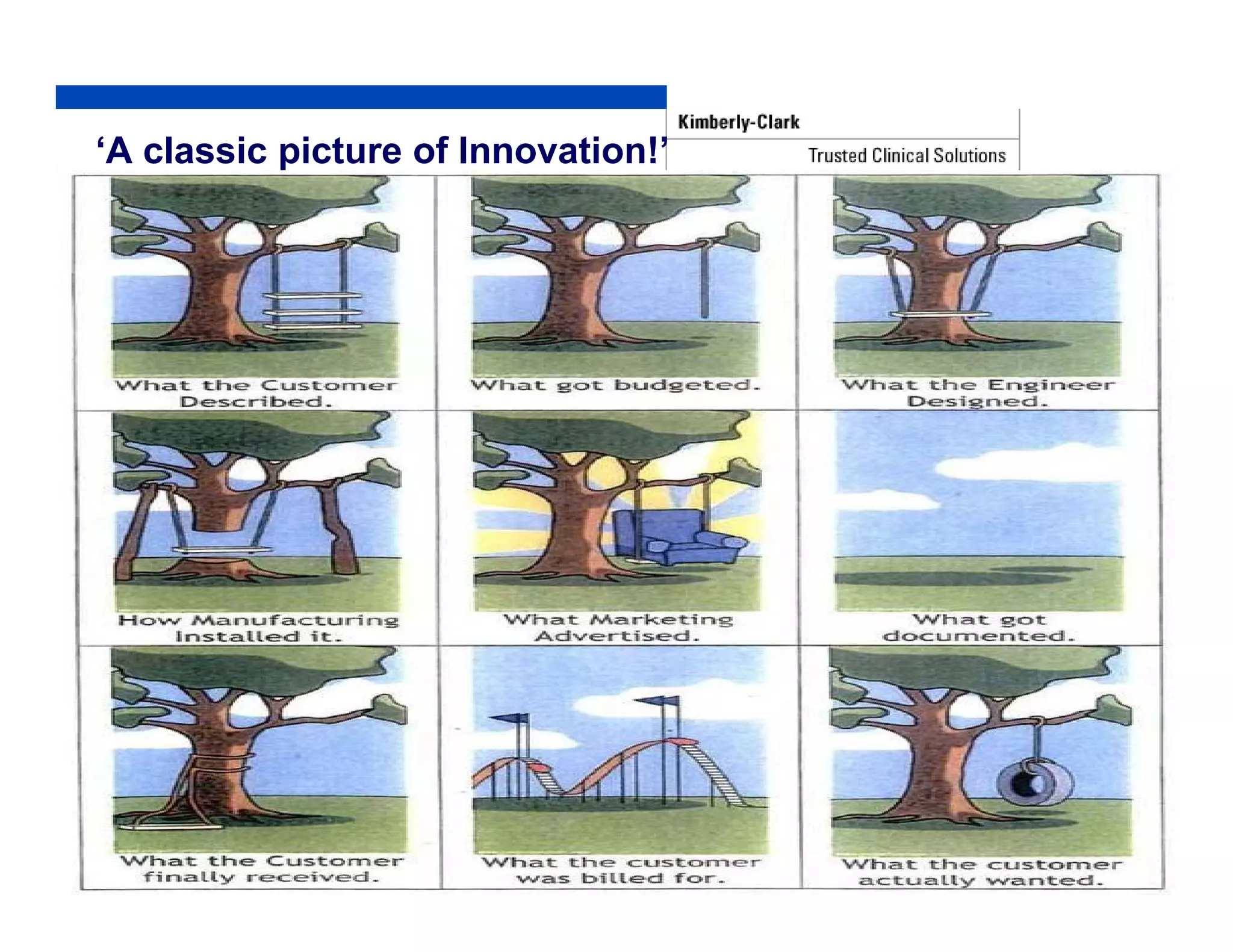
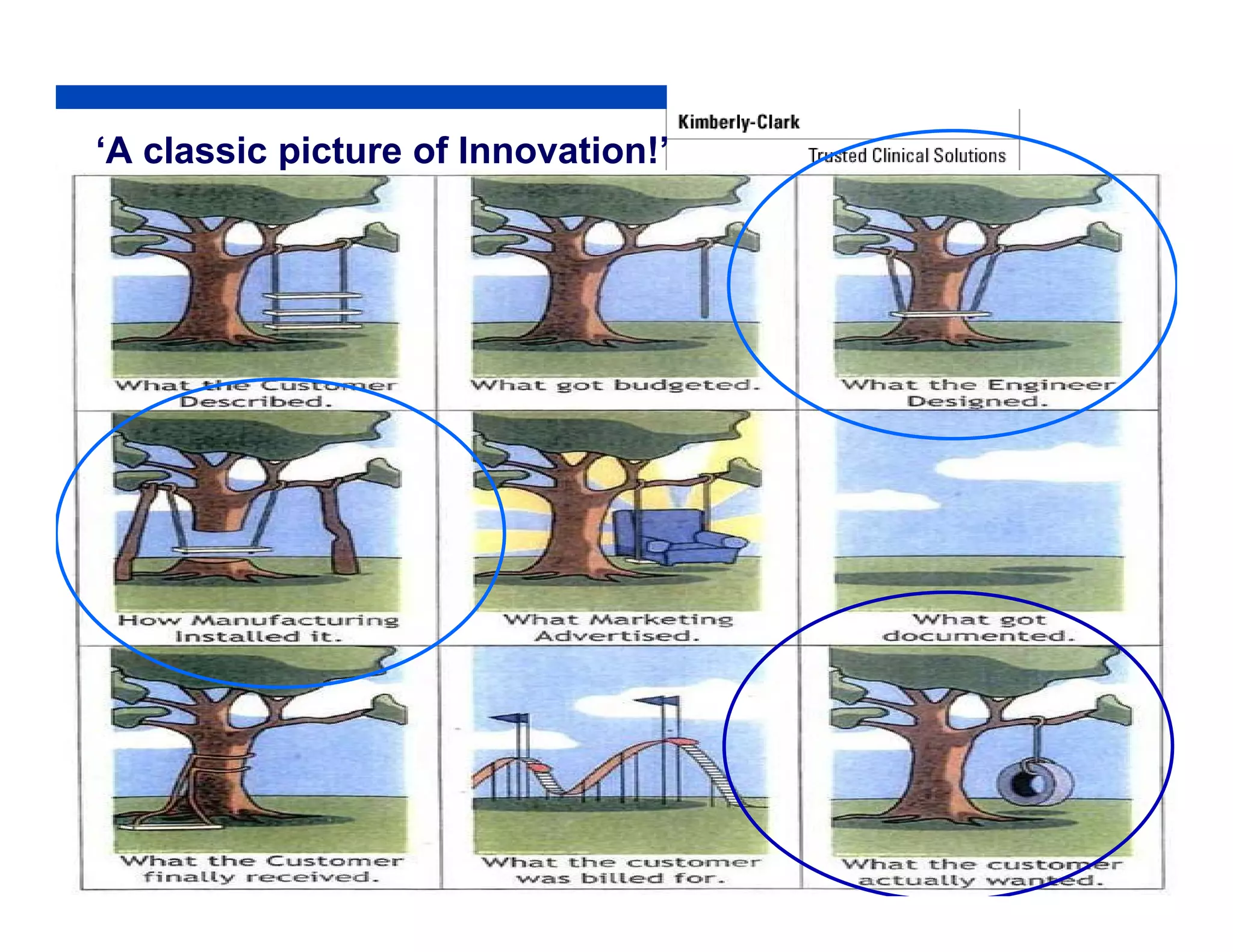
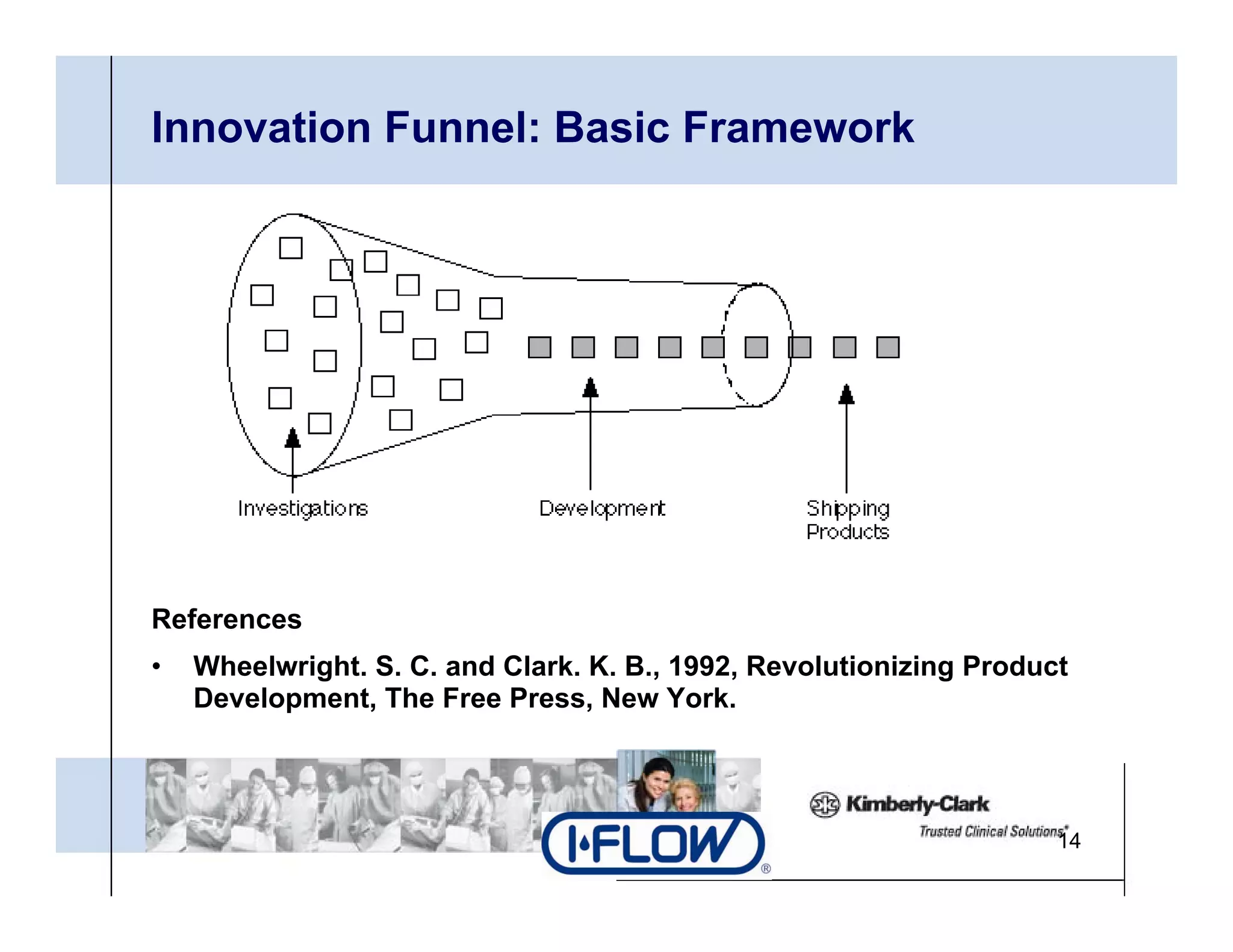
