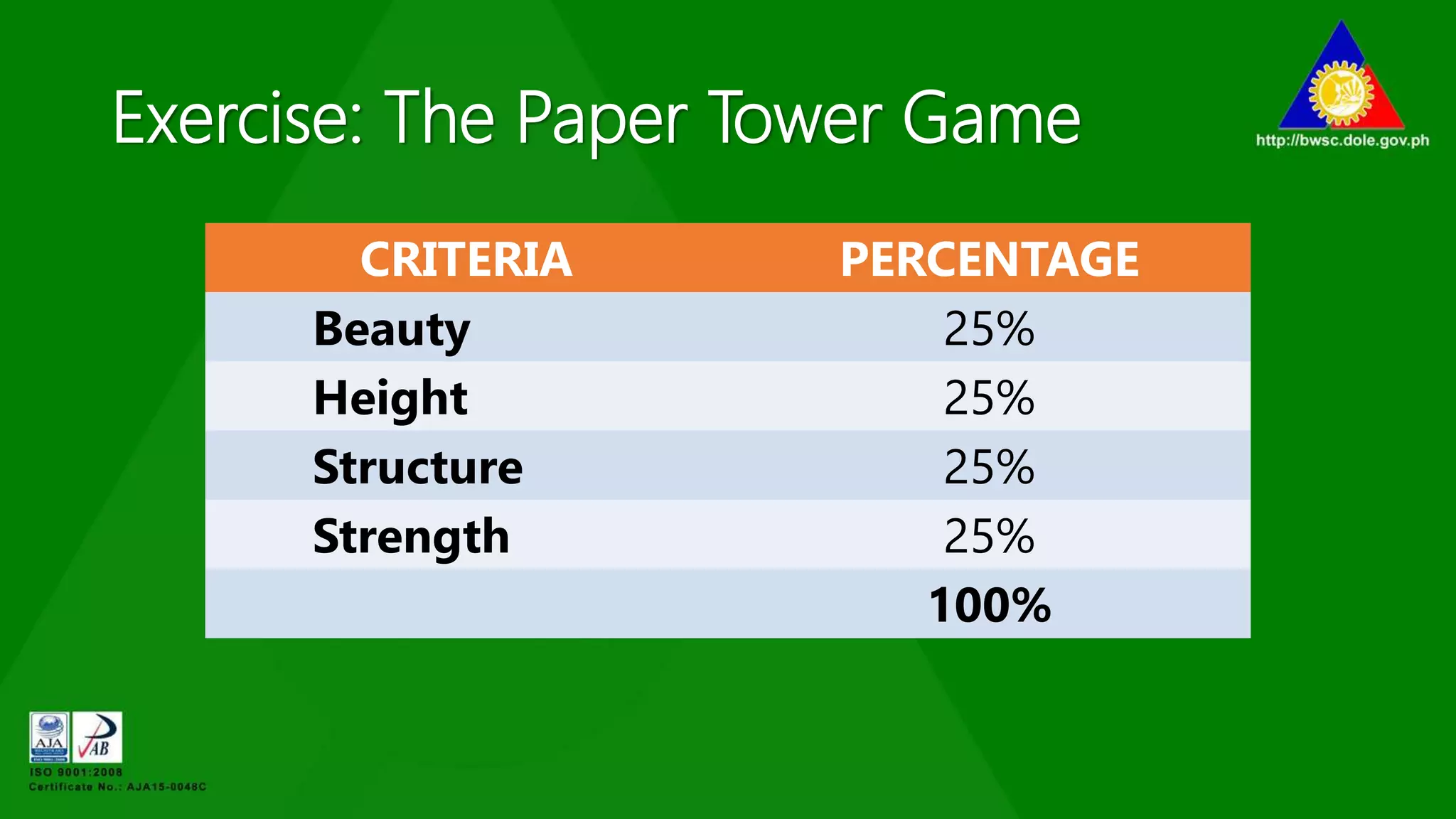
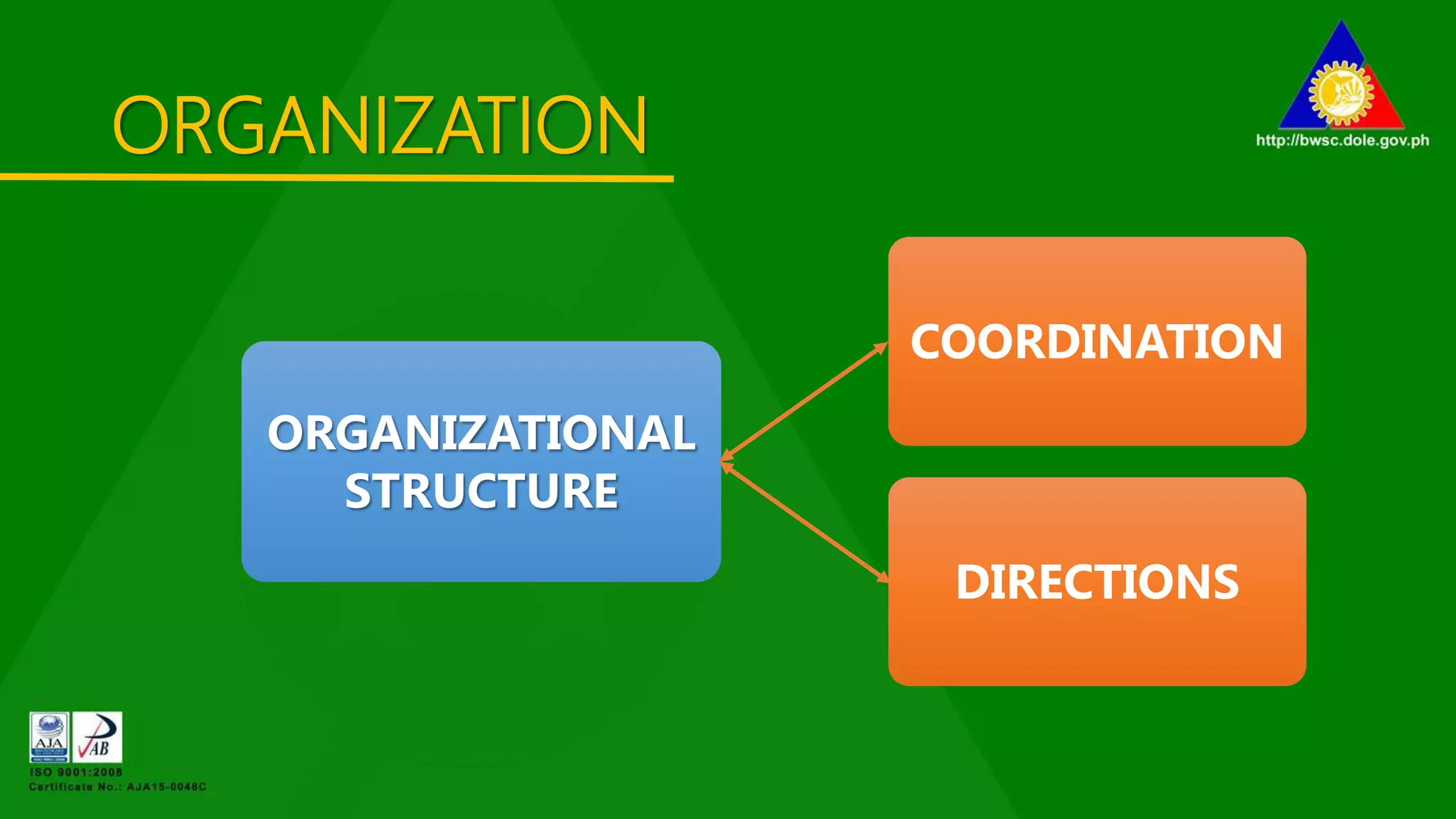
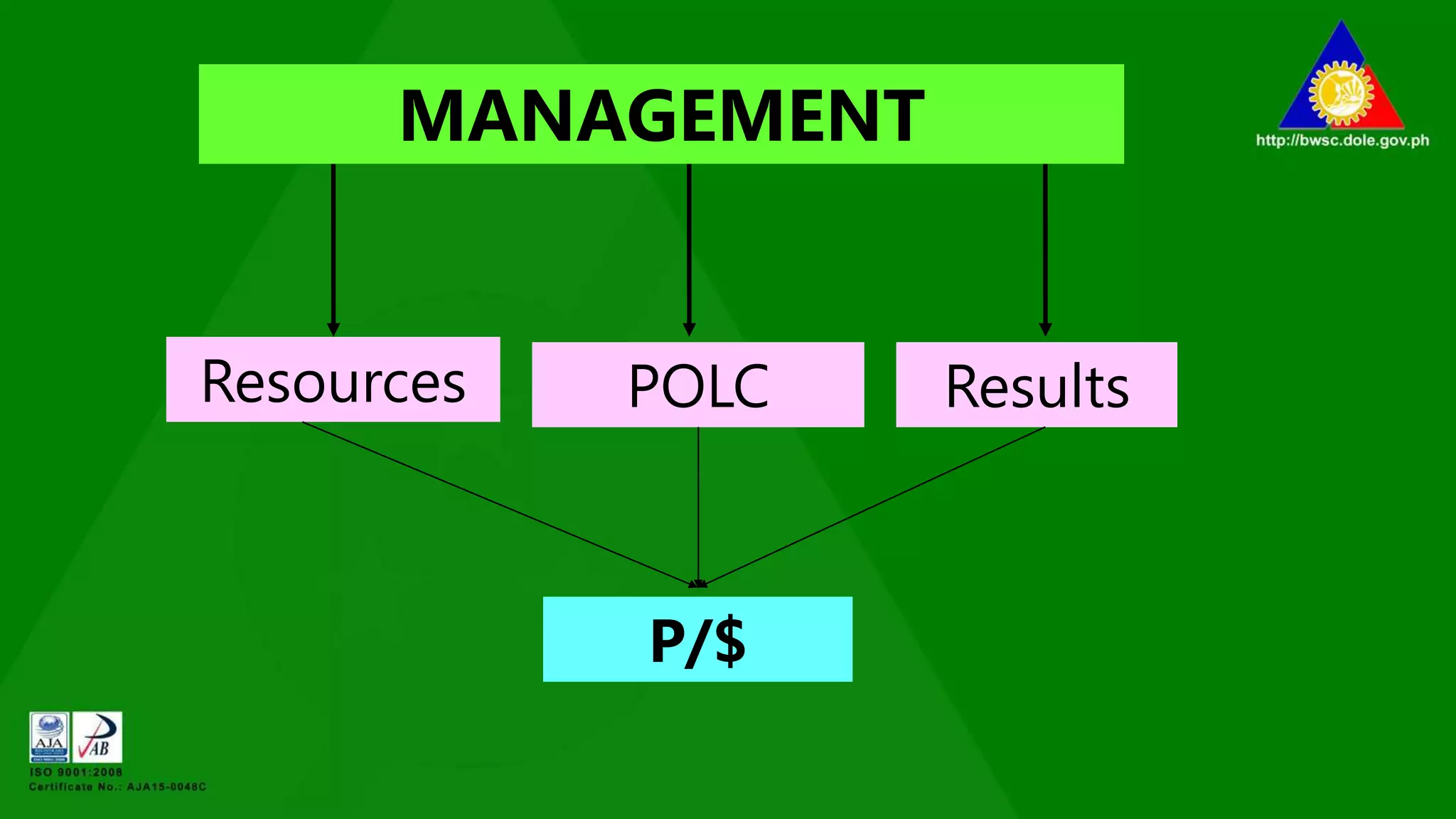
