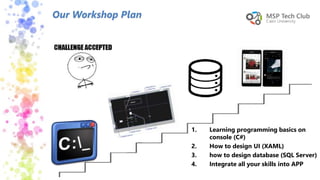
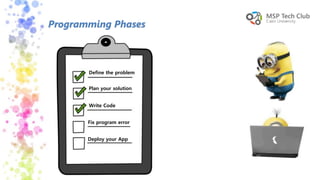
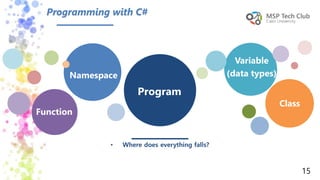
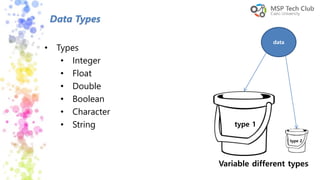
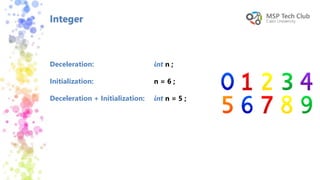
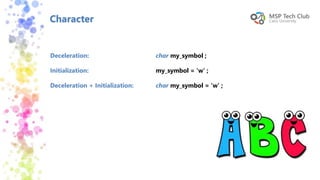
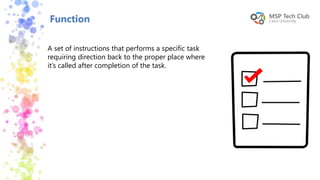
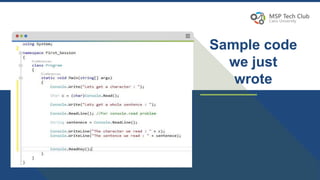
This document provides an introduction to universal applications and C# programming. It was prepared by Mohamed Samir and Khaled Taher, two computer science students. The document outlines their workshop plan to teach programming basics in C#, how to design user interfaces with XAML, integrate with databases using SQL Server, and build apps. It also covers computer programming concepts like variables, data types, functions, classes, and namespaces. Contact information is provided at the end for any questions.