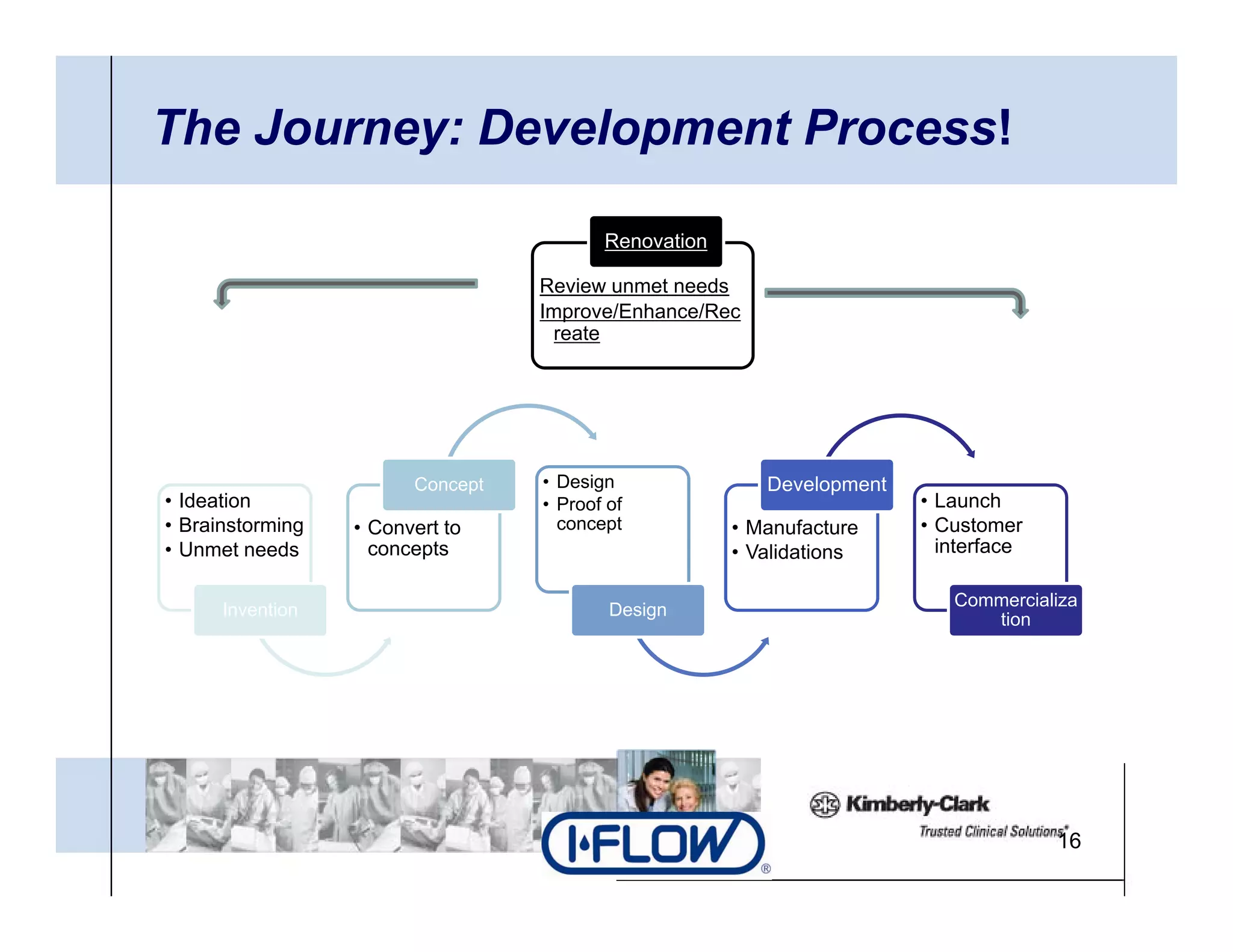
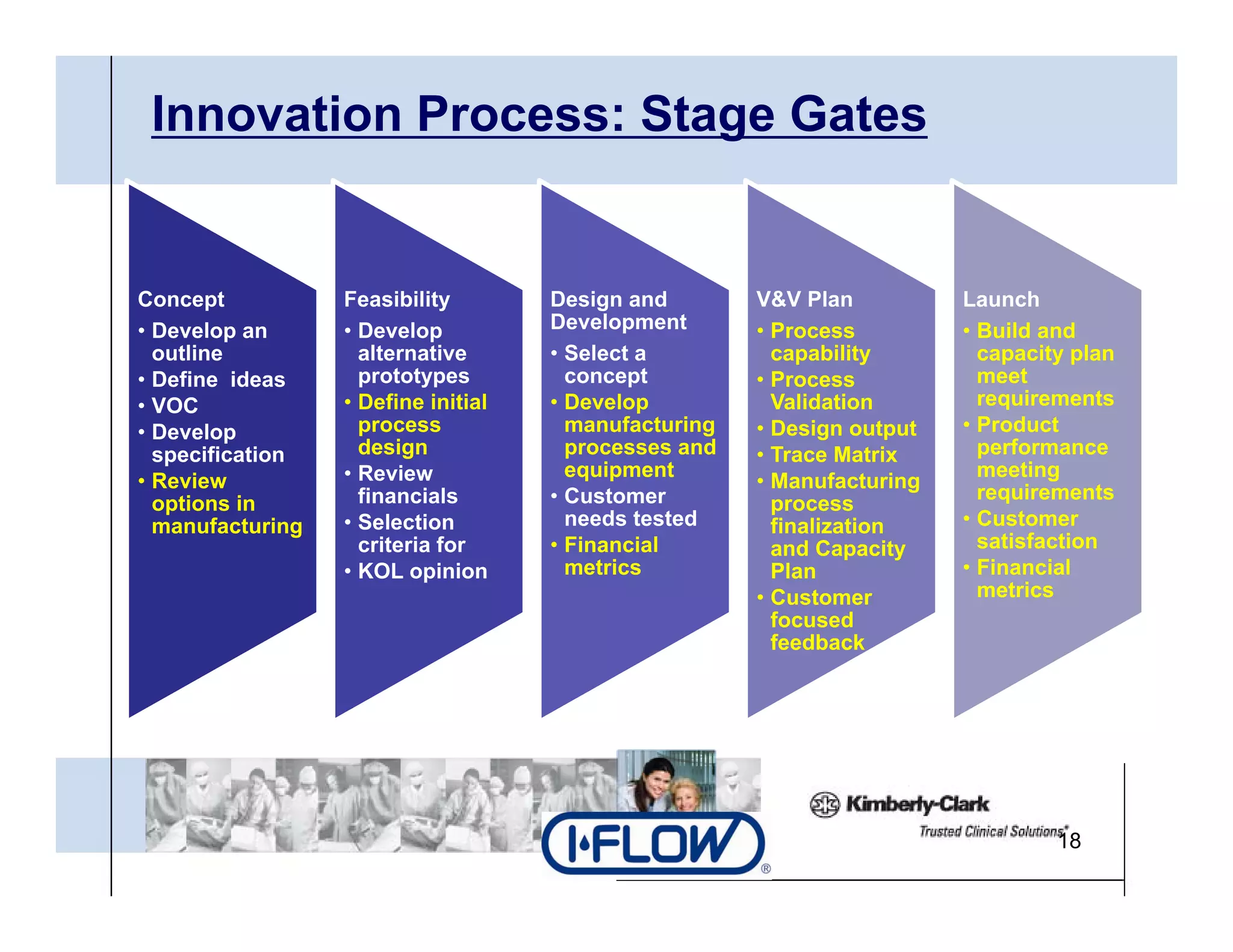
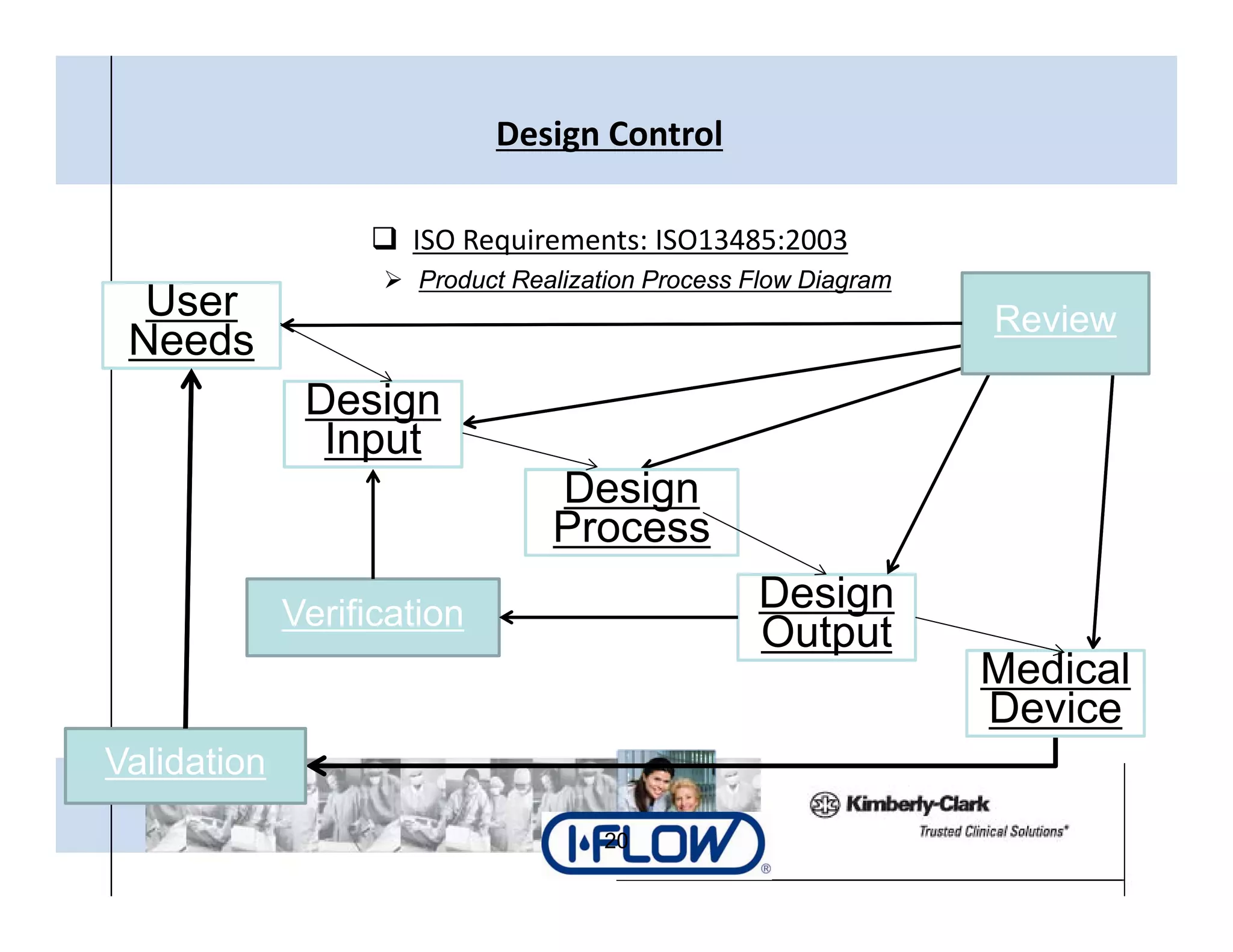
