The document provides an introduction to a session on knowledge management. It discusses several key topics:
- The objective of the session is to understand and explain the basics of knowledge management and its importance for individuals, groups, and organizations.
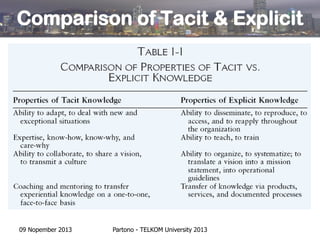
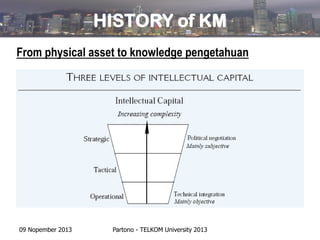
- Knowledge is considered an intellectual asset that can be reused without being consumed, transferred without being lost, and is abundant yet not always easy to apply.
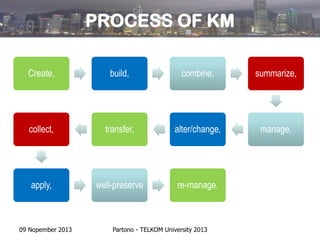
- Knowledge management involves systematically capturing, structuring, managing, and disseminating knowledge throughout an organization to work more efficiently and reduce costly mistakes.
- The benefits of knowledge management include facilitating knowledge transfer, minimizing knowledge loss, and identifying critical knowledge areas for the organization.