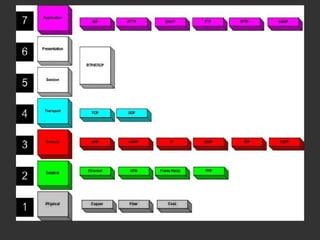
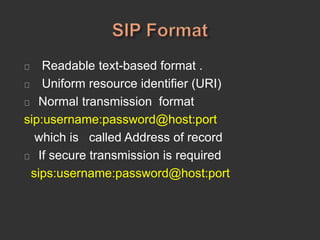
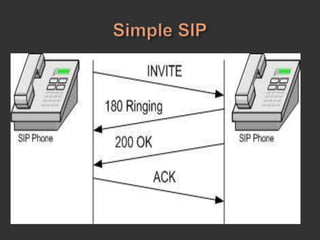
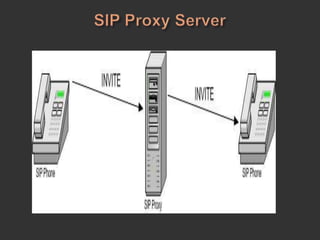
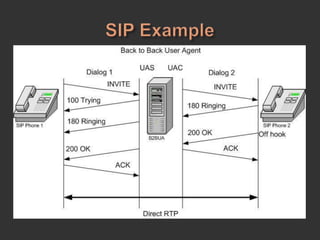
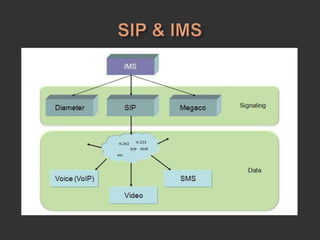
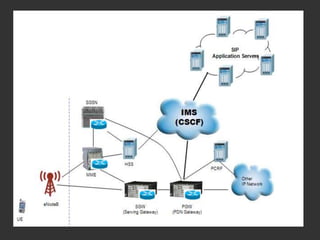
SIP is a signaling protocol used to establish, modify, and terminate multimedia sessions over IP networks. It was originally designed in 1996 to make voice and video calls over IP and has since expanded to support additional applications like instant messaging, file transfer, and presence information. SIP works by defining messages passed between endpoints to initiate, manage, and terminate calls or sessions. It is an application layer protocol that can operate over various transport protocols like TCP, UDP, and SCTP.