The document discusses four environmental issues:
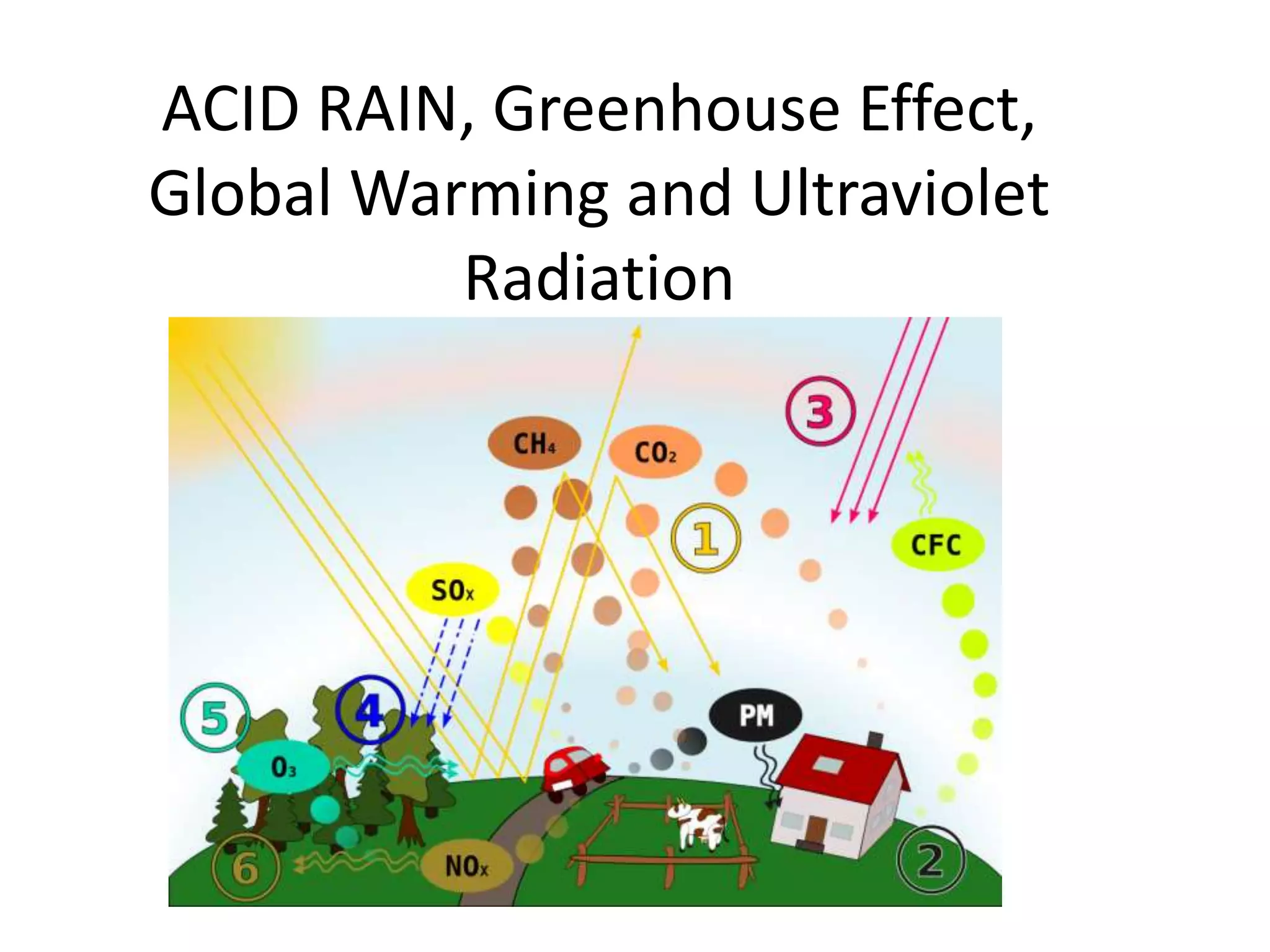
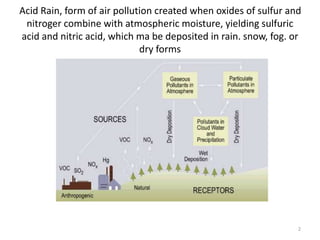
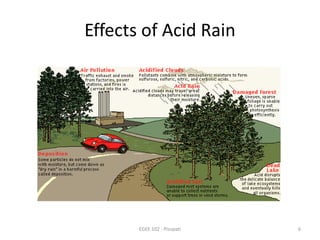
1) Acid rain is formed when sulfur and nitrogen oxides combine with water, forming acids that can damage structures, crops, forests and aquatic life.
2) The greenhouse effect refers to the atmosphere trapping heat from the sun, warming the Earth's surface. Increased CO2 and methane from human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation enhance the greenhouse effect and global warming.
3) Sulfates and nitrates from air pollution impair visibility and increase illness from particulate matter.
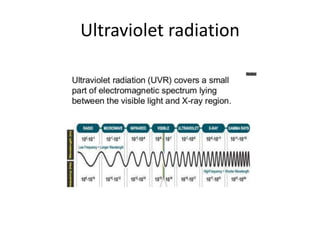
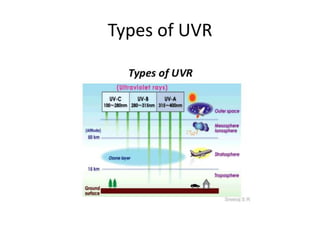
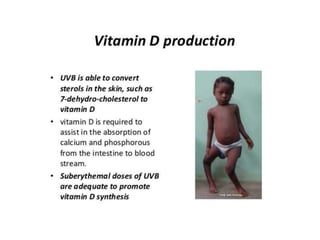
4) Ultraviolet radiation from the sun has different types that can impact human health.