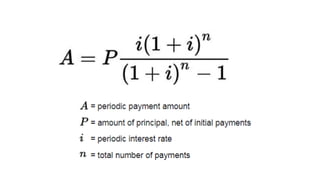
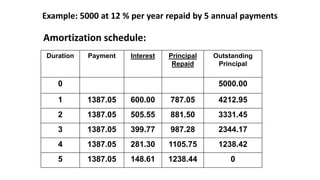
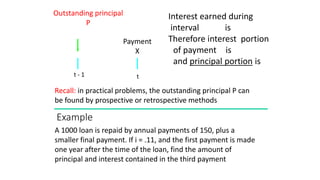
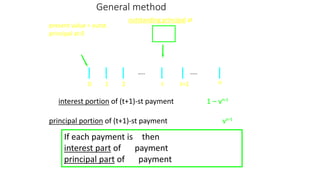
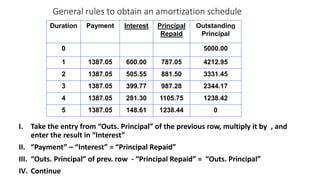
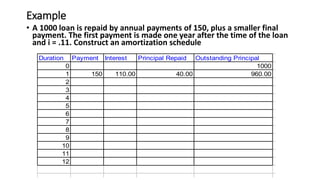
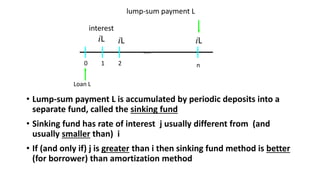
This document discusses amortization and sinking funds for repaying loans. Amortization involves making regular installment payments that divide each payment into interest and principal portions, with the outstanding principal decreasing with each payment. A sinking fund allows keeping the loan principal constant while accumulating a separate fund with deposits and interest to repay the principal in a lump sum later. Examples are provided for calculating payment amounts under each method. Yield rates equalize the value of payment streams for investors.