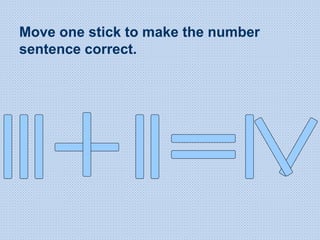
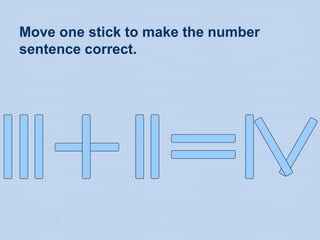
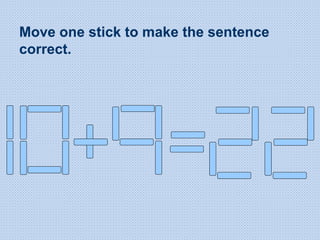
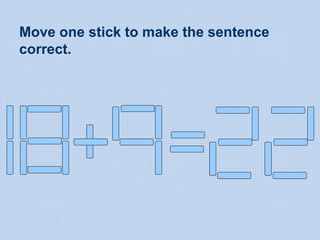
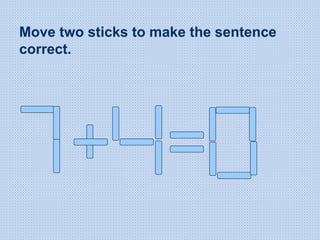
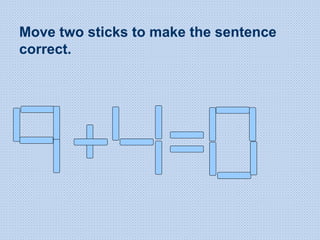
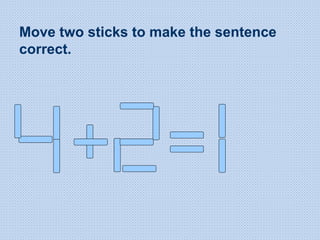
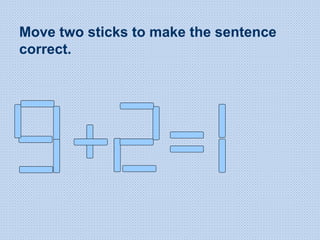
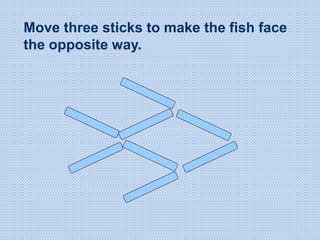
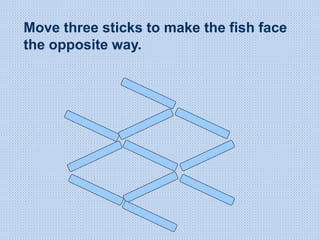
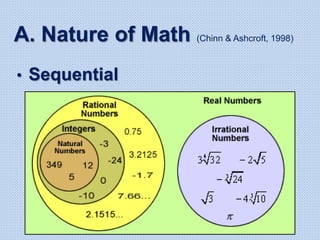
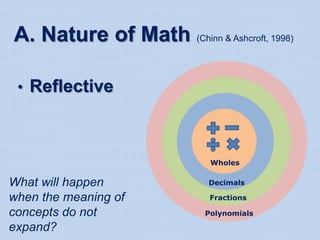
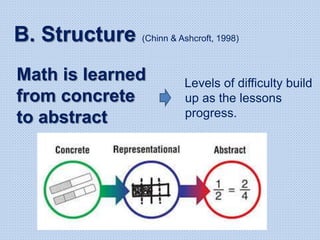
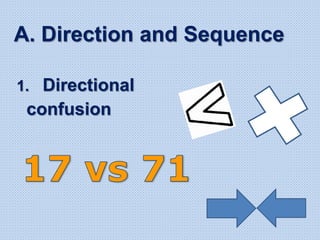
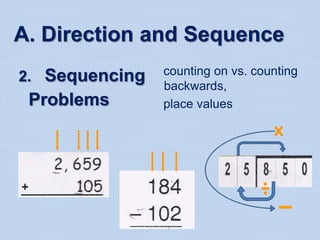
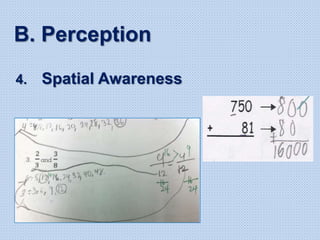
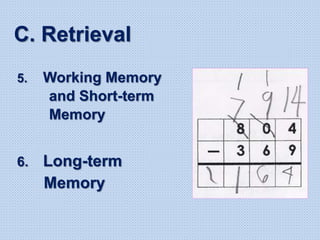
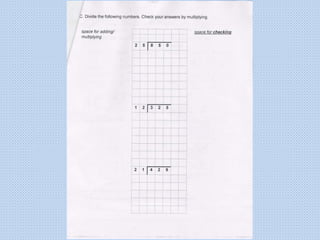
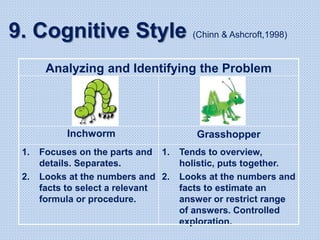
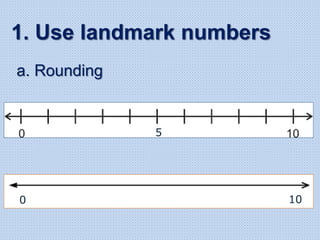
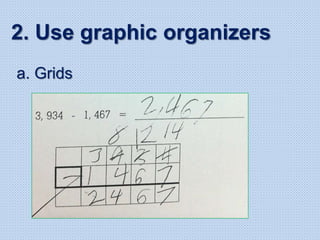
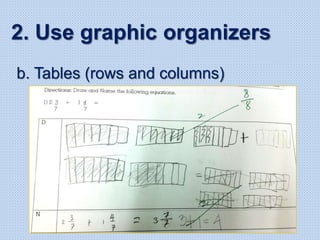
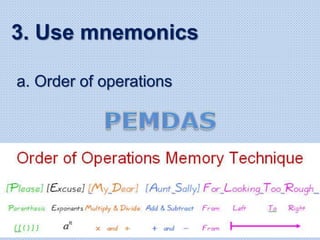
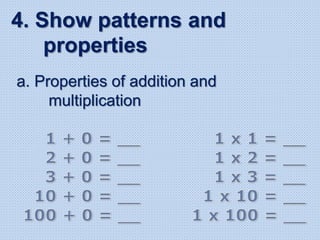
The document discusses common math difficulties and strategies for math intervention. It identifies several potential areas of difficulty in learning math, such as directional confusion, weak working memory, math language issues, and math anxiety. Error analysis of student work is presented as an important tool to identify specific difficulties. The document then covers principles of remedial instruction, such as building on student strengths, acknowledging different learning styles, using a concrete-to-abstract approach, and employing effective math vocabulary. A variety of teaching strategies are proposed, like using graphic organizers, mnemonics, showing patterns, and visualization.