Embed presentation
Download to read offline
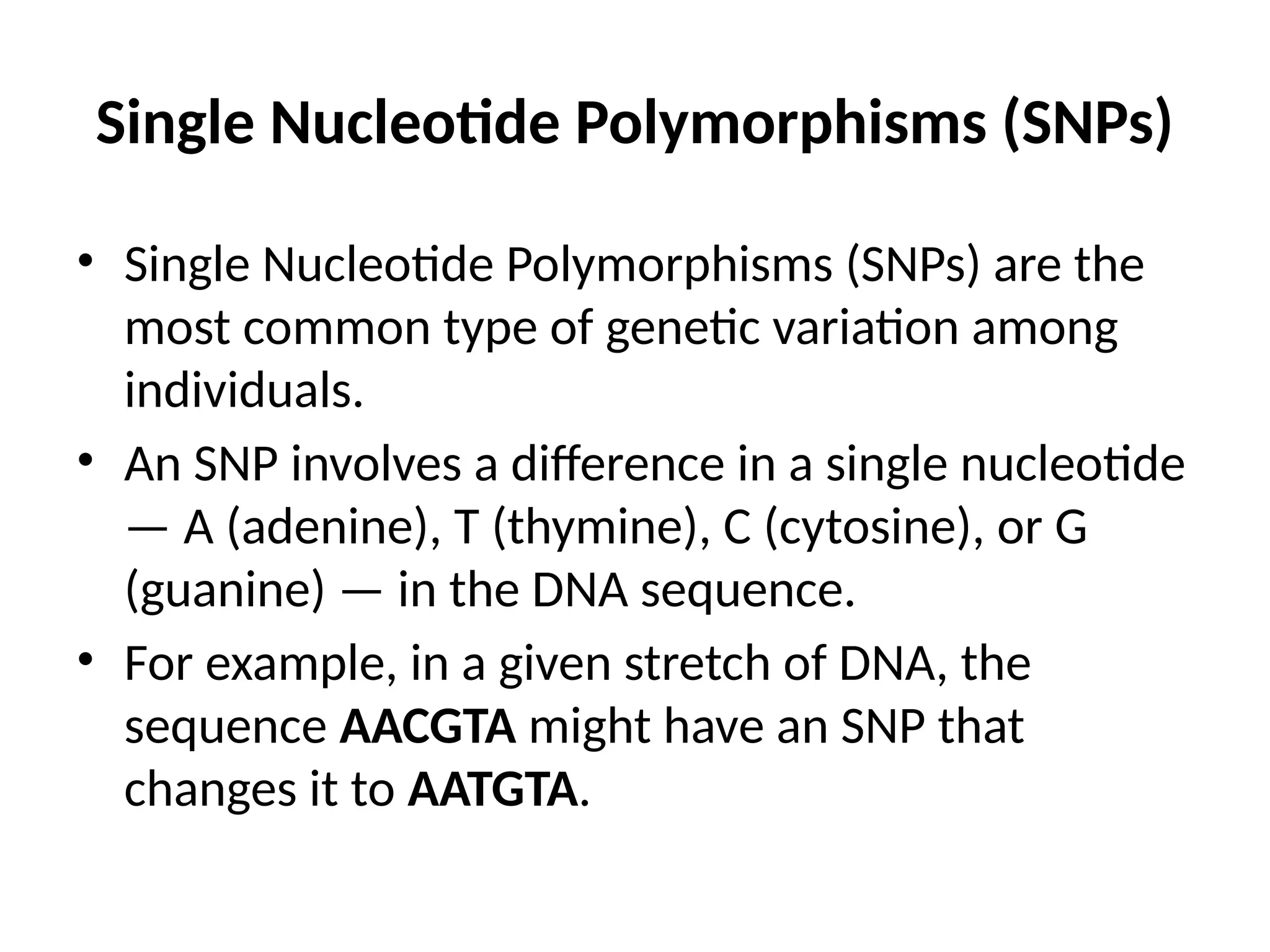
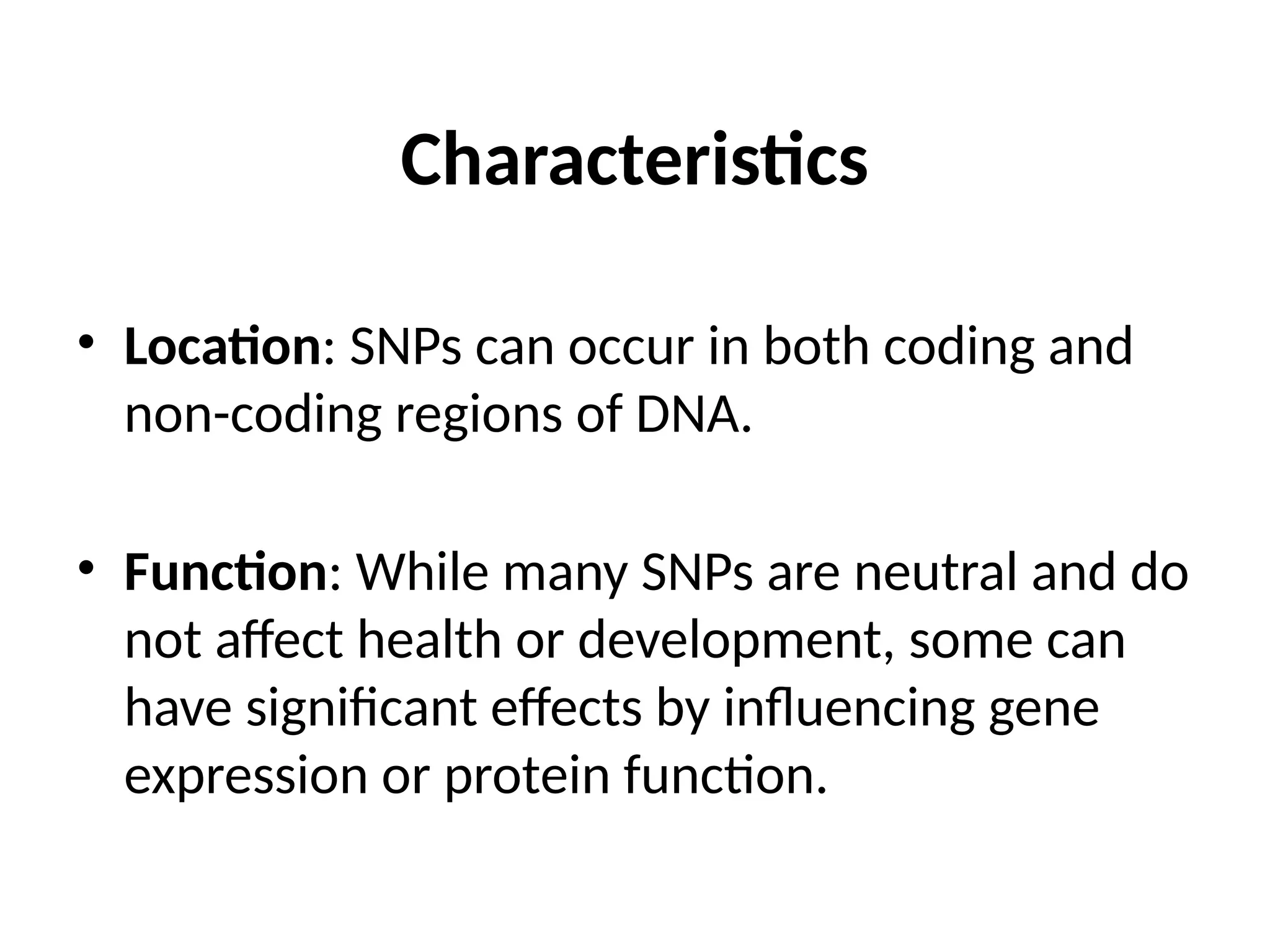

Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are the most common type of genetic variation, involving a change in a single nucleotide in the DNA sequence. They can occur in both coding and non-coding regions, with some SNPs influencing gene expression and disease susceptibility, while others may impact drug metabolism. SNPs are valuable in genetic mapping for tracking disease inheritance patterns.


