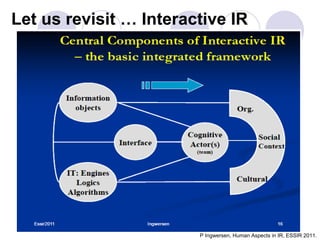
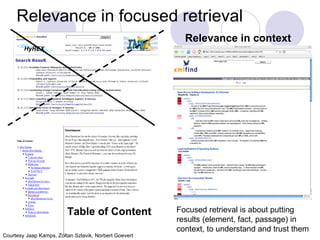
This document discusses user engagement in information retrieval over query sessions. It begins with an introduction of the author and their research topics related to engagement.
The main topics covered are:
1) Motivations for looking beyond result relevance and search sessions to consider engagement.
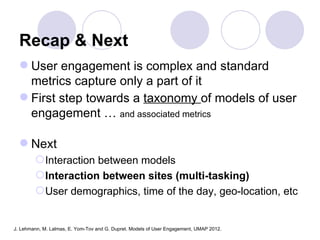
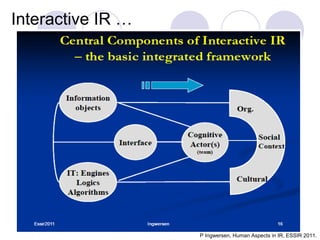
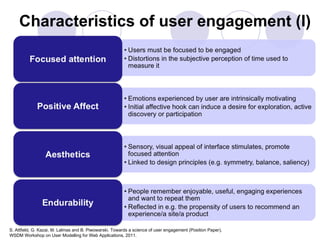
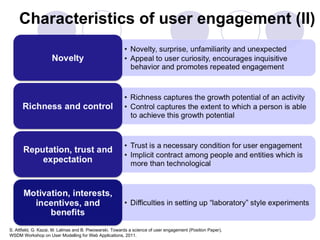
2) A definition of engagement as the emotional, cognitive and behavioral connection between a user and technology. Characteristics of engagement like concentration, interest and actions are discussed.
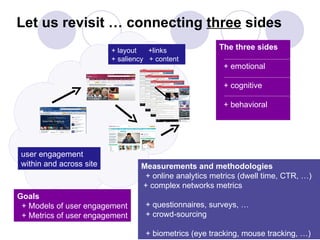
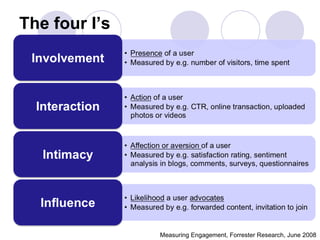
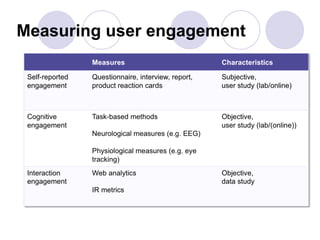
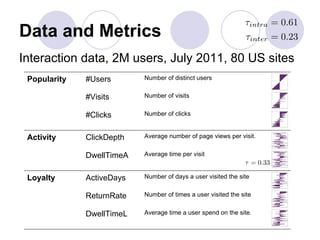
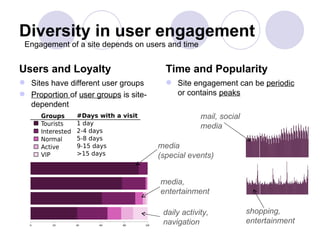
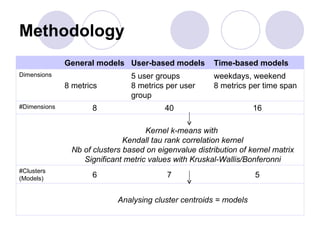
3) Models of user engagement are proposed based on metrics of popularity, activity and loyalty for general engagement models as well as user-based and time-based models. The models capture different aspects of engagement for sites.
Future directions discussed include analyzing interactions between models









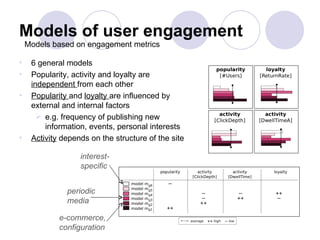
![Models of user engagement
Models based on engagement metrics, user and time
User-based [7 models] Time-based [5 models]
Models based on engagement per Models based on engagement
user group over weekdays and weekend
navigation game, sport
hobbies, daily news
interest-specific
Sites of the same type (e.g. mainstream media) do not necessarily belong to
the same model
The groups of models describe different aspects of engagement, i.e. they are
independent from each other](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecir2002-120331105125-phpapp01/85/Session-focus-and-engagement-22-320.jpg)