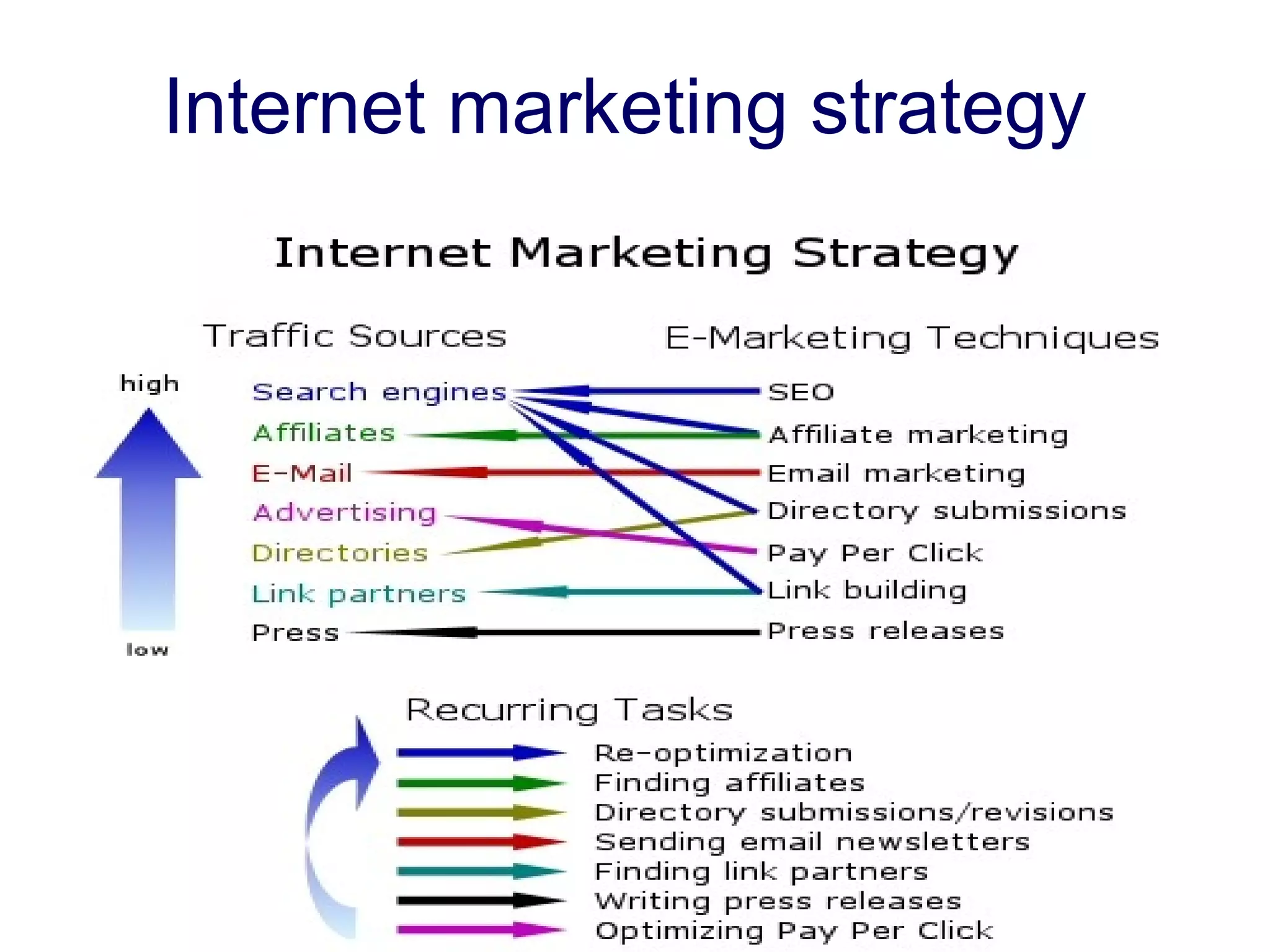
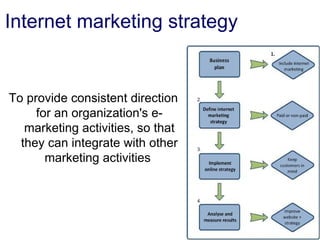
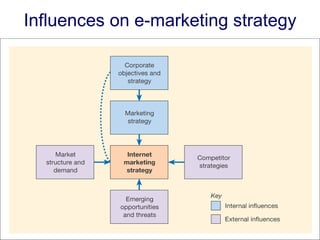
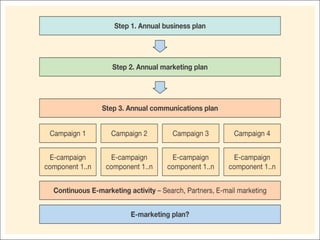
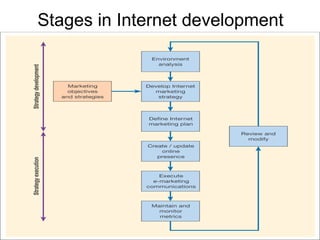
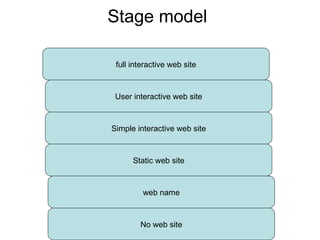
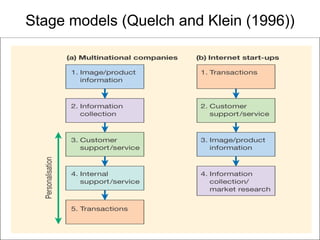
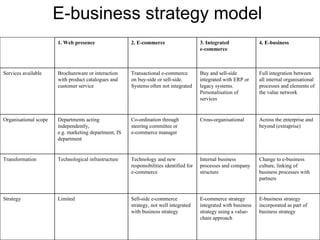
An e-marketing strategy is needed to provide consistent direction for an organization's online activities and integrate them with other marketing. The strategy should define how the organization will communicate benefits of the online channel, prioritize targeted audiences and products, and hit sales targets. It also needs to manage integration across channels. Without a strategy, companies risk underestimating online demand, losing market share, duplicating resources, and missing opportunities.