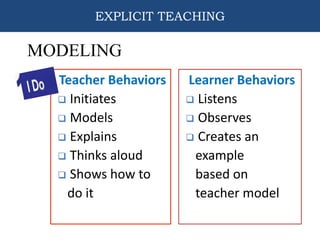
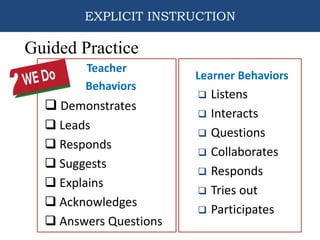
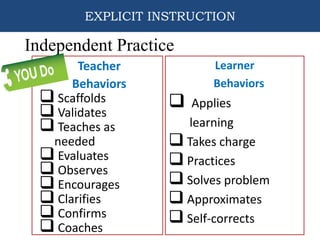
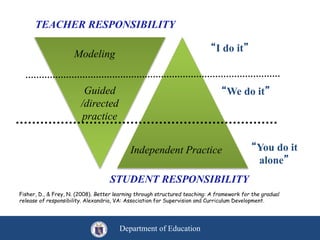
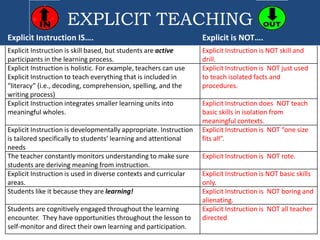
This document provides information about an training on explicit teaching. The objectives of the training are to define explicit teaching, recognize its importance, describe its underlying principles, identify the components of an explicit teaching framework, and demonstrate mini-lessons using explicit teaching methodologies. It then discusses the components of explicit teaching, including modeling, guided practice, and independent practice. It also outlines the structure of an explicit lesson, including the opening, teaching, and closing sections. Teachers are responsible for modeling and guiding practice, while students are responsible for independent practice. The document emphasizes that explicit teaching is skill-based but active for students, and should be tailored appropriately for different contexts and students.