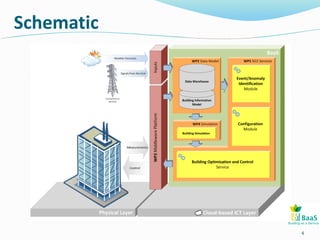
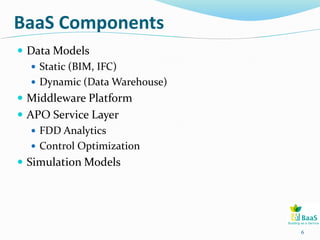
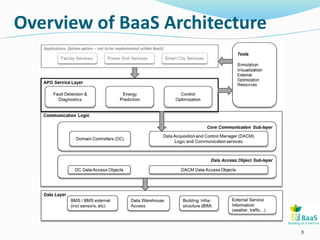
The BAAS project focuses on improving energy efficiency in buildings through the integration of information and communication technologies. It aims to address issues such as interoperability and operational inefficiencies by developing generic ICT tools for monitoring and optimizing energy performance. The project involves multiple test beds and demonstration buildings across Europe, funded by the European Commission under the FP7 program.