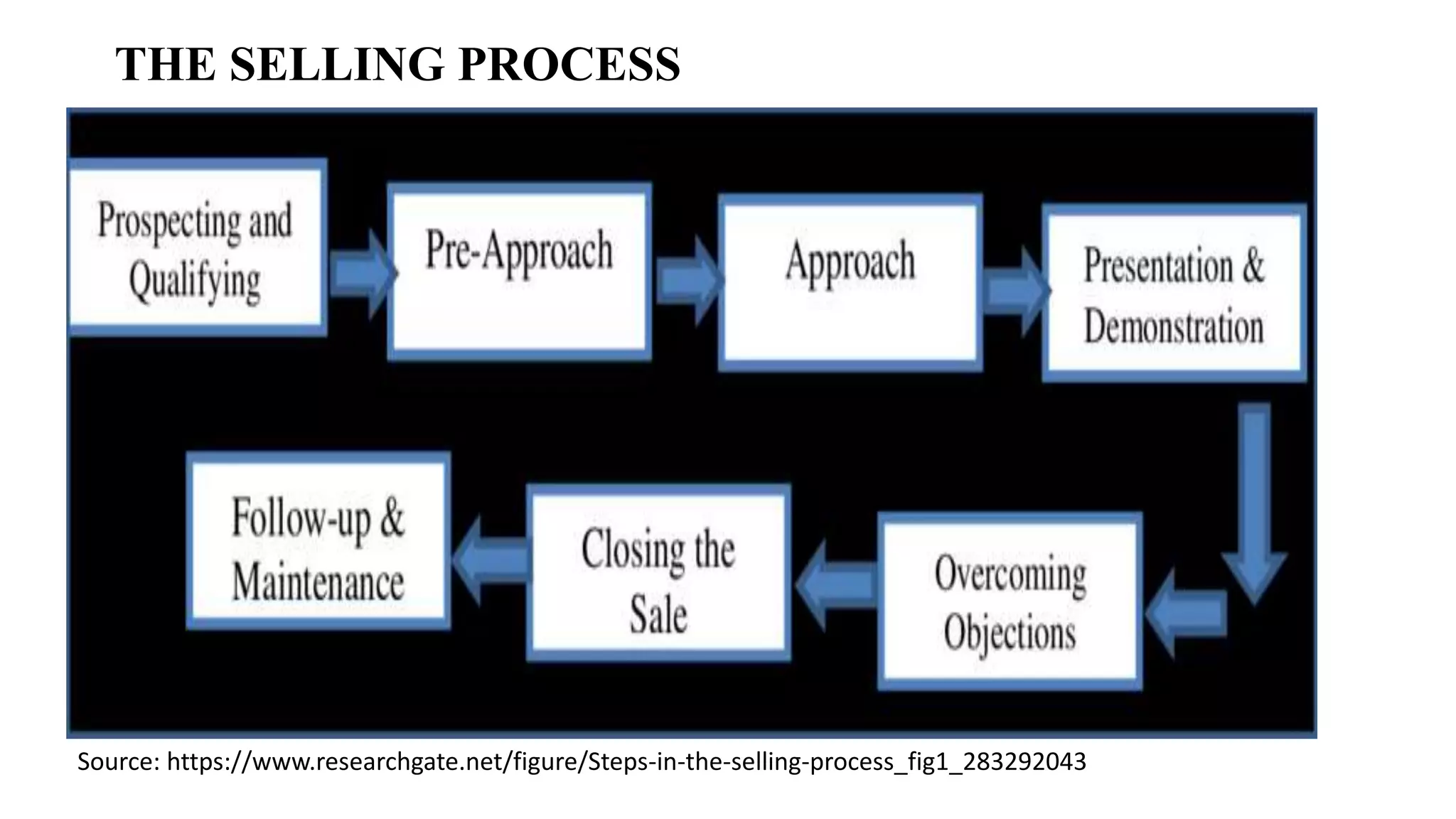
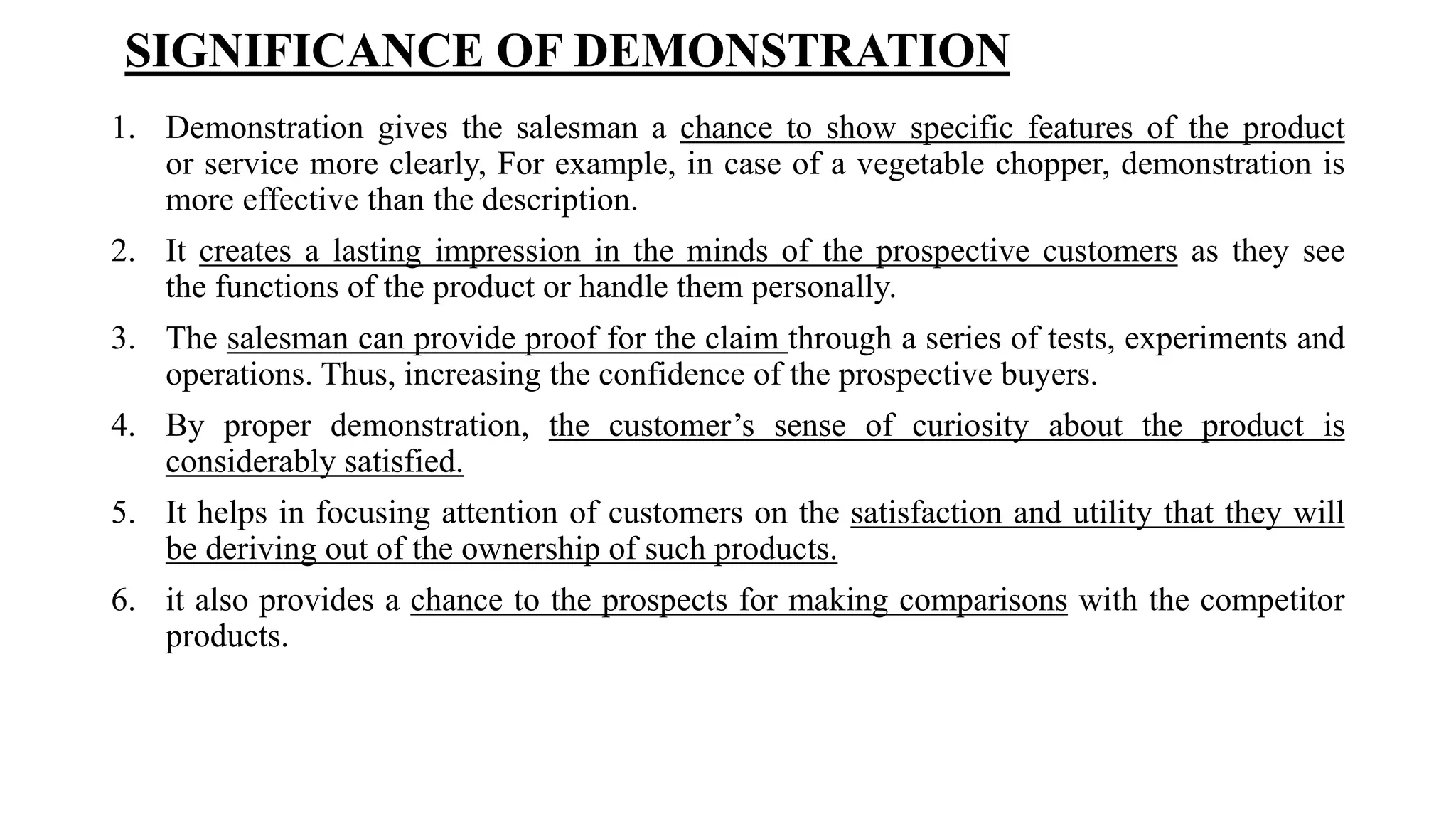
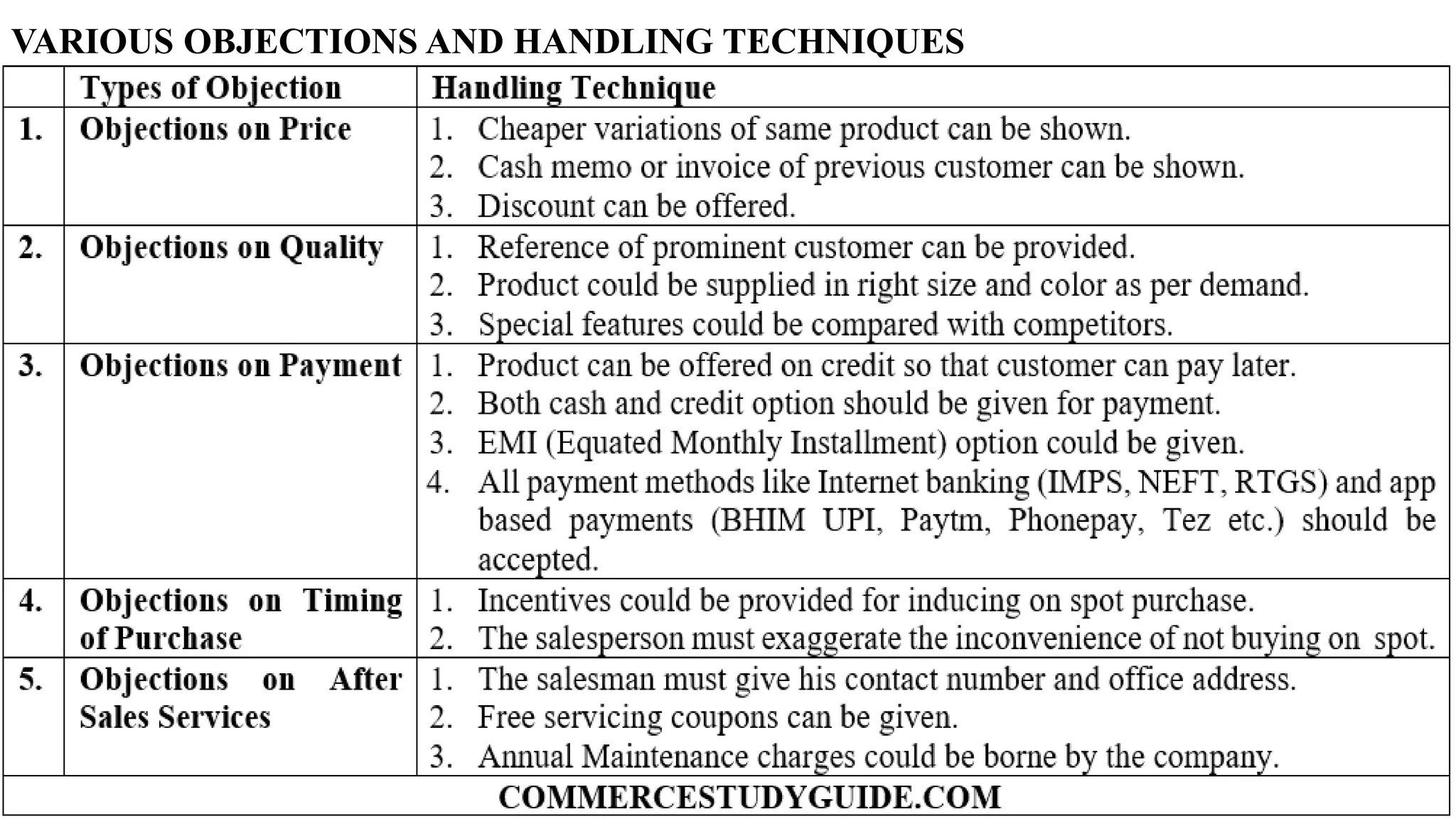
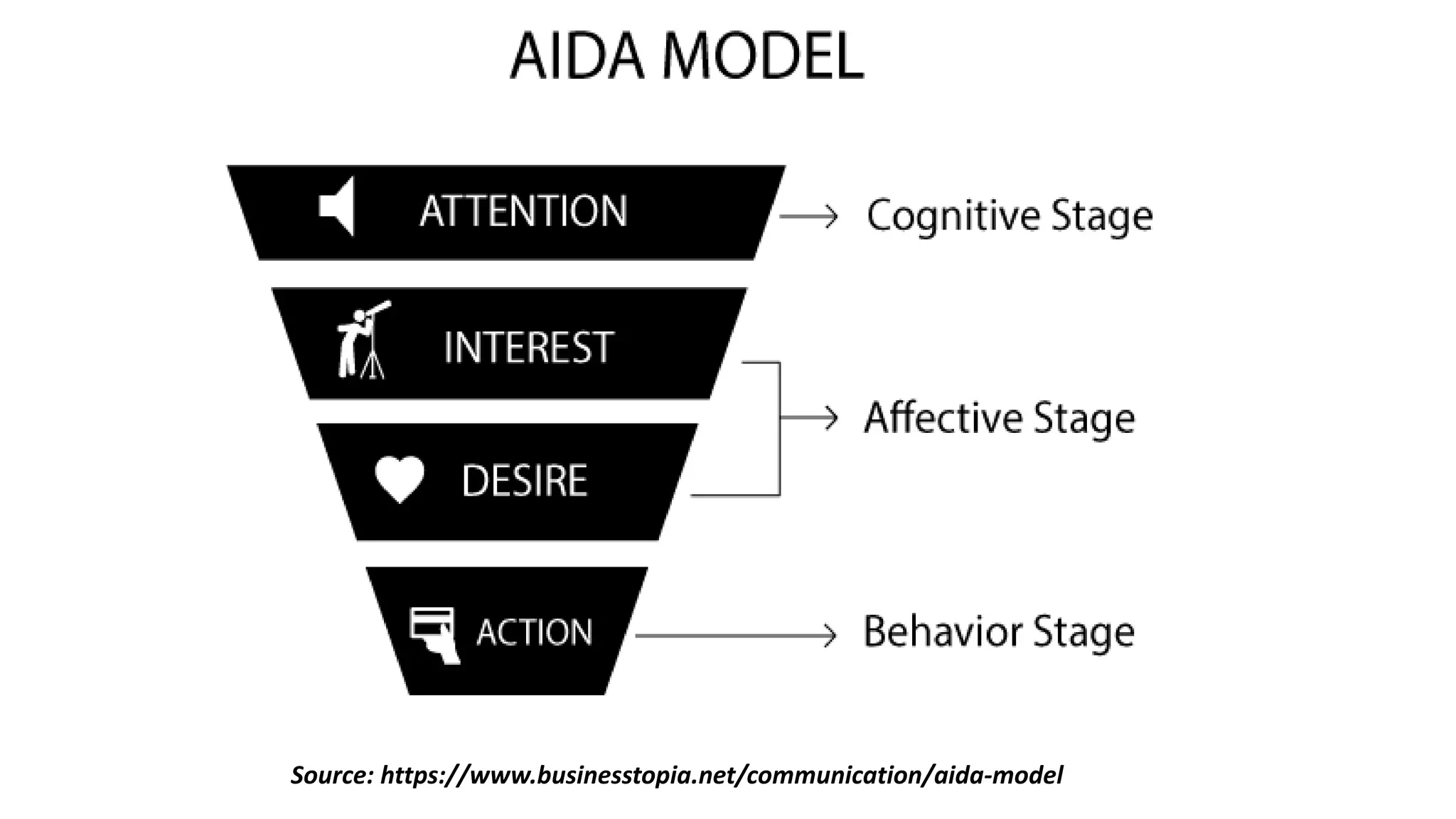
The document outlines the selling process, beginning with prospecting and qualifying potential customers, highlighting methods for identification such as cold canvassing and referrals. It emphasizes the importance of pre-approach and approach steps to gather information and establish rapport with prospects, as well as the significance of effective presentations and demonstrations in closing sales. Lastly, it discusses the necessity of after-sales service to build customer relationships and ensure satisfaction.