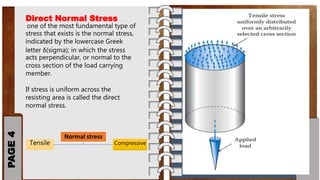
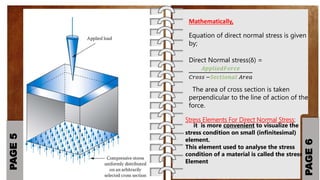
This document provides an overview of basic concepts in strength of materials, including stress, strain, and different types of stresses. It defines stress as the internal force of resistance per unit area offered by a body against deformation. Stress is calculated as force divided by area. Normal stress acts perpendicular to the cross-sectional area and can be tensile or compressive. Shear stress refers to a cutting action and is represented by the symbol tau. The document also defines strain as the change in length divided by the original length, represented by epsilon. It provides stress elements and equations to calculate direct normal and shear stresses.