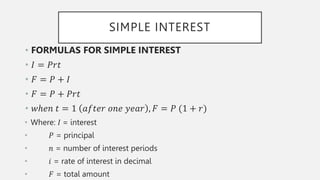
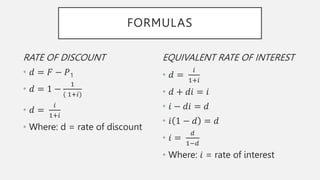
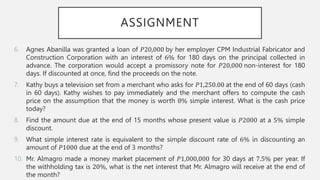
This document outlines the topics and concepts covered in the CE 213 Engineering Economics course. It includes 17 topics related to engineering economic analysis such as simple and compound interest, annuities, depreciation, present worth analysis, and rate of return. The introduction defines engineering economy as the analysis and evaluation of economic factors that affect the success of engineering projects to ensure capital is best utilized. The document then provides detailed explanations and formulas for simple interest, discount rates, and sample problems.