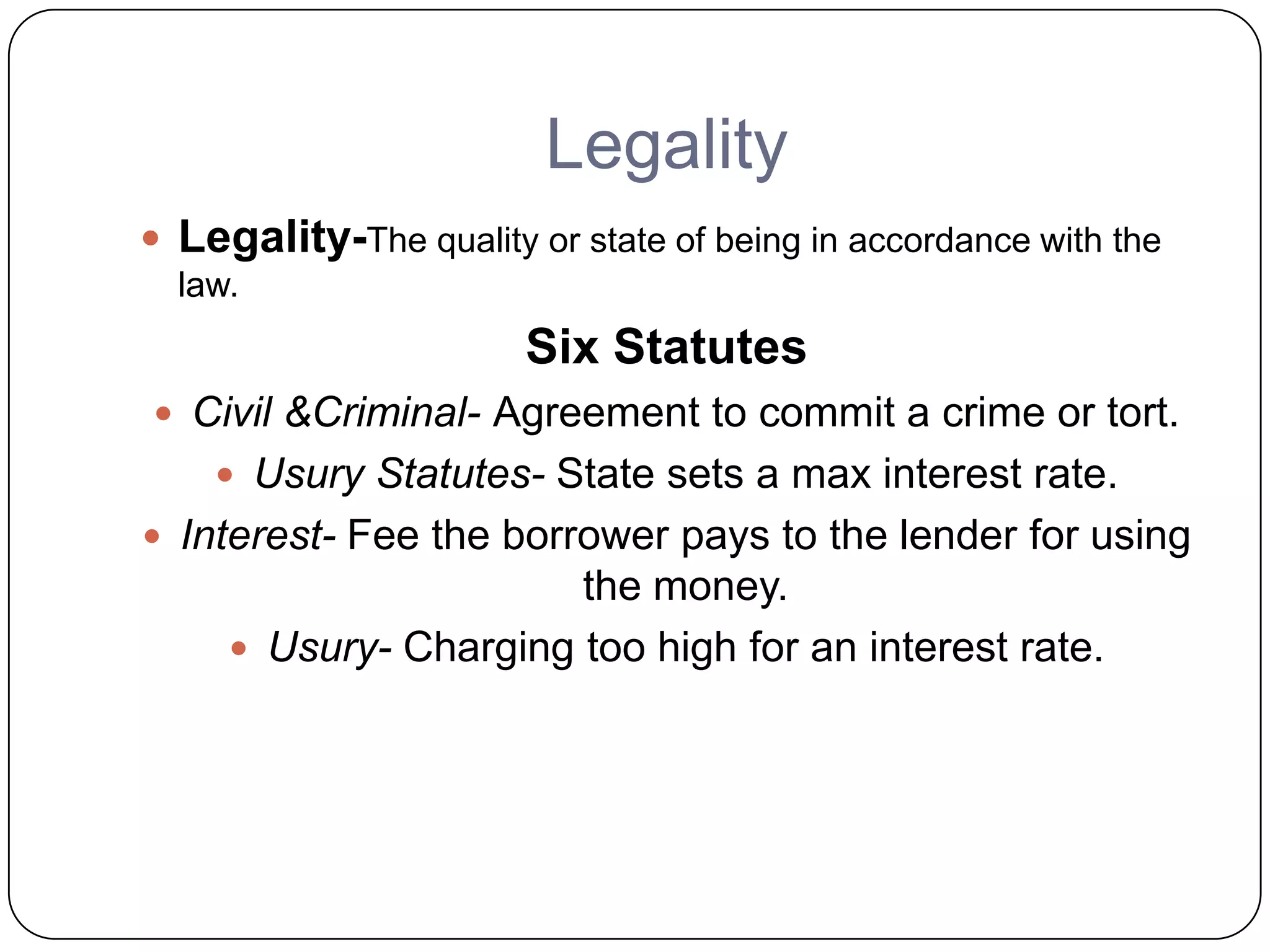
This document summarizes the six elements of a valid contract: 1) offer, which is a proposal made with serious intent by an offeror to an offeree; 2) acceptance, which is an unqualified agreement to the offer's terms without modification; 3) genuine agreement between the parties to create a final contract; 4) consideration, which is the exchange of benefits and detriments by the parties; 5) contractual capacity of the parties to enter into an agreement; and 6) legality in accordance with civil and criminal law as well as public policy.