1) Interest is the amount paid for using borrowed money or the income earned from money that has been loaned. Simple interest is calculated using only the principal amount and ignores interest earned in previous periods.
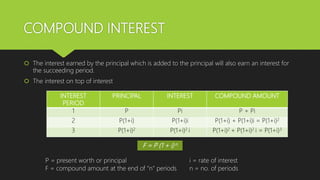
2) Compound interest differs in that the interest earned is added to the principal amount and also earns interest in subsequent periods, allowing the total to grow more quickly over time.
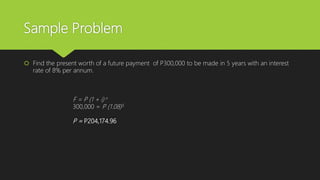
3) Examples show calculations for simple and compound interest rates as well as determining present worth values given future amounts, interest rates, and time periods.





![Sample Problem
If you borrowed money from your friend with simple interest of 12%, find the present worth of
P50,000; which due at the end of 7 months.
F = P + I
F = P + Pin
F = P (1 + in)
P = F = 50,000
(1+in) [1+0.12(7/12)]
= P46,728.97](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engineeringeconomyinterest-170929043046/85/Simple-and-Compound-Interest-7-320.jpg)