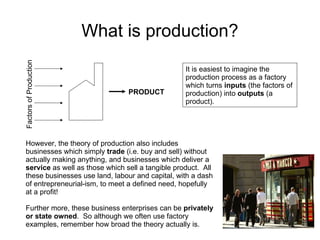
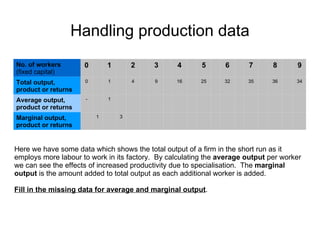
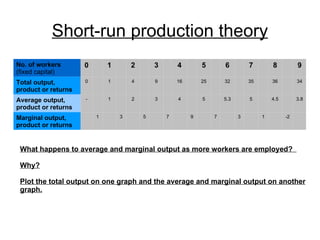
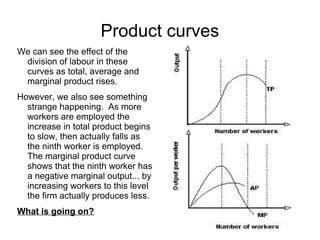
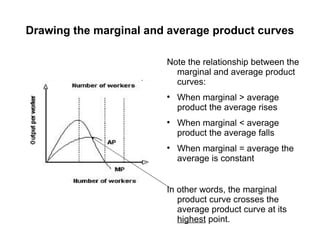
Short-run production theory examines how output is affected by adding a variable factor of production, like labor, to fixed factors. Initially, marginal output increases due to specialization and division of labor. Eventually, marginal output decreases due to diminishing marginal returns, as the variable factor is added beyond the point where it yields high returns relative to the fixed factors.