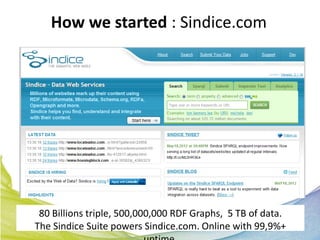
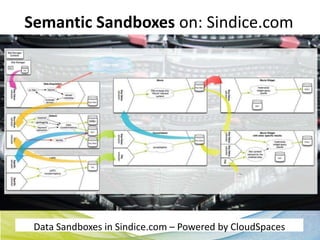
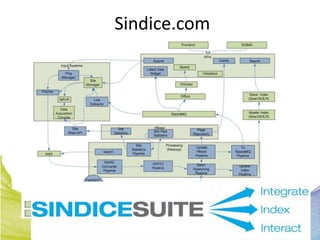
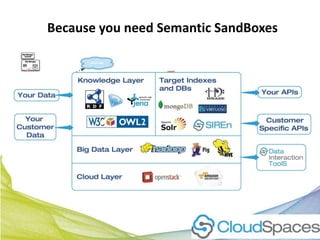
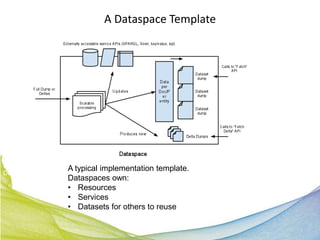
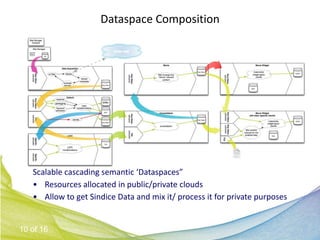
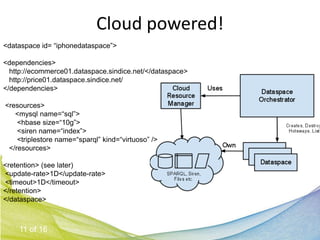
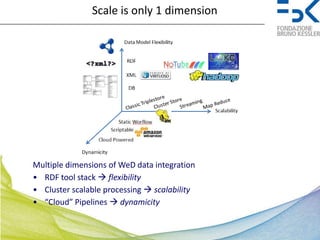
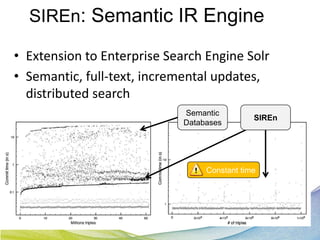
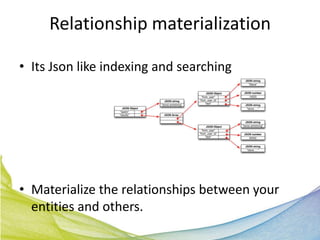
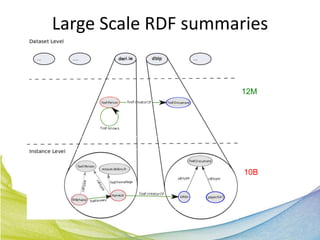
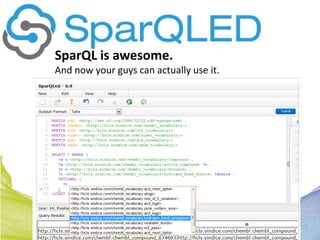
This document discusses Real Time Semantic Data Warehousing (RETIS) technology provided by Sindice.com. RETIS allows pharmaceutical companies to integrate diverse public and private data sources in real-time to help data scientists discover new insights and connections. It provides unified search and browsing of live internal and external datasets. Sindice's semantic warehousing approach uses Linked Data clouds, semantic sandboxes, and cloud computing to easily integrate new databases with unprecedented flexibility and scale.