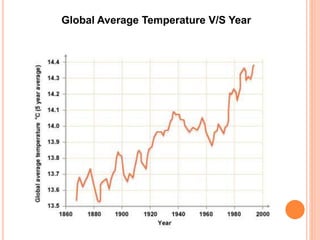
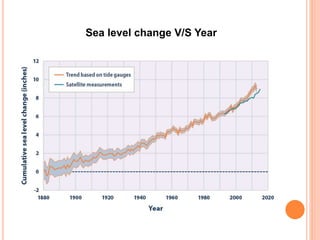
This document discusses greenhouse gases and global warming. It begins by defining a greenhouse as a structure made of glass used to grow plants in cold climates. Greenhouse gases like CO2, methane, and CFCs trap heat in the atmosphere similar to how glass traps heat in a greenhouse. The four main greenhouse gases and their contributions to global warming are identified. The document then discusses the impacts of global warming, such as rising global temperatures and sea levels. Global warming is projected to increase temperatures by 1.4-5.8°C by 2100 and raise sea levels by 0.2-1.5 meters over the next 50-100 years. This will negatively impact food production, human health, and climate patterns.
![GREEN HOUSE & GLOBAL WARMING
Name :- Darshan Rajput [16BEITV124]
Dhrumil Patel [16BEUTV123]
Ankur Sangani [16BEITV122]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esseminar-170310144313/75/seminar-for-collage-level-1-2048.jpg)