1. The document discusses lessons learned from fostering entrepreneurship activities in Central-Eastern Europe through various workshops, trainings, grants, and clusters.
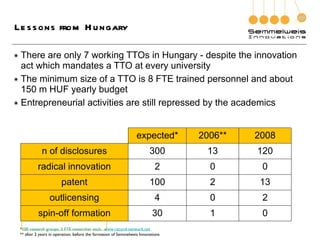
2. It notes that while Hungary has laws mandating technology transfer offices (TTOs) at universities, in practice there are only 7 functioning TTOs, and they are still limited by academics.
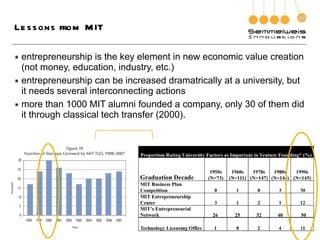
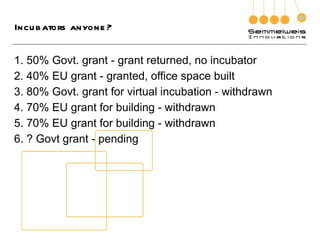
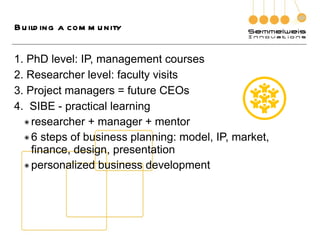
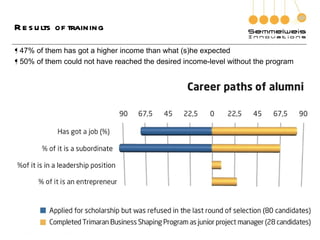
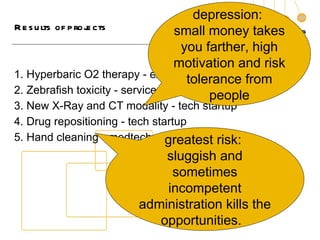
3. The document outlines the goals, components, and lessons from various entrepreneurship and incubation programs, finding that structured mentoring, coaching, and introducing trainees to real case studies through a step-by-step process are most effective.