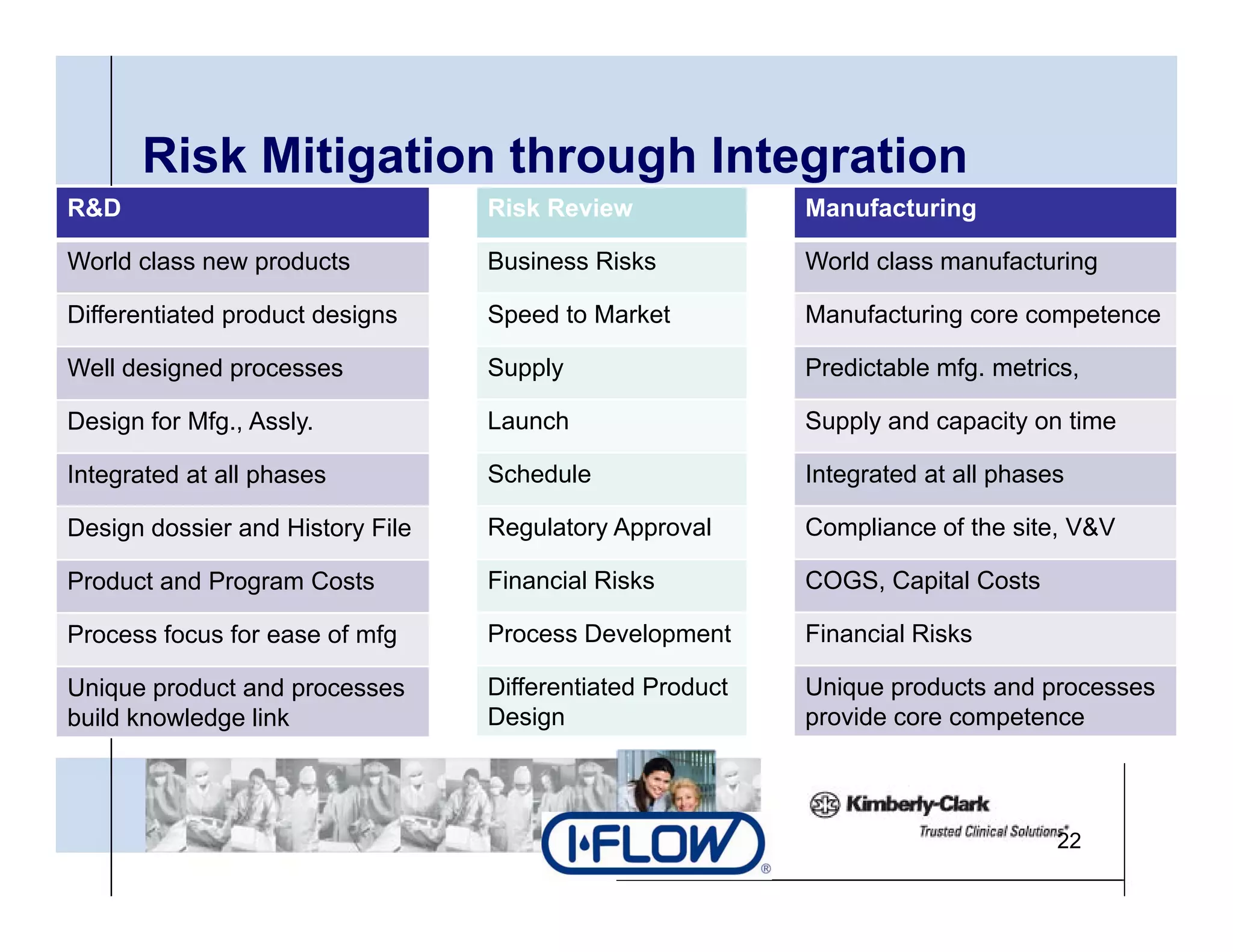
The document outlines strategies for successful design transfer from research and development to manufacturing in the medical device sector, emphasizing the importance of alignment between R&D and manufacturing processes. It discusses critical elements, case studies, and the role of innovation throughout the process, highlighting that successful design transfer is vital for delivering high-quality products. Key takeaway factors include thorough planning, stakeholder engagement, and validation at each stage of development and manufacturing.