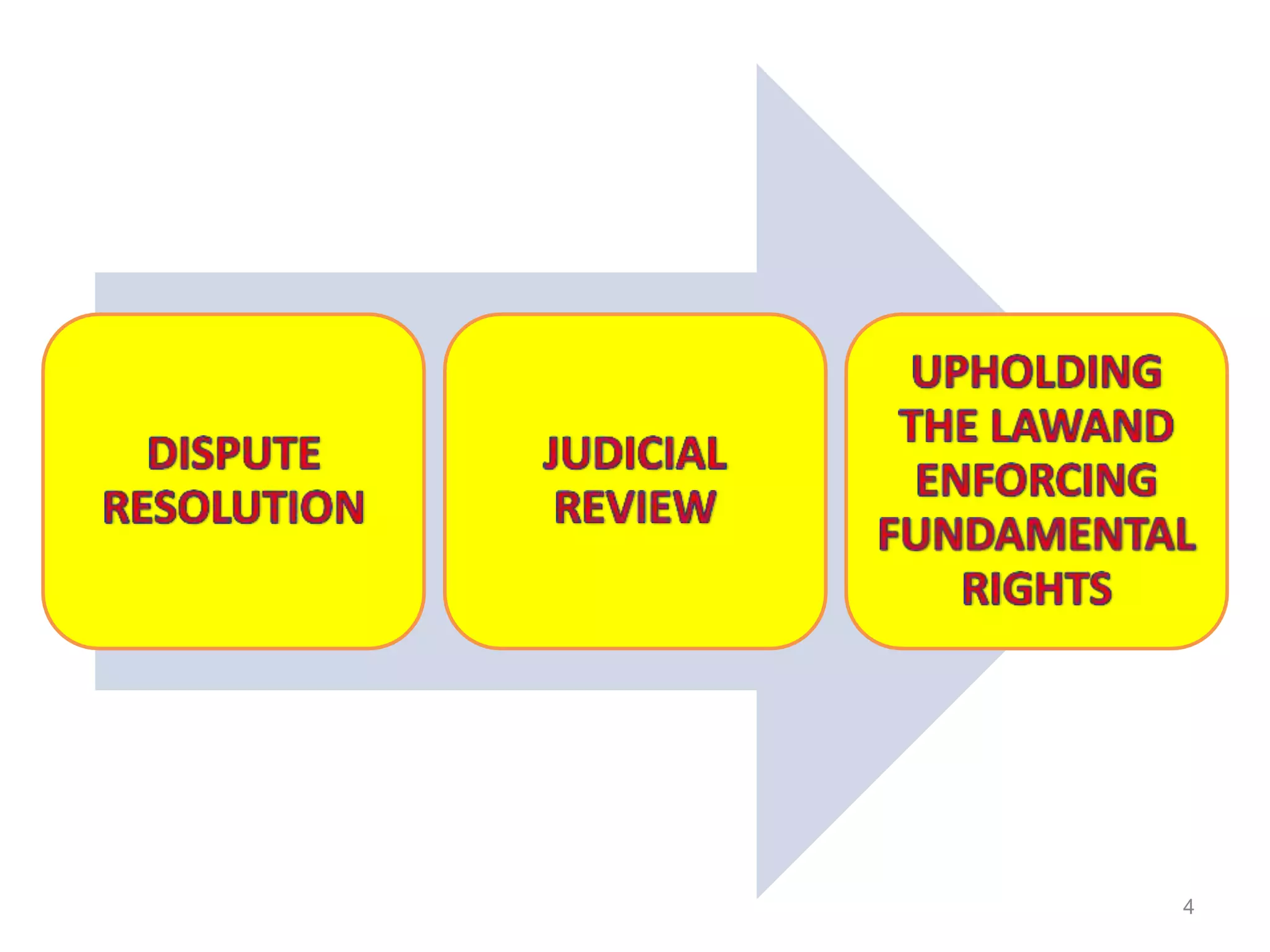
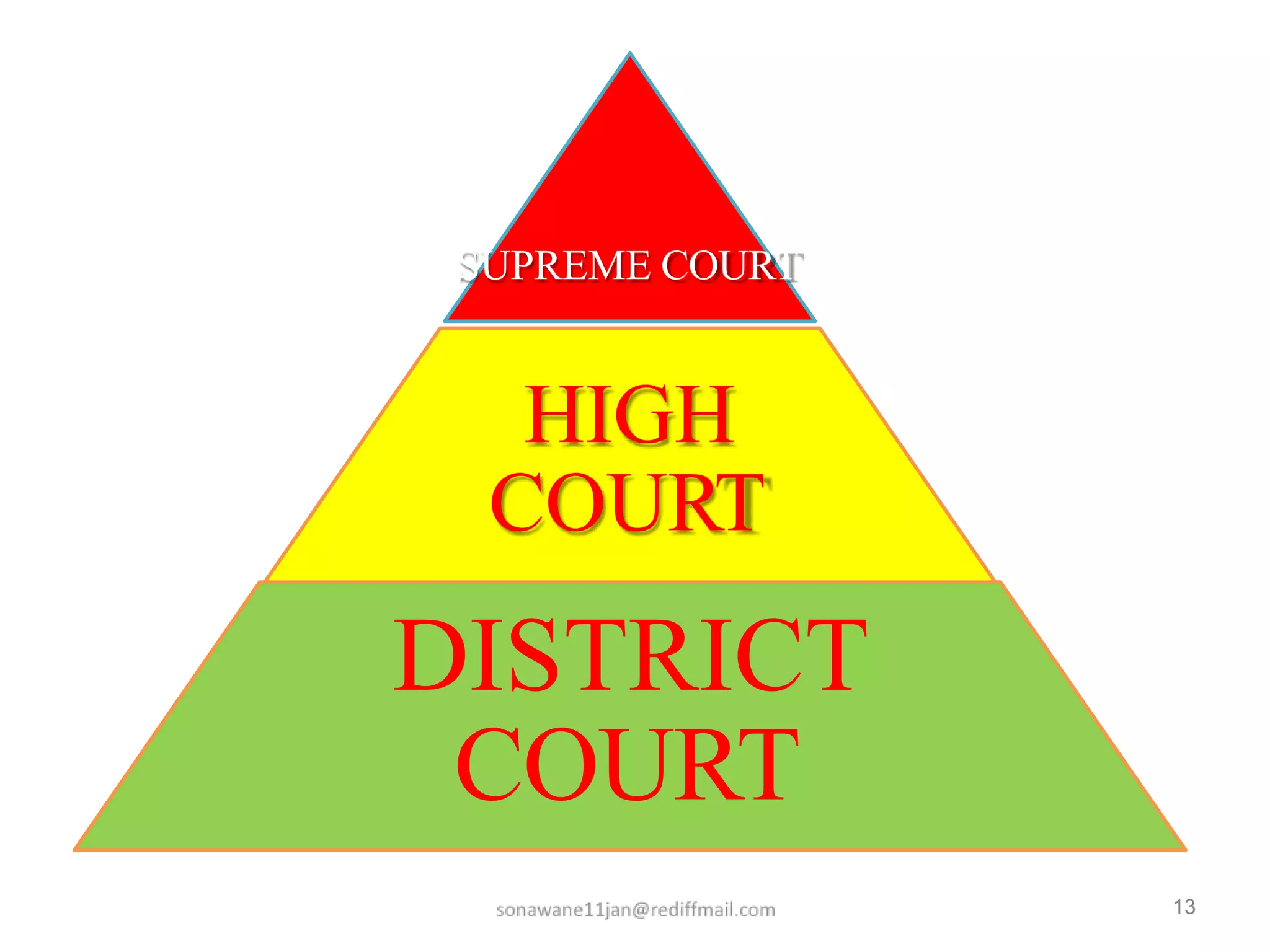
The document discusses the role and structure of the judiciary in India. It notes that the judiciary enforces the rule of law and equal application of laws through a system of courts. It then describes the roles of the judiciary as resolving disputes, interpreting the constitution and protecting fundamental rights. It outlines the structure of courts from district courts up to the Supreme Court. It also distinguishes between civil and criminal law. The document emphasizes that while in principle all citizens can access courts, in reality access is difficult for many poor citizens, though public interest litigation has helped address this.