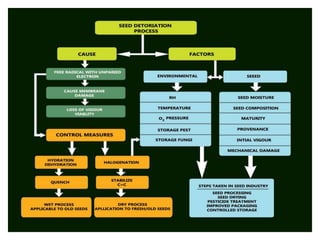
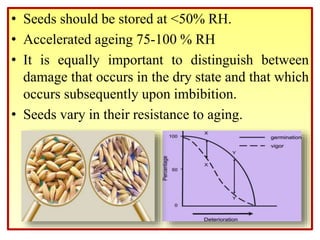
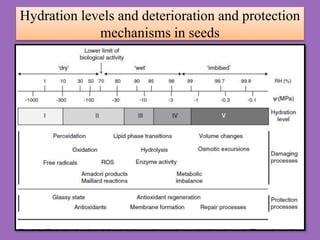
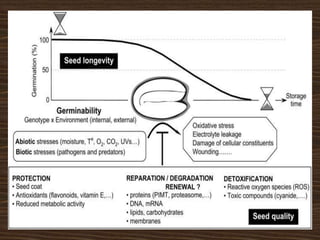
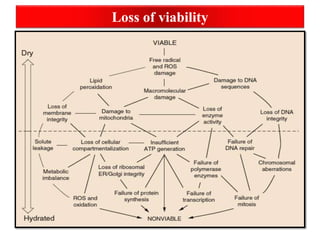
Seed deterioration is a cumulative process that increases a seed's vulnerability over time. It decreases a seed's ability to survive and is an undesirable aspect of agriculture. Seed deterioration is separate from seed development and germination. Several factors influence seed deterioration rates, making it difficult to critically evaluate. Moisture content and storage temperature greatly impact seed life, with lower levels extending life. Damage mechanisms differ depending on whether seeds are dry or wet.