15000
10000
5000
0
2005 2006 2007
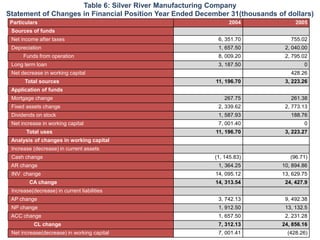
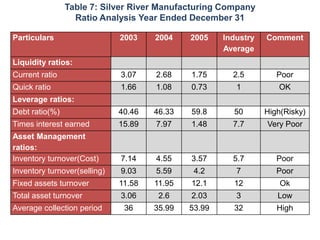
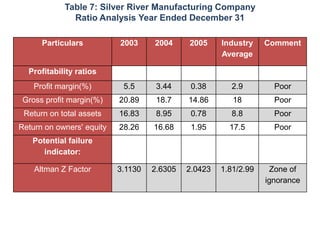
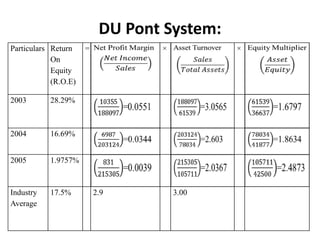
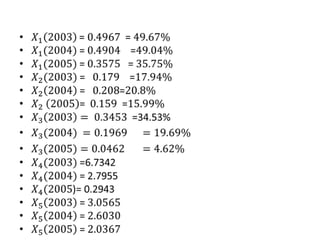
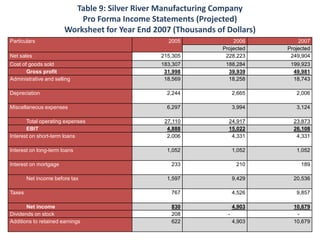
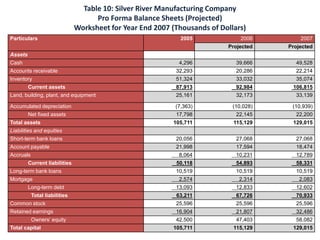
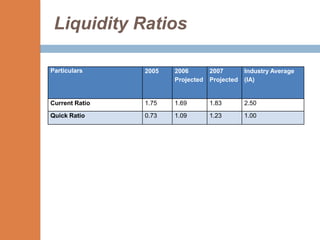
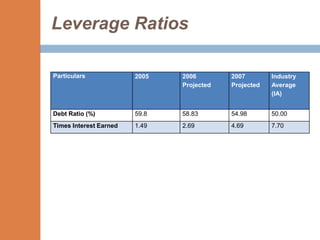
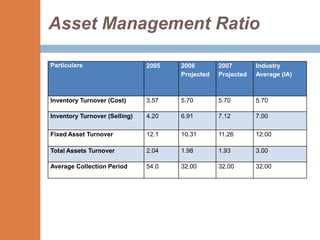
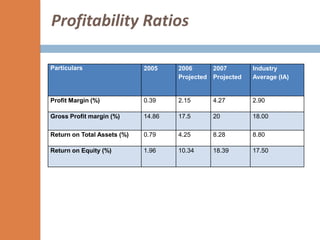
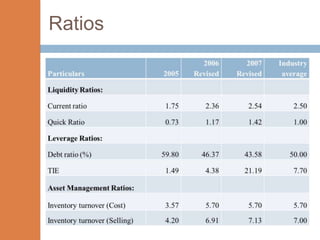
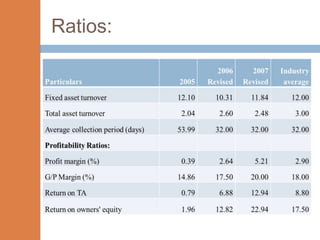
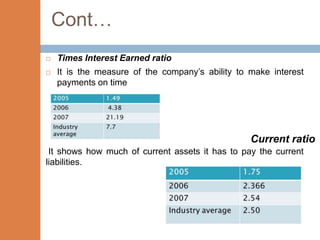
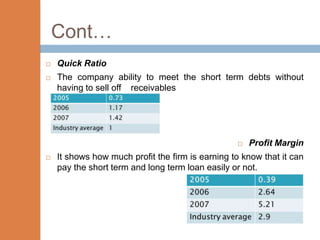
- The financial ratios of SRM are projected to improve in 2006 and 2007 compared to 2005. However, they remain below industry averages.
- While liquidity, leverage, and asset management ratios improve, profitability ratios only marginally increase and remain poor.
- A key weakness is low profit margins, despite improvements in sales, inventory management, and debt repayment. Increased expenses constrain profits.
- Repaying debt improves financial stability in the short term, but sustained profitability is still lacking for long term financial health.