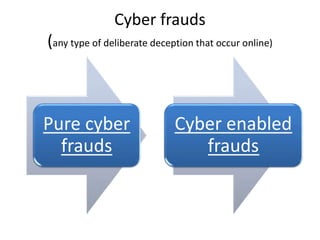
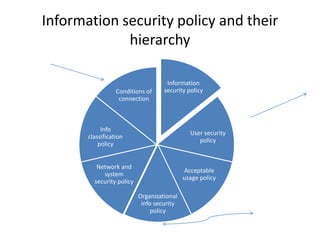
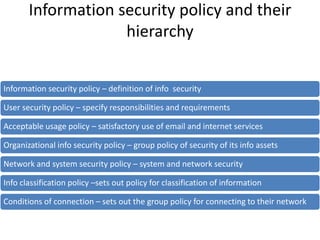
This document discusses various techniques used to commit cyber fraud such as hacking, cracking, data diddling, denial of service attacks, and social engineering. It also covers the impact of cyber frauds on enterprises like financial loss, legal issues, loss of credibility. Examples provided include unauthorized access of Citi Bank data and the Sony email hack. Reasons for cyber frauds mentioned are organizations needing to update security practices, smart fraudsters, and failures of internal security controls. The document defines cyber frauds and differentiates between pure cyber frauds and cyber-enabled frauds. It outlines components of an information security policy including its purpose, security infrastructure, response mechanisms, and legal compliances. Finally, the document discusses the hierarchy of