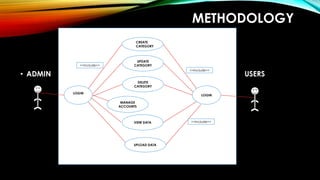
This document presents a project on developing a knowledge management system for lawyers. It discusses how knowledge is defined as what we know and is constructed over time through interaction and experience. It also reviews technologies that can support knowledge creation and sharing like data mining, business intelligence, and decision support systems. The project aims to adopt new technologies to help lawyers properly manage records, store documents, and collaborate on cases. The proposed system will create a data warehouse for case details and allow users to upload, categorize, and share information.