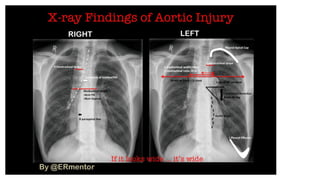
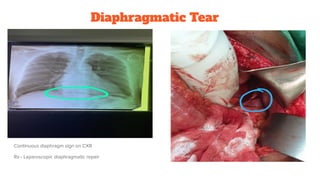
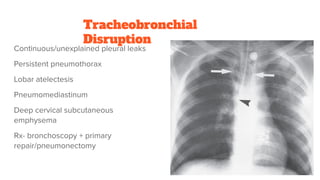
1. Shock is defined as cellular hypoxia due to reduced oxygen delivery, increased oxygen consumption, or inadequate utilization and can progress from cellular to systemic effects if unchecked.
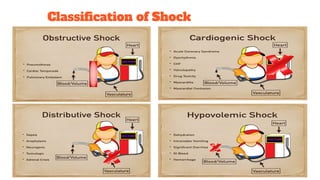
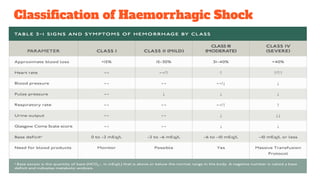
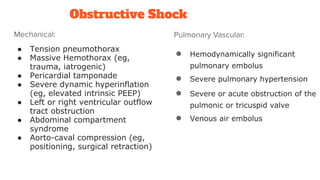
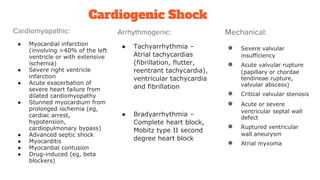
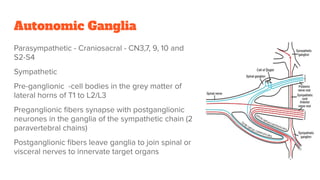
2. Shock is classified based on pathophysiology into hypovolemic, cardiogenic, obstructive, distributive, and neurogenic types.
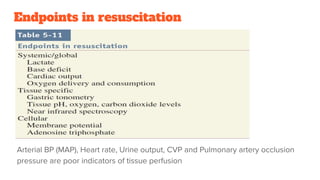
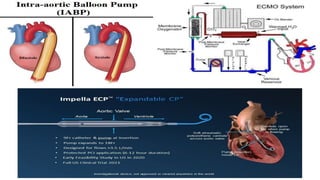
3. The document provides an overview of the pathogenesis, classification, treatment goals and strategies for each shock type to guide clinical management.