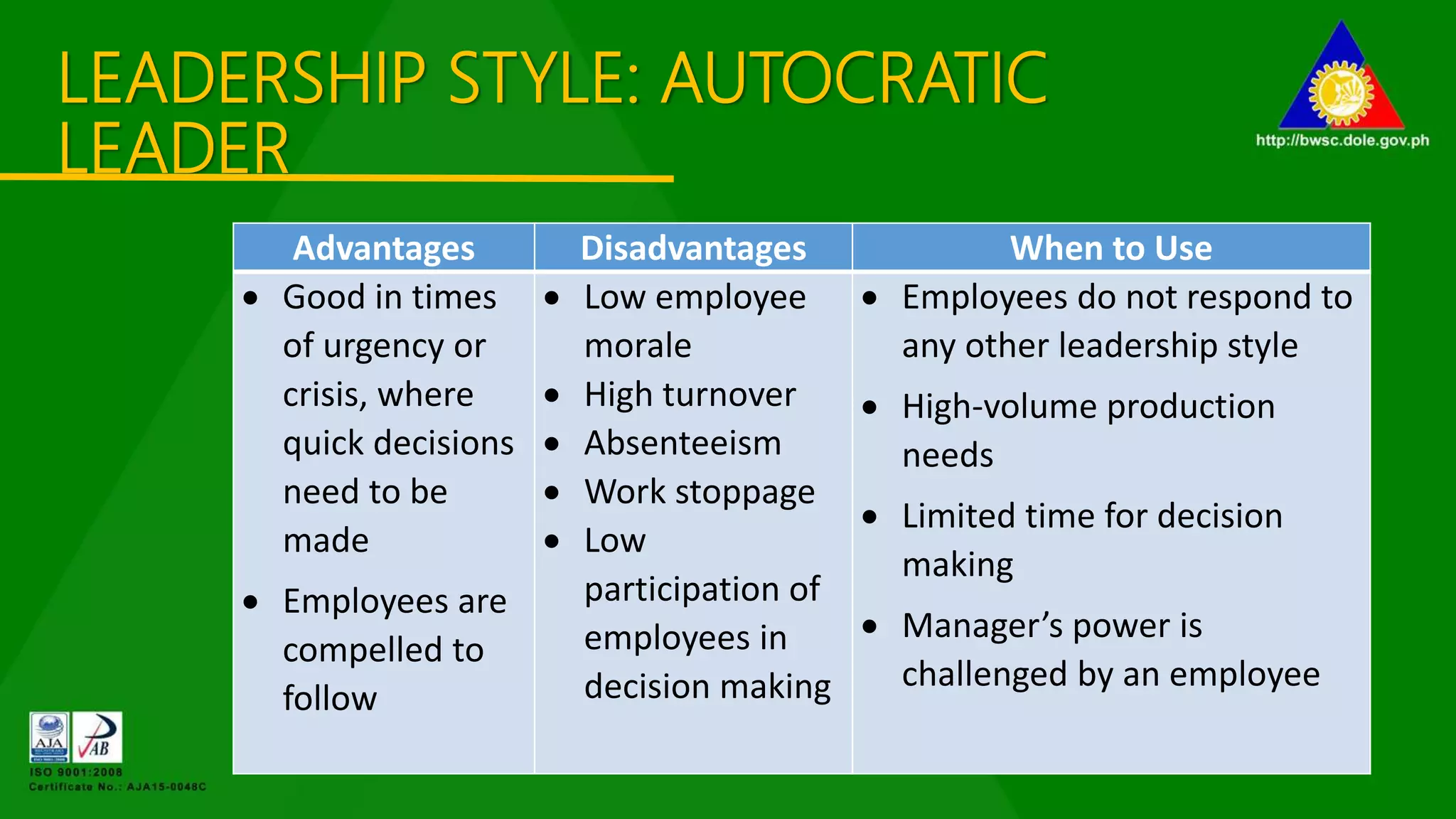
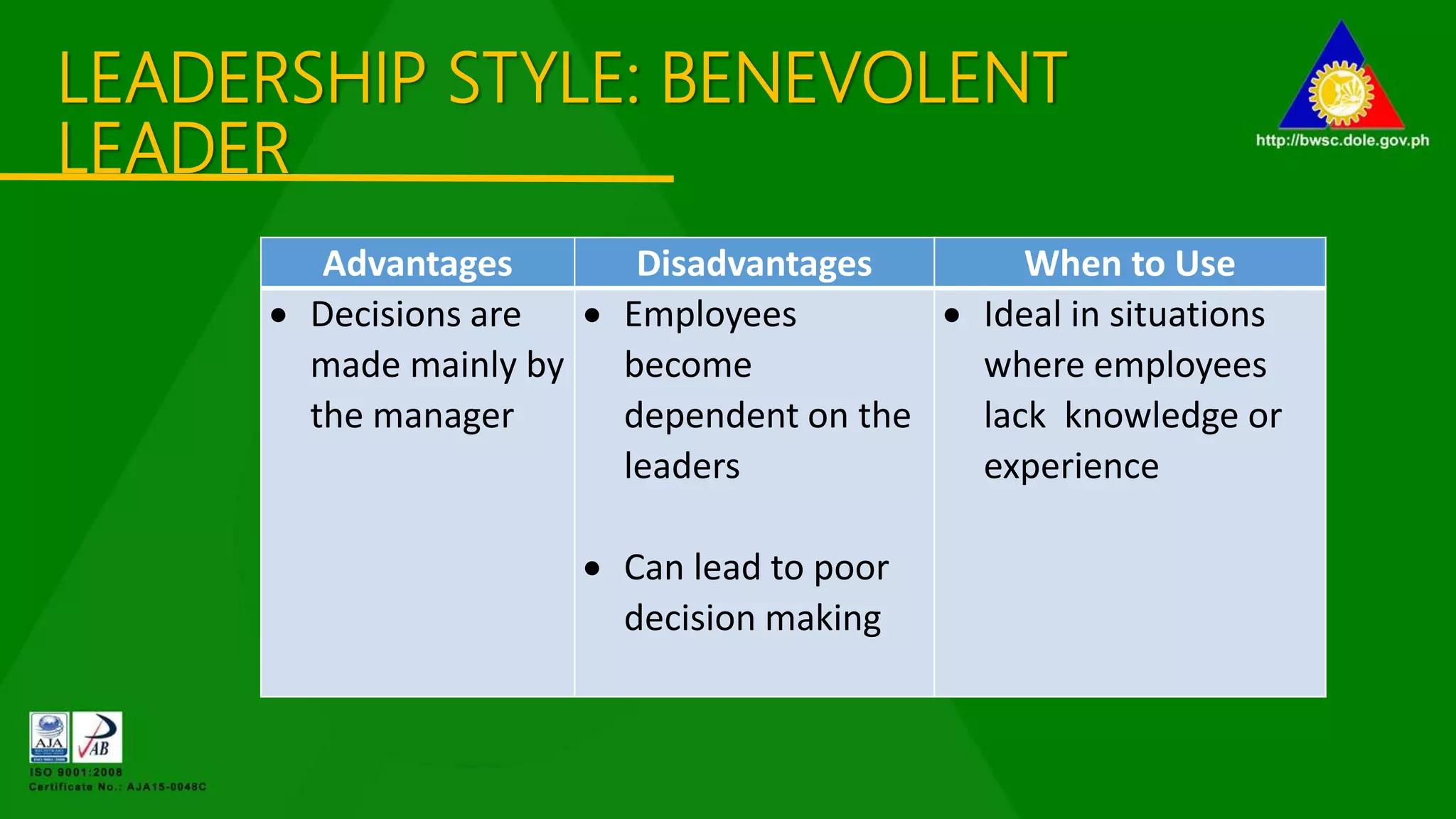
The document outlines various management principles, including organizational structure, leadership styles, and types of managers. It details the functions of management (planning, organizing, leading, and controlling) and discusses five distinct leadership styles: autocratic, benevolent, democratic, laissez-faire, and their appropriate use cases. Additionally, it categorizes managers into five types based on their behaviors and methodologies, providing insights into their strengths and weaknesses.